Your chest muscles are among the stars of your upper body show. They’re essential not only for the aesthetic appeal but also for practical purposes. These muscles play a pivotal role in many everyday activities, from pushing and lifting to postural support. Building these muscles, therefore, improves not just your physical appearance but also your functionality and overall health.
Having a well-developed chest has numerous benefits. These include improved posture, increased upper body strength, and level up your overall athletic performance. Moreover, the added muscle mass revs up your metabolic rate, while the additional strength supports your upper body, making it more injury-resistant. Last but not least, a well-defined chest enhances your appearance, often leading to a boost in confidence and self-esteem.
If you’re on a mission to build strength and size in your chest, random workouts just won’t cut it. These workouts target your muscles systematically, inducing more efficient muscle growth and strength gains. They ensure that you’re progressively overloading your muscles, a key principle in muscle development, while also minimizing the risk of injury. A smart chest workout routine involves combining a variety of exercises to hit different parts of the chest, while also considering important elements like rest and nutrition, crucial allies for muscle recovery and growth.
Understanding the Chest Muscles
Anatomy of the Chest Muscles (Pectoralis Major and Minor)
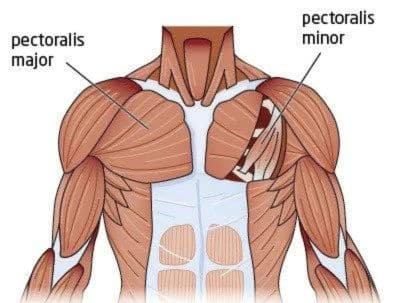
Your chest is primarily home to two muscles, the pectoralis major and the pectoralis minor. The pectoralis major, the larger of the two, is a fan-shaped powerhouse that blankets most of your chest. It begins its journey from the sternum and clavicle and ends at the upper humerus. This muscle plays a big role in motions like flexing, rotating, and adducting the humerus. Nestled underneath the pectoralis major is the aptly named pectoralis minor, a smaller yet vital muscle that kicks in for the movement and stabilization of the shoulder blade. It starts from the middle ribs and fastens to the scapula.
Role of these Muscles in Daily Life and Sports
The chest muscles, particularly the pectoralis major, are involved in many everyday activities like pushing a door open, lifting or carrying items, and even stabilizing your body during movement. In sports, these muscles are vital for activities such as swimming, boxing, and any sport that involves throwing. They contribute to the power and precision of these movements.
How Chest Exercises Contribute to Overall Upper Body Strength
Chest exercises help to improve the strength and size of the chest muscles, but they also contribute to overall upper body strength. Many chest exercises are compound movements, meaning they engage multiple muscles at once. For instance, the bench press, a staple in chest training, also works the triceps and shoulders. By improving chest strength, you’ll also enhance the strength of these associated muscles. Additionally, a strong chest can help improve your performance in other exercises that rely on upper body strength, contributing to a more balanced and powerful physique.
Key Factors in Building Chest Muscles
Importance of Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is a key principle in strength training and muscle building. It refers to the process of gradually increasing the stress placed on your muscles during exercise. This can be achieved by increasing the weight lifted, increasing the number of repetitions or sets, or decreasing the rest time between sets. Progressive overload forces your muscles to adapt, leading to increases in muscle size and strength.
The Role of Nutrition and Rest in Muscle Growth
Exercise is only one part of the equation when it comes to muscle growth. Nutrition and rest are equally important. Consuming adequate protein is crucial as it provides the building blocks for muscle repair and growth. Adequate calories are also needed to support the energy demands of intense training. Furthermore, rest is essential for recovery and growth. During rest, your body repairs the micro-tears in muscle fibers caused by exercise, leading to increases in muscle size.
The Influence of Genetics on Muscle Development
While you can significantly influence your muscle development through training, nutrition, and rest, genetics also plays a role. Some people naturally have more muscle fibers or respond better to resistance training. However, everyone can improve their muscle size and strength with consistent, well-designed training, and proper nutrition.
The Importance of Correct Form and Injury Prevention
Maintaining correct form during exercises is paramount not only for effective muscle stimulation but also for injury prevention. Incorrect form can lead to imbalances, strains, or serious injuries. Therefore, learning and maintaining proper form should be a priority, especially when performing complex movements or lifting heavy weights. Regularly incorporating stretching and mobility work can also help prevent injuries.
