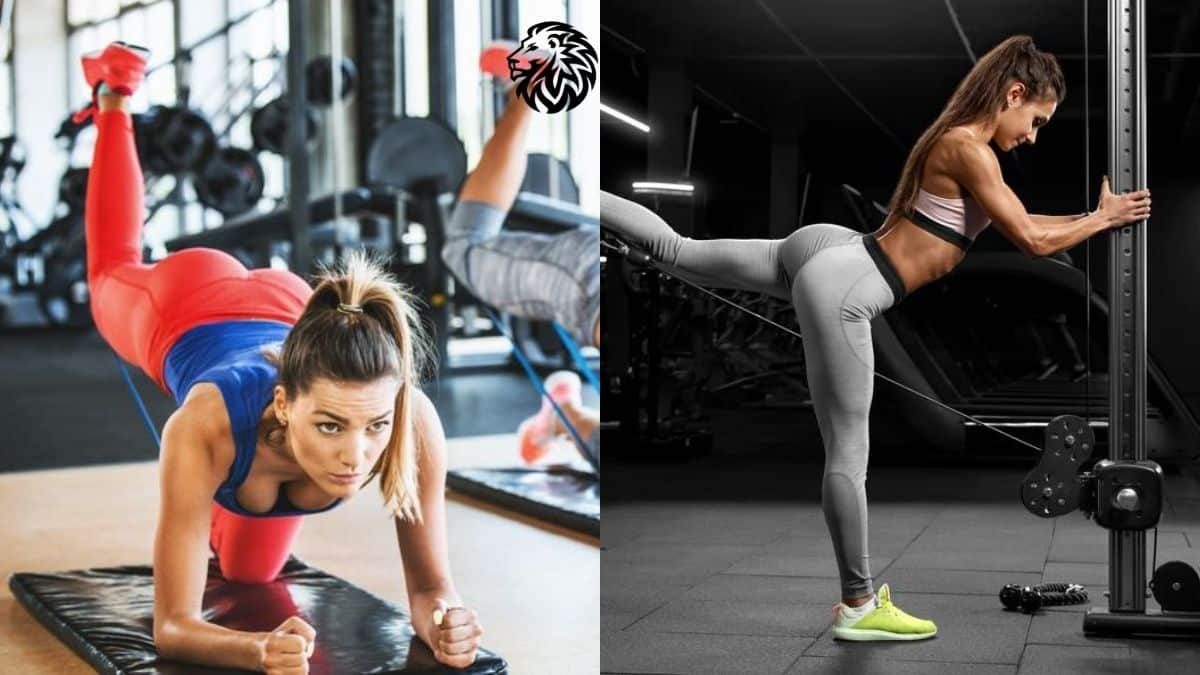
The gluteal muscles, encompassing the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus, aren’t just vital for an aesthetically pleasing physique. They play a pivotal role in enhancing our overall body functionality and athletic performance. Our glutes are engaged in numerous movements, including standing, sitting, climbing, jumping, and running, acting as a powerhouse for lower body strength and stability. Strengthened glutes provide essential support to the pelvic region and assist in maintaining an upright posture, thereby reducing the risk of lower back pain and injuries.
Embarking on a journey to sculpt the glutes requires incorporating a range of exercises that target these muscles from various angles. This article aims to delve into a selection of exercises recognized for their efficacy in building and defining the glute muscles. From the classic squats and lunges to more targeted moves like hip thrusts and donkey kicks, we’ll explore how each exercise contributes to shaping and strengthening your rear, all while offering variations to cater to different fitness levels.
Sculpted glutes go beyond mere aesthetics; they are synonymous with a strong, well-balanced physique. Strengthened glutes contribute to improved posture, enhanced athletic abilities, and a reduced risk of injuries, particularly in the lower back and knee regions. Moreover, a robust gluteal region can augment power in various sports, assisting in activities that require jumping, running, and changing directions. Furthermore, in a world increasingly focused on wellness and fitness, well-toned glutes often symbolize dedication to health and can, in turn, boost self-esteem and body confidence.
In the ensuing sections, we will delve deeper into the anatomy of the glutes, demonstrate the most effective exercises for toning this region, and explore various strategies to seamlessly integrate these exercises into your workout regime. Whether you are a fitness novice or an experienced gym enthusiast, this guide will offer invaluable insights to assist you on your path to acquiring those sculpted, powerhouse glutes.
Anatomy of the Glutes
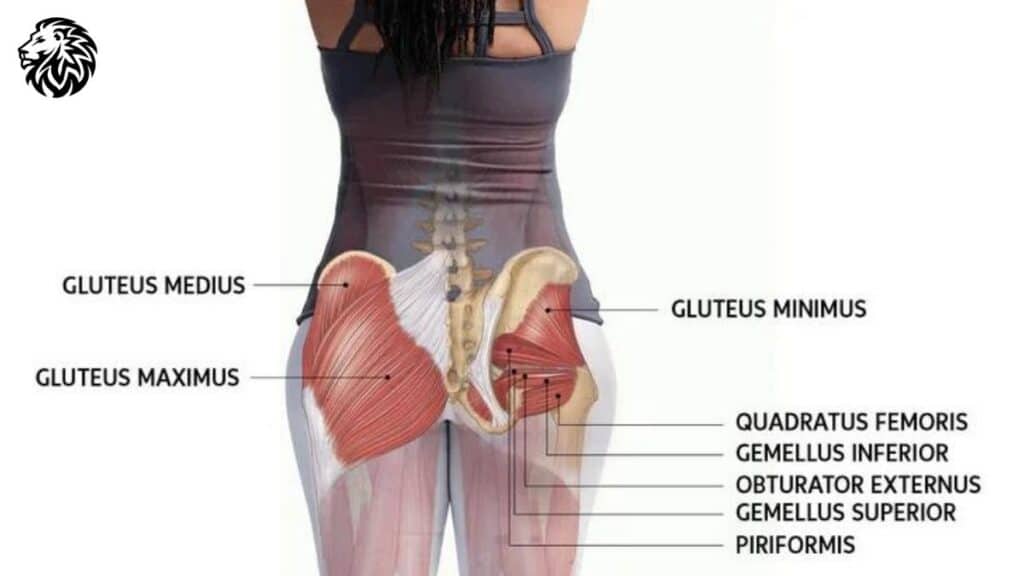
Explanation of the Gluteal Muscles and Their Function
The gluteal region is primarily composed of three main muscles: the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus, each contributing to various movements and stability of the pelvic and hip region.