Chest Building Techniques
Different Exercise Techniques (Hypertrophy vs Strength Training)
Hypertrophy training focuses on increasing muscle size, usually involving moderate to high repetitions (8-15 reps per set) with moderate weight. Strength training, on the other hand, emphasizes increasing the amount of weight lifted, typically involving lower repetitions (1-6 reps per set) with heavier weight. Both techniques can be effective for building chest muscles, and incorporating a mix of both in your training regimen can lead to optimal results.
Benefits of Compound and Isolation Exercises
Compound exercises involve multiple joints and muscle groups, offering a more functional approach to training, and typically allowing you to lift heavier weights. They also stimulate a larger release of muscle-building hormones like testosterone and growth hormone. Examples of compound exercises for the chest include the bench press and dips. Isolation exercises focus on one muscle or muscle group, allowing you to target specific muscles more directly. Examples for the chest include flyes and cable crossovers.
The Importance of Incorporating Both in a Training Regimen
Incorporating both compound and isolation exercises in your training regimen ensures a well-rounded approach to muscle development. Compound exercises provide the foundation for strength and size, while isolation exercises allow for targeted development and shaping. This combination can help to maximize muscle growth and improve overall aesthetics.
Top Exercises for Chest Development
Barbell Bench Press
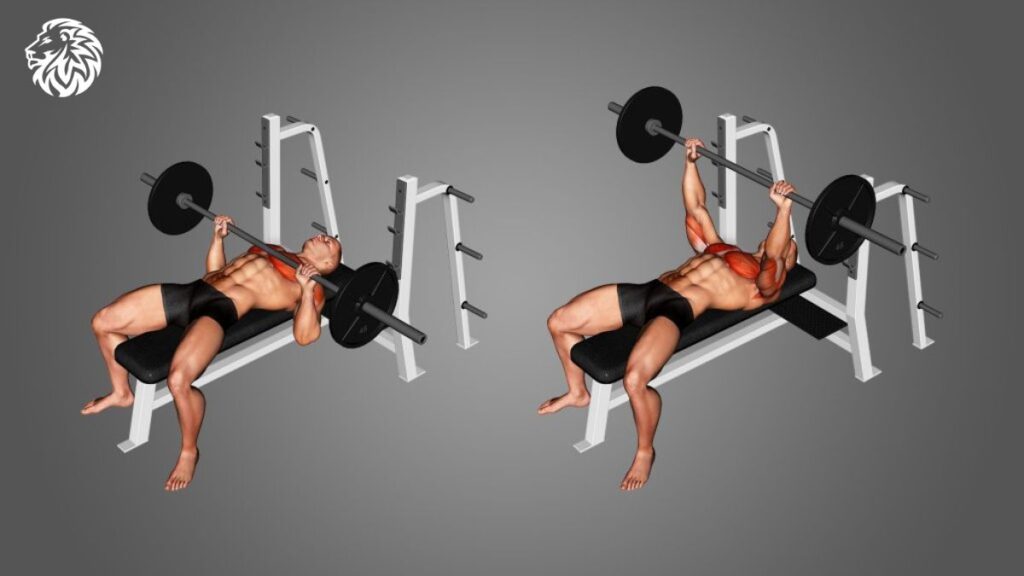
Considered the king of chest exercises, the barbell bench press primarily targets the pectoralis major while also working the anterior deltoids and triceps.
To do this exercise, lie on your back on the bench. Hold the bar with hands slightly wider than shoulder-width. Lower the bar to your chest, then push it back up. Typically perform 3-4 sets of 8-12 reps.
Incline Dumbbell Bench Press
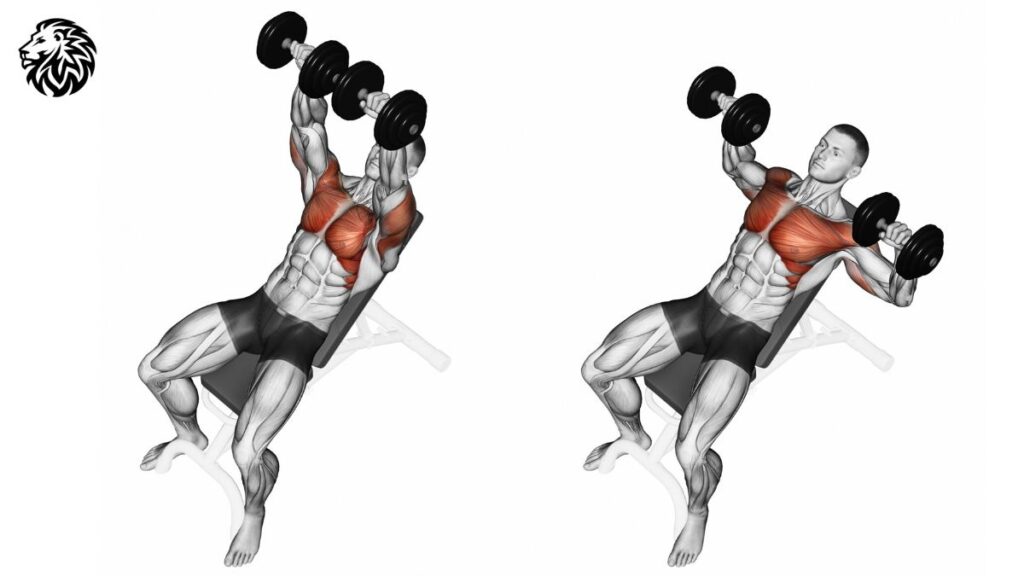
By setting the bench to an incline, you can place more emphasis on the upper part of the chest and the anterior deltoids.
To do this exercise, set the bench to an incline of 30-45 degrees. Hold a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder width, then press the dumbbells up and bring them back down. Perform 3-4 sets of 8-12 reps.
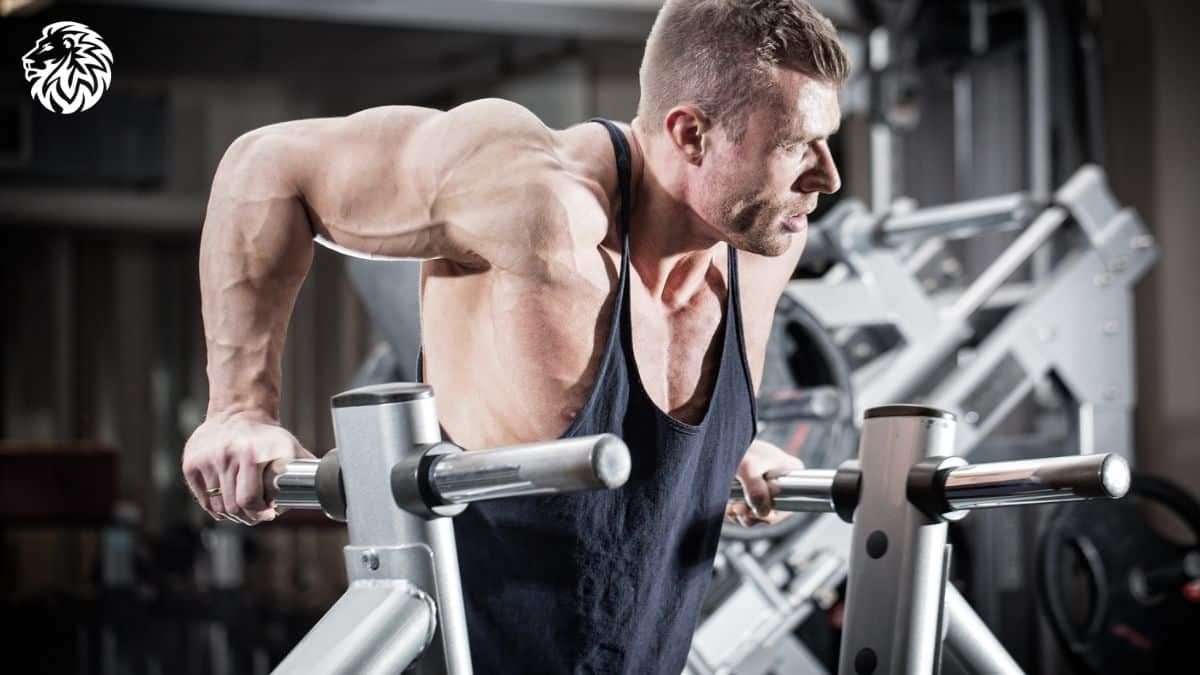
Dips for Chest
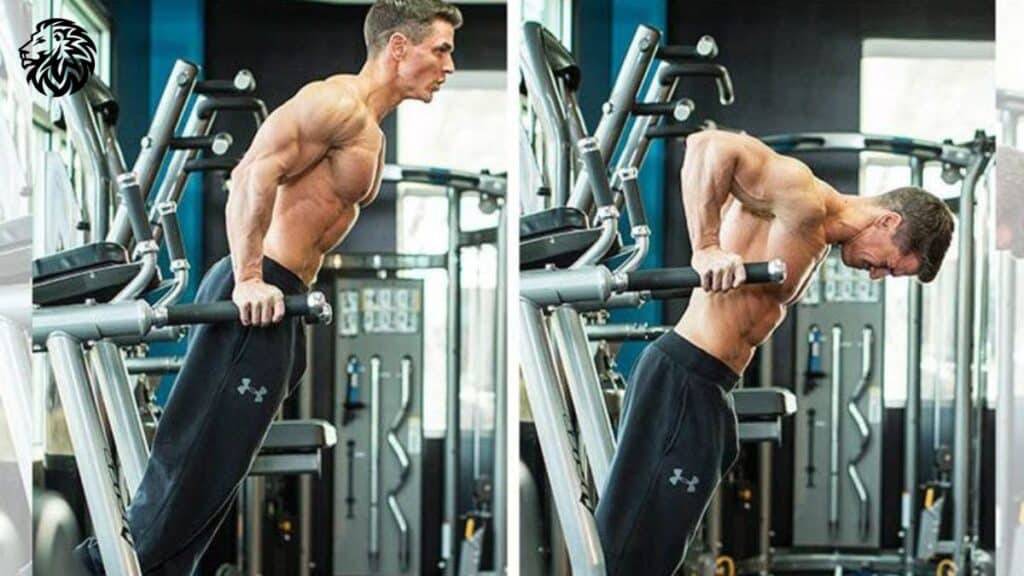

Dips, when performed with the torso leaning forward, target the lower part of the pectoralis major.