- Gluteus Maximus: The largest of the three, the gluteus maximus, is responsible for hip extension, outward rotation, and elevation of the pelvis. It plays a pivotal role in activities like standing up from a sitting position, climbing stairs, and running.
- Gluteus Medius: Situated on the outer surface of the pelvis, the gluteus medius primarily facilitates hip abduction (moving the leg away from the midline of the body) and medial rotation. It’s essential for pelvic stability, especially during unilateral activities like walking or running.
- Gluteus Minimus: The smallest and deepest of the glute muscles, the gluteus minimus assists with hip abduction and internal rotation. It works hand in hand with the gluteus medius to stabilize the pelvis during movement.
Understanding the anatomy and functionality of these muscles is fundamental for targeting them effectively during workouts, ensuring balanced development and avoiding injuries.
Importance of the Glutes in Overall Body Strength and Posture
Robust glute muscles provide a solid foundation for various upper and lower body movements, owing to their central location in the body’s biomechanics. They act as stabilizers for the pelvis, ensuring optimal alignment and posture. When you engage in activities like running, jumping, or lifting, your glutes are instrumental in providing power and stability. Furthermore, well-developed glutes can prevent anterior pelvic tilt, a postural deviation that can result in excessive lumbar lordosis, ensuring a neutral spine and healthy posture.
Correlation Between Glute Strength and Lower Back Health
A direct correlation exists between glute strength and lower back health. Weak or underactivated glutes can lead to an over-reliance on the lumbar muscles during activities that require hip extension, which may contribute to lower back pain and strain. The gluteal muscles help to control the movement and stability of the pelvis, which, in turn, influences the alignment and functionality of the lower back. A solid glute training routine, therefore, is not only crucial for sculpting the buttocks but also plays an intrinsic role in mitigating lower back issues and ensuring a healthy, pain-free lumbar spine.
In the following sections, the knowledge of glute anatomy will be applied to understand the mechanisms and benefits of various exercises and how they contribute to a powerful, well-rounded posterior that supports overall body health and functionality.
Importance of Working Out the Glutes
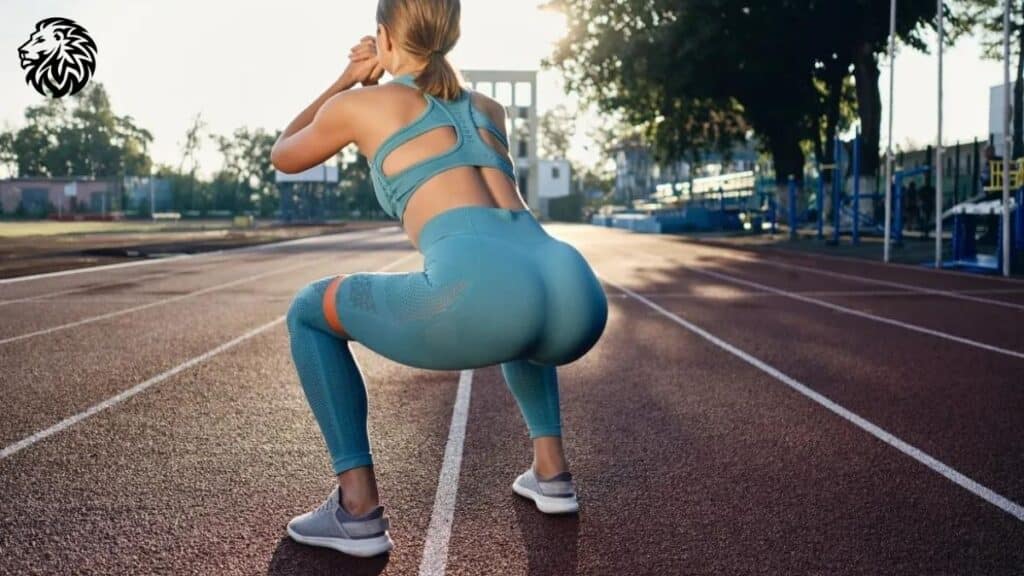

Enhancement of Athletic Performance
- Power and Speed: Strong glutes are fundamental in providing the thrust needed to power various athletic pursuits. Whether sprinting, jumping, or cycling, robust glutes enhance speed and explosive strength by propelling the body forward and upward.
- Agility: Athleticism isn’t just about speed and power; it’s also about the ability to change direction swiftly and effectively. Glutes assist in stabilizing the pelvis and controlling lower body movements, thereby facilitating improved agility during sports and activities.
- Endurance: Fortified glutes enable sustained engagement in physical activities by minimizing the overuse of secondary muscles, thus enhancing endurance and staving off early fatigue during prolonged efforts.
Improvement in Posture and Alignment
- Spinal Alignment: Robust glutes maintain pelvic alignment and reduce the risk of excessive lumbar curvature, contributing to a neutral spine and preventing undue stress on the lower back.
- Pelvic Stability: Engaging and strengthening the glutes enhances pelvic stability, ensuring that each leg operates independently of the other without pelvic drop, particularly relevant during unilateral activities like walking or running.
- Reduced Anterior Pelvic Tilt: Consistent glute training aids in correcting and preventing anterior pelvic tilt by offsetting the dominant pull of the hip flexors, thereby improving overall body posture and alignment.
Aesthetics and Body Confidence
- Physical Appearance: Well-sculpted glutes contribute to a balanced and proportionate physique, enhancing aesthetic appeal, and complementing both casual and athletic wear.
- Clothing Fit: A toned gluteal region influences how clothing fits and drapes on the body, often providing a more flattering silhouette in various fabric types and clothing styles.
- Boosted Confidence: Achieving a desired physical shape and strength in the glutes can significantly bolster body confidence and self-esteem, contributing positively to mental and emotional well-being.
- Social and Cultural Perception: While the societal and cultural ideals of beauty should be navigated with a healthy perspective, it’s undeniable that sculpted glutes are often associated with fitness and vitality in various social contexts.
Emphasizing glute training in your workout regimen translates to more than just aesthetic appeal; it’s a commitment to enhancing overall physical functionality, ensuring postural integrity, and fortifying the body’s capability to engage effectively and healthily in both athletic and daily life activities. As we delve deeper into specific exercises in the upcoming sections, consider these benefits as fundamental motivations to prioritize and enjoy your glute training journey.
Exercise Considerations

Importance of Warm-Up and Stretching
- Preparation for Physical Activity: Warming up helps to gradually increase heart rate, improve blood flow to muscles, and prepare the body for more intense physical activity.
- Injury Prevention: Engaging in dynamic warm-up exercises specific to the glutes and lower body, like leg swings or gentle squats, ensures that the muscles are primed and joints are lubricated, reducing the risk of strain or injury.
- Enhancing Flexibility: Implementing a consistent stretching routine (both pre and post-workout) facilitates improved flexibility, aids in muscle recovery, and supports optimal performance during exercises.
Selecting Appropriate Weights and Resistance
- Starting Point: Beginners should prioritize mastering form with body-weight exercises before gradually introducing additional resistance or weights.
- Progressive Overload: Progress should involve a gradual increase in resistance and weights to continually challenge the muscles and spur growth and strengthening.
- Safety First: It’s crucial to select weights that challenge the muscles without compromising form or risking injury.
Ensuring Proper Form to Avoid Injury
- Technique Mastery: Focusing on mastering the technique of each exercise, such as maintaining a neutral spine during squats or keeping the knees in line with toes during lunges, is paramount to avoiding injury.
- Engagement of Target Muscles: Ensuring that the glutes are effectively engaged and activated during exercises maximizes results and minimizes the risk of overloading adjacent muscles.
- Professional Guidance: Seeking advice and feedback from fitness professionals can aid in ensuring proper form and safe progression.
Modification for Various Fitness Levels
- Beginner Modifications: Novice individuals should focus on simpler variants of exercises, possibly utilizing body weight or lighter resistance to build foundational strength and muscle memory.
- Intermediate and Advanced Progressions: As proficiency develops, incorporate advanced variations and greater resistance to continue stimulating muscle growth and development.
- Accommodating Limitations: Individuals with physical limitations or injuries should explore alternative exercises or modifications that allow them to work their glutes safely and effectively.
Engaging in glute exercises with a well-considered approach – prioritizing warm-up, optimal form, appropriate resistance, and accommodating different fitness levels – ensures that your workout regime is not only effective but also sustainable and safe in the long term. As we move forward to explore specific exercises, keep these considerations in mind to maximize benefits and support your journey towards sculpted, powerful glutes.
Top Exercises for Glute Sculpting
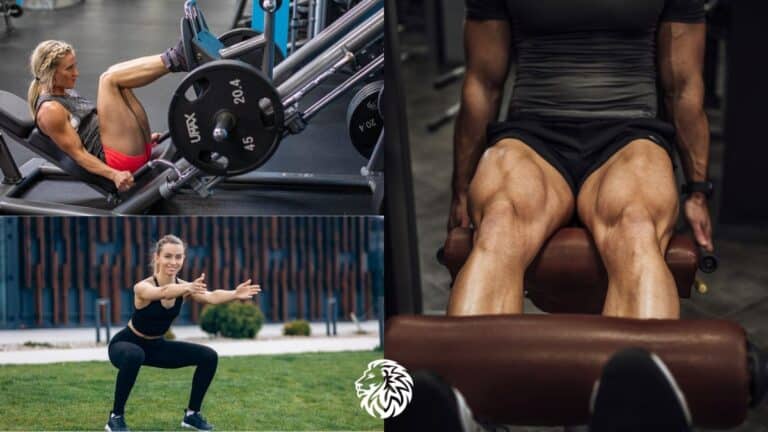
1. Squats
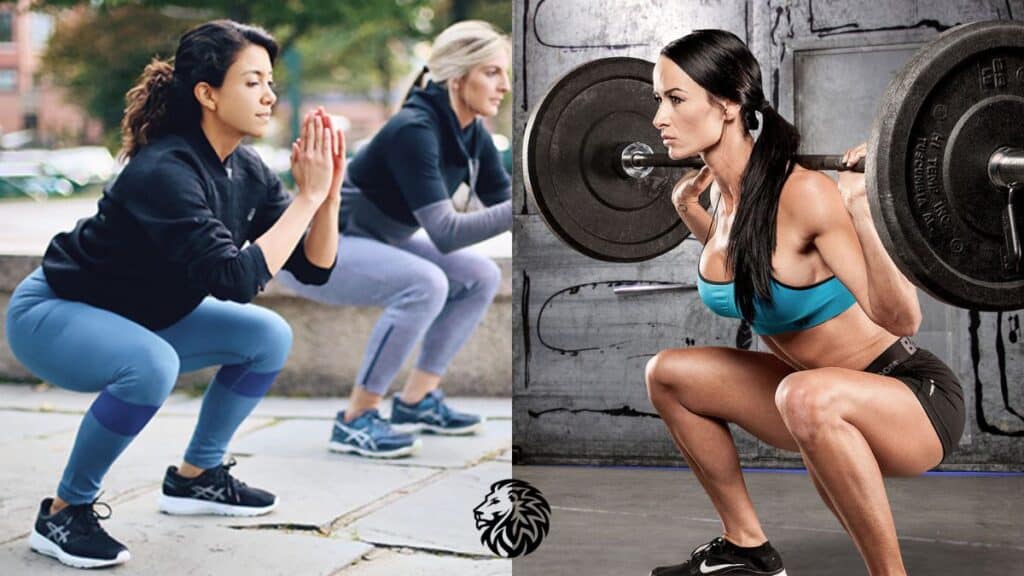
Squats are a quintessential exercise for developing and sculpting the glutes, alongside benefiting various other muscle groups in the legs and core. The comprehensive engagement of the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus during squats makes it an invaluable addition to any glute-focused workout regimen.