To do this exercise, position yourself on the parallel bars, lean forward, then lower your body until your arms are at a 90-degree angle before pushing back up. Perform 3-4 sets to failure.
Cable Flyes
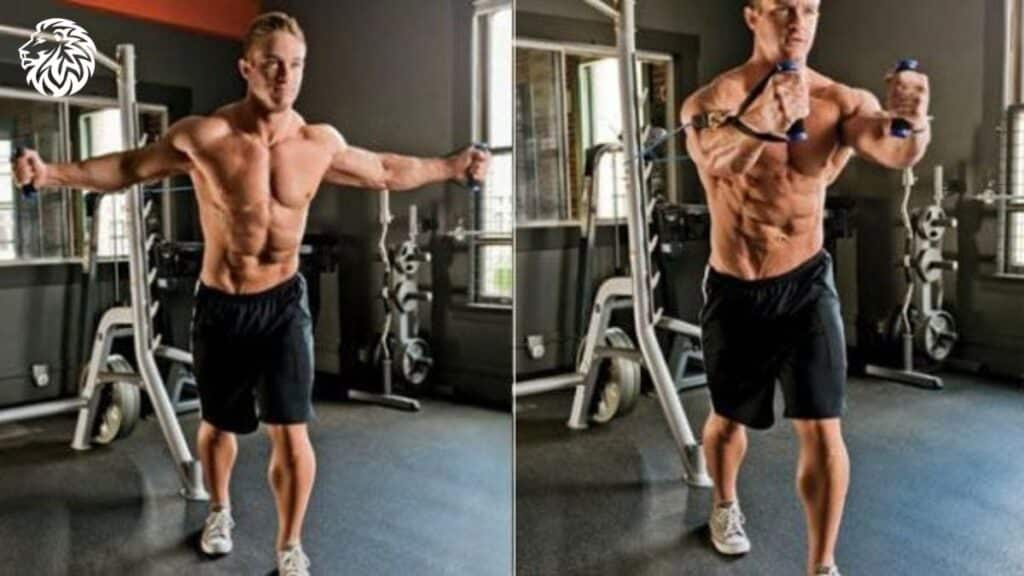

This isolation exercise targets the pectoralis major, providing a unique tension curve that can stimulate muscle growth.
To do this exercise, stand in the middle of a cable machine, grab the handles with a slight bend in your elbows, then bring your hands together in a wide arc. Perform 3-4 sets of 10-15 reps.