1. Proper Form and Variations
- Basic Squat Form:
- Start with feet hip-width apart, toes slightly pointed outward.
- Engage your core and keep a neutral spine.
- As you descend, bend at the hips and knees, ensuring the knees track over the toes.
- Lower your body as far as your flexibility allows, ideally until thighs are parallel to the ground, while keeping the chest lifted and back straight.
- Push through your heels to return to the starting position, squeezing your glutes at the top.
- Variations:
- Bodyweight Squats: Perfect for beginners or as a warm-up, focusing on mastering the technique without additional resistance.
- Weighted Squats: Introduce dumbbells, kettlebells, or a barbell to add resistance and further challenge the glutes.
- Sumo Squats: With a wider stance and toes pointing more outward, this variant emphasizes the inner thighs and different aspects of the glutes.
- Pulse Squats: Introducing small pulsing movements at the lowest squat point to maintain muscle engagement and increase intensity.
- Box Squats: Utilizing a box or bench to touch down on at the bottom of the squat, ensuring depth and aiding those with mobility limitations.
- Goblet Squats: Holding a kettlebell or dumbbell close to the chest, focusing on upright torso posture and deeper engagement of the glutes and quads.
2. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Knees Caving In:
- Be mindful to keep your knees in alignment with your toes throughout the movement.
- Engage your glutes and think about pressing your knees outward, especially as you stand back up.
- Excessive Forward Lean:
- Focus on keeping your chest lifted and maintaining a neutral spine to avoid undue stress on the lower back.
- Consider practicing in front of a mirror or recording yourself to assess and correct your form.
- Lifting Heels or Shifting Weight to Toes:
- Ensure your weight is distributed evenly through your feet, with a slight bias towards the heels.
- Practice bodyweight squats focusing on form and keeping the heels grounded.
- Skipping Full Range of Motion:
- Aim to achieve depth in your squats to maximize glute engagement.
- Utilize aids like a box to ensure consistent squat depth and gradually improve flexibility.
- Fast and Uncontrolled Movements:
- Execute each squat with control, ensuring muscle engagement throughout and avoiding momentum-based movements.
- Consider a tempo, such as 3 seconds down and 1 second up, to maintain control and enhance muscle tension.
2. Lunges
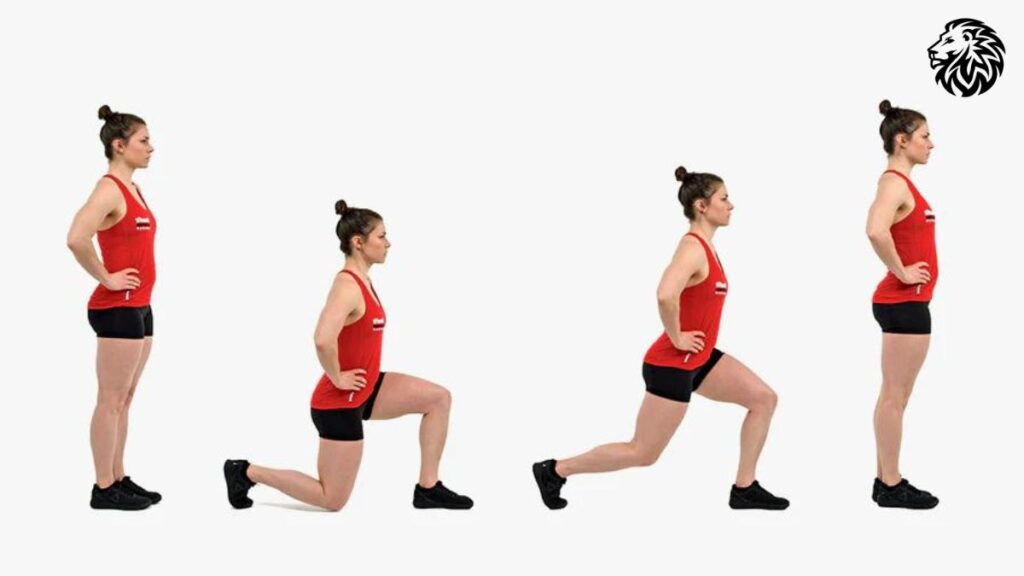

1. Explanation of Diverse Lunge Styles
- Basic Lunge: Involve stepping forward into a split stance, lowering your body until both front and back legs are bent at approximately 90 degrees, and returning to the starting position.
- Reverse Lunge: Involves stepping backward into the lunge, offering slightly more stability and less pressure on the knees compared to forward lunges.
- Walking Lunge: Encompassing forward motion, where each lunge progresses you forward. This variation is excellent for stability and dynamic movement.
- Side Lunge (Lateral Lunge): Involves stepping to the side, bending the stepping leg while keeping the other straight, targeting the glutes, and incorporating inner thigh engagement.
- Curtsy Lunge: Incorporates crossing the lunging leg behind the stationary one, targeting the gluteus medius and minimus.
- Jumping Lunges: A plyometric variant, where an explosive jump switches the feet between lunges, enhancing cardiovascular and power training.
2. Incorporation of Lunges into Routines
- Warm-Up or Cool Down: Utilize lighter, controlled lunges during warm-up or cool down to engage and stretch the glutes, quads, and hamstrings.
- Strength Training: Incorporate lunges with added weights or resistance bands to build muscle strength and endurance in the glutes and legs.
- Cardio Workouts: Include dynamic variations, such as walking or jumping lunges, to elevate the heart rate and enhance cardiovascular fitness.
- Circuit Training: Blend lunges into circuit training, alternating between upper body, core, and other lower body exercises, ensuring comprehensive workout routines.
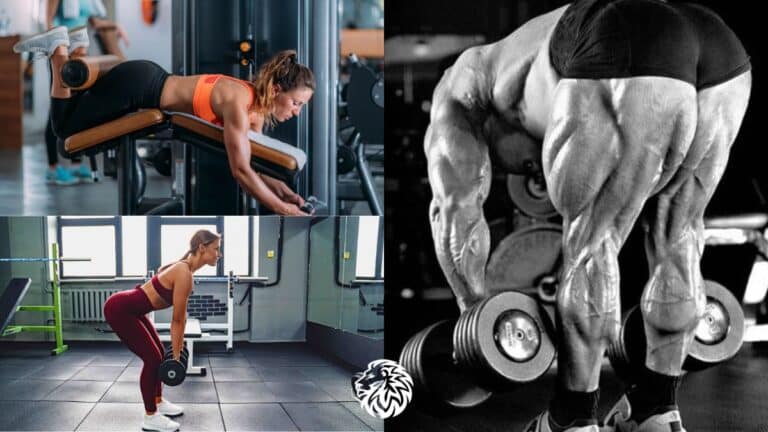
3. Deadlifts
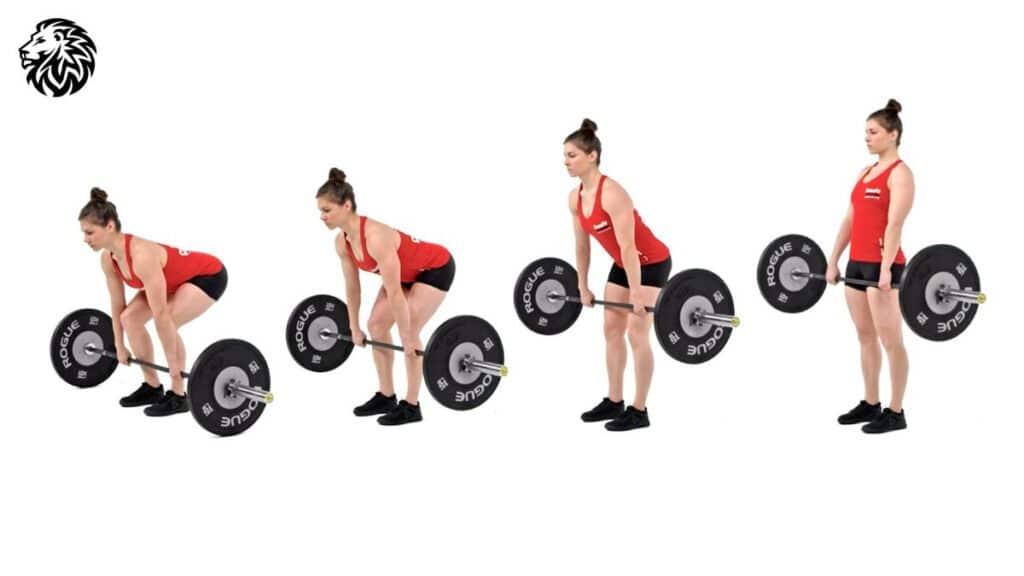

1. Importance and Method
- Importance: Deadlifts are pivotal for targeting the posterior chain, which includes the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back, enhancing functional strength, posture, and power generation.
- Method:
- Begin with feet hip-width apart, hinging at the hips and bending the knees slightly.
- Keep the back straight and chest lifted while gripping your weight (dumbbell, kettlebell, or barbell).
- Engage your core and glutes, lifting the weight by extending your hips and knees until you reach a fully upright position.
- Lower the weight by hinging at the hips and allowing the knees to bend slightly, maintaining a neutral spine throughout.
2. Variations of Deadlifts Suitable for Beginners to Advanced
- Traditional Deadlift (Conventional Deadlift): Suited for intermediate to advanced individuals, involving a barbell and a wider stance, targeting the entire posterior chain comprehensively.
- Romanian Deadlift: Ideal for beginners to advanced individuals, maintaining straighter legs, and primarily targeting the hamstrings and glutes.
- Single-Leg Deadlift: A progression suitable for all levels, incorporating balance and isolateral strength development, with or without added weights.
- Sumo Deadlift: Adopting a wider stance and an upright torso, placing less stress on the lumbar spine, suitable for various fitness levels with appropriate weights.
- Trap Bar Deadlift: Utilizing a trap bar, this variant is suitable for beginners and those with lower back considerations due to its ergonomic design and reduced lumbar strain.
4. Hip Thrusts
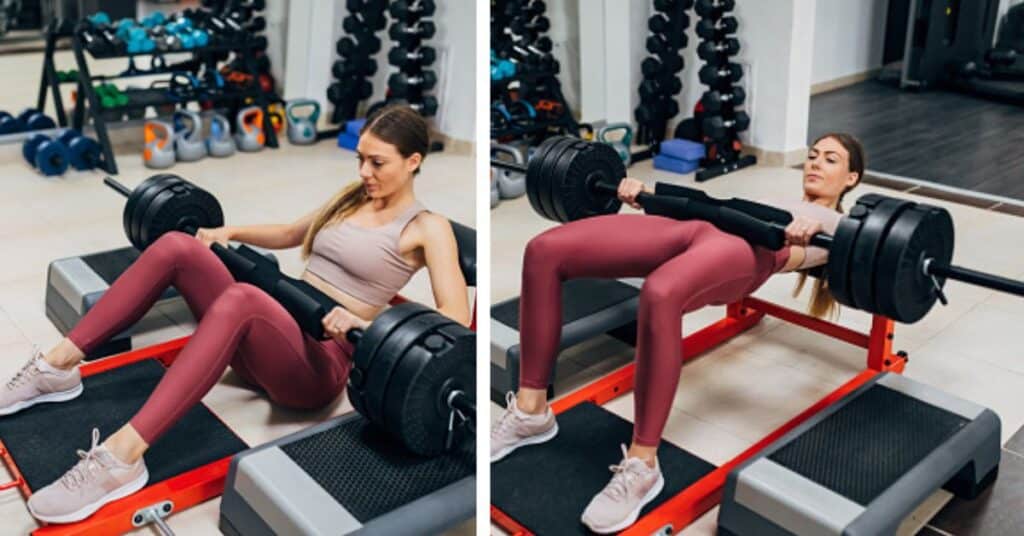

1. Methodology and Benefits
- Methodology:
- Begin seated on the ground with a bench directly behind you. Have a loaded barbell over your legs.