Pushups
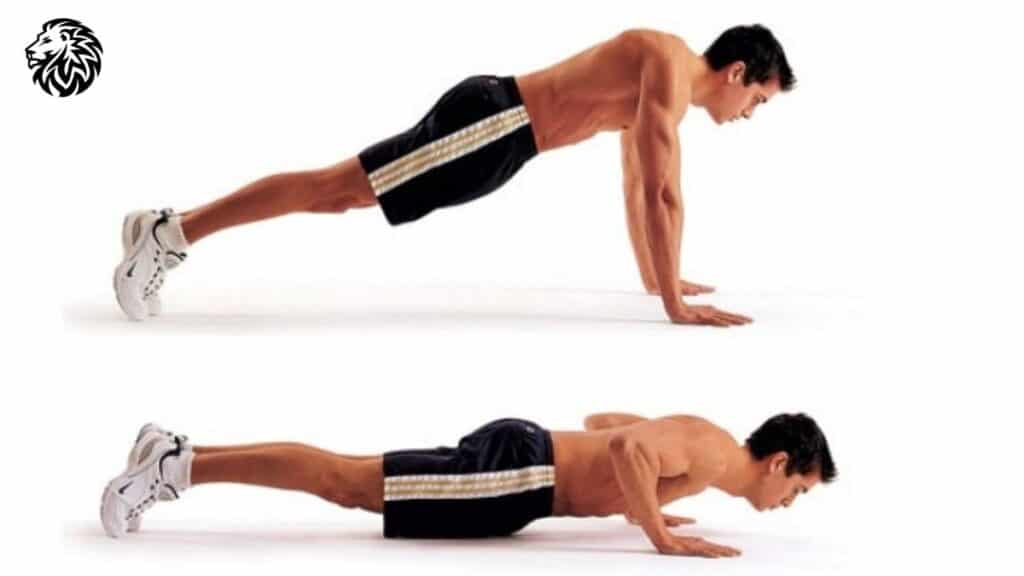

A bodyweight exercise that targets the chest muscles and also engages the deltoids and triceps.
To do this exercise, start in a high plank position, lower your body until your chest nearly touches the floor, then push back up. Perform 3-4 sets to failure.
Example of a Comprehensive Chest Workout Routine
Weekly Schedule Incorporating Aforementioned Exercises
Day 1:
- Barbell Bench Press: 4 sets of 8-12 reps
- Incline Dumbbell Bench Press: 4 sets of 8-12 reps
- Cable Flyes: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
Day 4:
- Dips for Chest: 4 sets to failure
- Pushups: 3 sets to failure
- Cable Flyes: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
Instructions on How to Adjust the Routine Based on Experience Level (Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced)
Beginners: Start with lighter weights and focus on mastering the correct form. You might begin with two days of chest exercises per week, with ample rest in between.
Intermediate: Start to add more weight and increase the volume (sets x reps) of your workouts. You could potentially add another day of chest exercises, depending on your recovery.
Advanced: Add more intensity techniques, such as drop sets, supersets, or rest-pause sets. Continue to increase volume and weight as tolerated. Advanced trainers might also focus on specific weaknesses or imbalances in their chest development.
Tips on Warming Up and Cooling Down
Warming Up: Always begin your workout with a warm-up to prepare your muscles and joints for the workout. This could be 5-10 minutes of light cardio followed by dynamic stretches or light, high-rep sets of the exercises you’re about to perform.
Cooling Down: After your workout, perform some static stretching or foam rolling for your chest muscles. This can aid in recovery and flexibility. Don’t forget to hydrate and consume a meal or protein shake to kickstart the recovery process.
The Role of Nutrition in Chest Development
Basic Principles of Nutrition for Muscle Growth
Nutrition plays a fundamental role in muscle growth. Consuming adequate calories and macronutrients – particularly protein – is essential. Protein provides the building blocks (amino acids) needed to repair and build muscle tissues, while carbohydrates provide the energy needed for your workouts. Fats are also necessary for hormone production and overall health.
Recommended Macronutrient Breakdown for Strength and Size
The exact macronutrient breakdown can vary depending on individual factors, but a common starting point is the 40/30/30 rule: 40% of calories from carbohydrates, 30% from protein, and 30% from fats. This provides a balanced intake that supports muscle growth and energy needs. However, individual requirements may vary, and it can be beneficial to consult with a dietitian or nutritionist.
Meal Timing and Its Importance in Muscle Recovery and Growth
Meal timing can also play a role in muscle development. Consuming a source of protein and carbohydrates shortly after your workout can kickstart the recovery process. This is often referred to as the “post-workout window” and can be a strategic time to fuel your body. Furthermore, ensuring a consistent intake of protein throughout the day can help maintain a positive protein balance, conducive to muscle growth. However, it’s important to note that total daily intake is still the most crucial factor in dietary success.