- Roll the barbell so that it is directly above your hips, and lean back against the bench.
- Drive through your feet and extend your hips by contracting your glutes, raising the barbell until your body forms a straight line from shoulders to knees.
- Slowly descend your hips back to the starting position.
- Benefits:
- Direct and potent engagement of the glute muscles, promoting hypertrophy and strength.
- Enhancement of hip mobility and stability.
- Improvement of explosive power through hip extension, beneficial for various sports and activities.
2. How to Intensify the Exercise
- Increase Weight: Gradually add more weight to the barbell to continue challenging your glute muscles.
- Pause Reps: Incorporate a pause at the top of the thrust, maintaining full hip extension and sustaining glute engagement.
- Single-Leg Variation: Perform the hip thrust with one leg elevated, intensifying the workload on the active glute.
- Use of Bands: Place a resistance band around your thighs to add a lateral component, working the gluteus medius.
5. Step-Ups
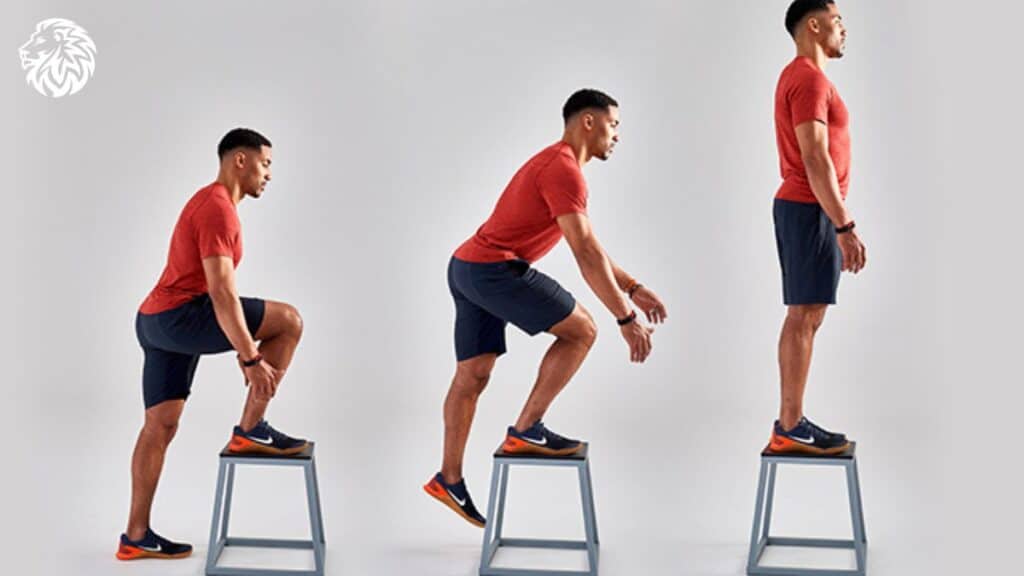

1. Performing Step-Ups for Maximum Benefits
- Begin with one foot on a stable platform or step, ensuring the whole foot is on the step.
- Engage your glutes and push through the heel of the elevated foot, lifting your body onto the step.
- Maintain control and balance as you step back down and consider alternating legs per rep or set for balanced development.
- Ensure the step height is challenging yet allows for full, controlled movement without straining the knees.
2. Adding Complexity to the Exercise
- Weighted Step-Ups: Hold dumbbells in your hands or use a weighted vest to increase resistance.
- Lateral Step-Ups: Step up from the side of the platform, engaging the glutes differently and incorporating more lateral movement.
- Step-Up with Knee Drive: As you step up, drive the trailing leg upward in a knee raise to engage the core and improve balance.
- Explosive Step-Ups: Add a jump as you step up, increasing the plyometric and cardiovascular component.