Common Mistakes When Trying to Build Chest Muscles
Overview of Common Errors in Technique, Programming, and Nutrition
- Technique: Some common mistakes include lifting too heavy at the expense of form, not fully extending or retracting during exercises, and not engaging the chest muscles adequately during exercises.
- Programming: Overtraining without giving the muscles enough time to recover, not applying the principle of progressive overload consistently, or focusing too much on either compound or isolation exercises instead of incorporating a balanced mix can hinder progress.
- Nutrition: Not consuming enough protein or overall calories to support muscle growth, or neglecting the importance of a balanced diet can also impede muscle development.
Ways to Avoid These Mistakes
- Technique: Always prioritize form over the weight lifted. Consider working with a trainer to learn and maintain correct form.
- Programming: Follow a balanced and structured workout plan that incorporates progressive overload and ensures adequate recovery time.
- Nutrition: Aim to consume a balanced, nutrient-dense diet with adequate protein. Consider consulting with a dietitian or nutritionist to develop an appropriate meal plan.
How to Overcome Plateaus in Chest Development
- Reassess your program: If you’re not seeing progress, it might be time to adjust your workout program. You may need to change up your exercises, set/rep scheme, or introduce new training methods.
- Review your nutrition: Are you consuming enough protein and overall calories? If not, this could be limiting your muscle growth.
- Consider recovery: Ensure you’re getting enough rest and not overtraining. Your muscles need time to repair and grow after workouts.
- Consistency is key: Building muscle takes time, and it’s important to stay consistent with both your training and nutrition plan. Be patient and persistent.
Conclusion
Building a strong and well-sized chest is more than an aesthetic goal; it’s about improving overall upper body strength and function. This article has detailed the anatomy and importance of chest muscles, key factors in muscle building, effective chest exercises, a comprehensive workout routine, the role of nutrition, common mistakes, and how to overcome plateaus.
Muscle building is a journey, not a sprint. It takes time, effort, and consistency to see results. Don’t be discouraged if progress seems slow; it’s important to celebrate every improvement, no matter how small. The key is to stay consistent with your training and nutrition, and over time, you’ll see your hard work pay off.
Always prioritize safety and correct form during your workouts to avoid injuries and ensure that you’re effectively engaging your muscles. Don’t forget the importance of a balanced program that includes both compound and isolation exercises, and make sure to give your muscles the rest they need to recover and grow. With persistence, discipline, and a well-designed program, you can build a strong and impressive chest. Happy lifting!
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it typically take to see significant growth in chest muscles with a regular workout routine?
The time it takes to see significant growth varies widely among individuals due to factors like genetics, diet, and workout intensity. However, with a consistent and well-structured chest workout routine, you might start noticing improvements in strength within a few weeks, and visible size increase can typically be seen after a few months of regular training.
I’m following a chest workout routine but not seeing progress. What could be the issue?
If you’re not seeing progress, several factors might be at play. You may not be eating enough protein or calories to support muscle growth. Alternatively, you could be overtraining your chest muscles without giving them enough time to recover and grow. It’s also possible that you aren’t applying progressive overload correctly, which is crucial for muscle development. Finally, your form might need adjustments to target the muscles more effectively.
Can I build a muscular chest using only bodyweight exercises?
Yes, you can build a muscular chest using bodyweight exercises. However, it might take longer compared to using weights due to the limit on how much resistance you can apply. Exercises like push-ups, dips, and different variations of these can effectively work your chest muscles. Remember the principle of progressive overload – as you get stronger, you’ll need to increase the difficulty of your exercises to continue challenging your muscles.
How many times per week should I train my chest for optimal growth?
For most people, training chest muscles 2-3 times per week is sufficient for growth and allows adequate recovery time. However, the optimal frequency can vary based on factors like your overall workout volume, intensity, recovery capabilities, and experience level.
What should I eat before and after my chest workout to optimize muscle growth?
Before a workout, aim to have a balanced meal with carbohydrates and protein to fuel your training. This could be something like a chicken and rice dish, or a protein shake with a banana. After your workout, consume a meal or snack that includes protein to aid muscle repair and carbohydrates to replenish your energy stores. This might look like a protein shake and a piece of fruit, or a meal with lean protein, veggies, and a starchy carb.