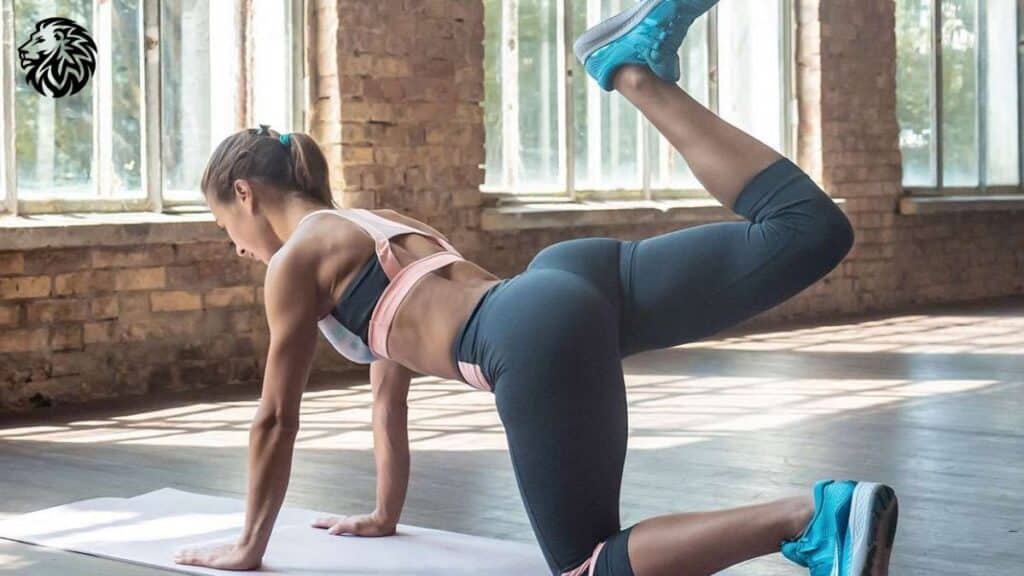
6. Donkey Kicks
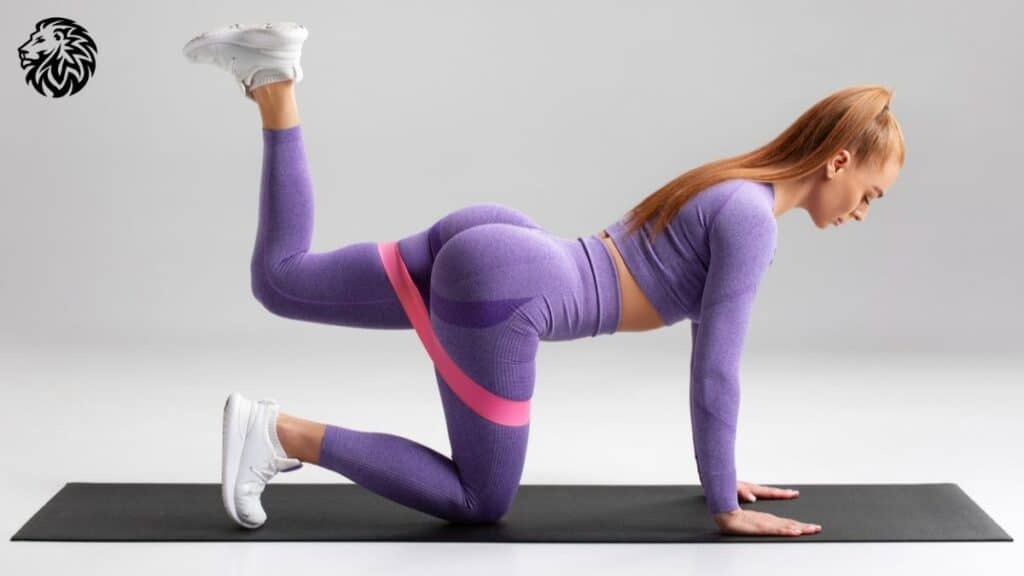

1. Technique and Benefits
- Technique:
- Start in a quadruped position with hands under shoulders and knees under hips.
- Maintain a neutral spine and engage your core.
- Lift one leg, keeping the knee bent, and push the foot upward towards the ceiling, contracting the glutes at the top.
- Slowly return to the starting position and ensure controlled movement throughout.
- Benefits:
- Targeted engagement of the gluteus maximus without the need for weights or equipment.
- Improvement of hip stability and posterior chain engagement.
- Suitable for beginners or those needing low-impact exercises.
2. Ensuring Joint Safety During Execution
- Maintain Neutral Spine: Ensure your back remains stable and neutral to prevent lumbar strain.
- Avoid Hyperextension: Ensure your leg lifts only to the point of maximal glute engagement without overarching the back.
- Controlled Movements: Perform each lift and lower with control to avoid unnecessary joint stress and ensure muscle engagement.
- Alternate Legs: Ensure balanced development and joint utilization by consistently alternating between legs.
Incorporating Glute Exercises into a Workout Routine

A robust and sustainable workout routine requires a blend of structured exercise, strategic recovery, and progressive challenges to sculpt and strengthen the glutes efficiently.
Creating a Balanced Routine
- Diversity of Movements: Include a variety of exercises that target the glutes from multiple angles and modalities (e.g., strength, endurance, and power).
- Whole-Body Approach: Ensure your workout routine also addresses other muscle groups (e.g., quads, hamstrings, core, and upper body) to foster balanced development and functional strength.
- Schedule: Devise a weekly schedule that allows you to work on different muscle groups and doesn’t overly focus on glutes to ensure balanced physical development.
Avoiding Overtraining and Allowing Adequate Recovery
- Rest Days: Allocate at least two rest days or active recovery days per week to facilitate muscle repair and growth.
- Sleep: Ensure adequate sleep each night, as sleep is pivotal for muscle recovery and overall well-being.
- Nutrition: Focus on a nutrient-dense diet with sufficient protein to support muscle recovery and growth.
- Stretching: Incorporate flexibility training and stretching to aid in recovery and maintain a healthy range of motion in the joints.
Progressive Overload Principle
- Gradual Increase: Incrementally increase the intensity of your workouts over time through added weight, increased repetitions, or enhanced complexity to continually challenge your muscles.
- Periodization: Consider employing a periodized training plan that strategically varies intensity and volume over time to optimize results and mitigate plateauing.
- Form and Technique: As you progress in weights and intensity, continuously ensure that your form and technique are not compromised.
Mixing Cardio and Strength Training Effectively
- Balanced Approach: Strive for a balance that includes both cardiovascular workouts and strength training sessions each week to enhance overall fitness.
- HIIT Workouts: Engage in High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) that can blend strength and cardio, offering efficient workouts for those seeking to optimize time and results.
- Steady-State Cardio: Integrate low-intensity, steady-state (LISS) cardio activities, like walking or cycling, which can be effective for recovery days while still promoting cardiovascular health.
- Cardio Selection: Choose forms of cardio that also engage the glutes, such as hill sprints, stair climbing, or cycling, to further accentuate your glute-training focus.
Creating a glute-focused workout regimen that thoughtfully balances intensity, variety, and recovery ensures you sculpt and strengthen effectively while preserving joint health and overall physical well-being. This comprehensive approach enables you to build a robust and aesthetically pleasing lower body, bolstered by a solid foundation of strength and functional capability.
Nutrition for Muscle Growth and Sculpting

Ensuring your glutes grow and sculpt effectively goes beyond the workout routine, with nutrition playing a pivotal role in muscle development, recovery, and overall health during your fitness journey.
Importance of Protein in Muscle Development
- Muscle Repair: Protein provides the essential amino acids needed for repair and rebuilding of muscle fibers that are stressed during workouts.
- Supporting Growth: Adequate protein intake supports the hypertrophy (growth) of muscle cells, vital for sculpting and enlarging the glutes.
- Satiety: Protein also aids in satiety, which can be beneficial for those managing their caloric intake.
- Recommendations: Reference the general guideline of 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, tailoring as per individual needs and goals.
Balanced Diet for Optimal Results
- Macro Balance: Ensure a balanced intake of macronutrients – proteins, fats, and carbohydrates – to furnish the body with the necessary energy and nutrients for workouts and recovery.
- Micronutrients: Pay attention to vitamins and minerals which are vital for muscle function, bone health, and overall well-being.
- Quality of Food: Opt for whole, nutrient-dense foods that provide sustained energy and optimal nutritional value.
Hydration and Its Role in Muscle Health
- Muscle Function: Adequate hydration is crucial for optimal muscle function and can help prevent cramps and stiffness.
- Recovery: Hydration assists in nutrient transportation and can support more efficient recovery post-exercise.
- Performance: Proper hydration supports peak performance during workouts, ensuring you can train effectively and safely.
- Recommendation: A general guideline is to consume at least 3 liters (around 13 cups) for men and 2.2 liters (around 9 cups) for women per day from all beverages and foods, and adjust based on activity level, climate, and individual needs.
Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition Tips
- Pre-Workout:
- Energy: Ensure your pre-workout meal/snack contains a balanced mix of protein and carbohydrates to provide sustained energy during your workout.
- Timing: Aim to consume your pre-workout meal/snack 1-3 hours before exercising, depending on individual tolerance and the size of the meal.
- Post-Workout:
- Recovery: Focus on protein to aid muscle recovery and carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores.
- Timing: Try to consume your post-workout meal/snack within a 2-hour window following your exercise session for optimal recovery.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in your nutrition both on workout days and rest days to support continuous muscle growth and recovery.
A nuanced and tailored approach to nutrition enhances the effects of your glute-sculpting workout routine, ensuring your muscles have the resources they need to grow and recover effectively. Balancing your macro and micronutrient intake, staying hydrated, and optimizing your pre- and post-workout nutrition synergistically supports your exercise regimen, propelling you towards your glute sculpting goals.
Common Mistakes and Their Corrections
Effective glute sculpting not only involves adopting the right exercises and nutrition but also circumventing potential pitfalls that might impair progress. Here we explore common mistakes made during glute training and how to correct them.
Poor Form and Technique
- Mistake: Implementing improper exercise forms, such as arching the back during squats or hip thrusts.
- Correction:
- Ensure alignment: Keep spine neutral and engage the core during exercises.
- Seek professional advice: Work with a fitness trainer or therapist to understand and implement correct forms.
Lack of Consistency in the Workout Routine
- Mistake: Inconsistently following the workout routine, which hampers sustained progress and muscle development.
- Correction:
- Establish a routine: Set fixed days and times for workouts.
- Make it enjoyable: Ensure the workout routine is fun and varied to maintain interest and commitment.
Neglecting Recovery and Stretching
- Mistake: Overlooking the importance of rest and flexibility, which can lead to overtraining and increase injury risk.
- Correction:
- Schedule rest days: Ensure at least two rest or active recovery days per week.
- Integrate flexibility training: Include stretching and possibly yoga to aid muscle recovery and maintain joint health.
Over-Emphasis on Quantity Over Quality
- Mistake: Prioritizing the number of reps and sets over maintaining proper form and muscle engagement, which can reduce efficacy and increase injury risk.
- Correction:
- Focus on form: Ensure each rep is performed with meticulous form, prioritizing muscle engagement.
- Adopt a mindful approach: Be present and mindful during each exercise, focusing on the muscle being worked.
Understanding and correcting these common mistakes ensures that your journey towards sculpting your glutes is not only effective but also sustainable and injury-free. A conscious approach, prioritizing form, consistency, recovery, and quality, ensures that your efforts in the gym (or at home) translate into tangible, healthy progress towards your fitness goals.
Conclusion
Navigating through the multifaceted journey to sculpted and robust glutes involves more than merely focusing on a set of exercises; it calls for a holistic approach that intertwines targeted workouts, considered nutrition, meticulous form, and ample recovery.
Summary of Key Points Discussed
- Anatomy and Functionality: An understanding of the gluteal muscles and their influence on overall body posture and strength.
- Diverse Exercise Regimen: The incorporation of varied exercises, such as squats, lunges, and hip thrusts, each contributing uniquely to glute development.
- Nutritional Backbone: Emphasizing the pivotal role of protein, a balanced diet, and hydration in supporting muscle growth and recovery.
- Avoidable Mistakes: Highlighting the importance of proper form, consistent routines, adequate recovery, and a quality-over-quantity approach to exercise.
Encouragement for the Journey to Sculpted Glutes
Embarking on a journey towards sculpted glutes is a commitment that transcends mere physical transformation. It’s an investment in your health, posture, and, potentially, your confidence and overall well-being. Celebrate each milestone, acknowledging that every step taken is a movement towards improved physical health and aesthetic goals.
Reminder of the Importance of Consistency, Proper Form, and Balanced Nutrition
- Consistency: Your regularity in the workout and nutritional plan compounds over time, gradually sculpting and strengthening your glutes.
- Proper Form: Ensuring impeccable form and technique not only enhances the efficacy of each exercise but also safeguards against unnecessary injuries.
- Balanced Nutrition: Remember that the efforts exerted in your workouts are synthesized and actualized with the support of a nutritious and balanced diet.
Your pursuit towards sculpting your glutes is a journey that’s likely to be speckled with challenges and triumphs. Embrace each phase, stay consistent, prioritize your health, and remember: the path to your goal is achieved by amalgamating focused workouts, strategic recovery, and nutritional diligence. Here’s to strong, sculpted glutes and the myriad of benefits they will usher into your fitness journey!







