The glutes, comprising the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus, are more than just a key aspect of physical attractiveness. They play a crucial role in overall body strength, stability, and function. Glute exercises, therefore, are not only essential for those seeking a bigger, more sculpted booty but also for anyone looking to enhance their overall physical health and performance.
Firstly, from an aesthetic perspective, well-developed glutes contribute significantly to the symmetry and proportion of the body. They add to the desired curvature and shape, which is a common fitness goal for many. However, the benefits of glute exercises extend far beyond their aesthetic appeal. Strong glutes can dramatically improve posture, alleviate lower back pain, and enhance athletic performance. They are the powerhouse for many movements, from walking and running to jumping and lifting.
Engaging in targeted glute exercises is the most effective way to achieve a firmer, larger, and more toned buttocks. These exercises are designed to challenge the glute muscles, leading to hypertrophy or muscle growth. Over time, consistent training increases muscle size and strength, contributing to the desired ‘bigger booty’.
Moreover, these exercises do more than just increase muscle size; they also improve muscle function. Stronger glutes can lead to better performance in a variety of sports and daily activities, reducing the risk of injuries and improving overall mobility and balance.
In the following sections, we will explore the top seven glute exercises that are not only effective in growing and strengthening these muscles but are also versatile and can be adapted to suit various fitness levels. From classic squats to innovative cable kickbacks, each exercise will be broken down to understand its impact on glute development and how it contributes to both a stronger and aesthetically pleasing lower body.
Glute Anatomy
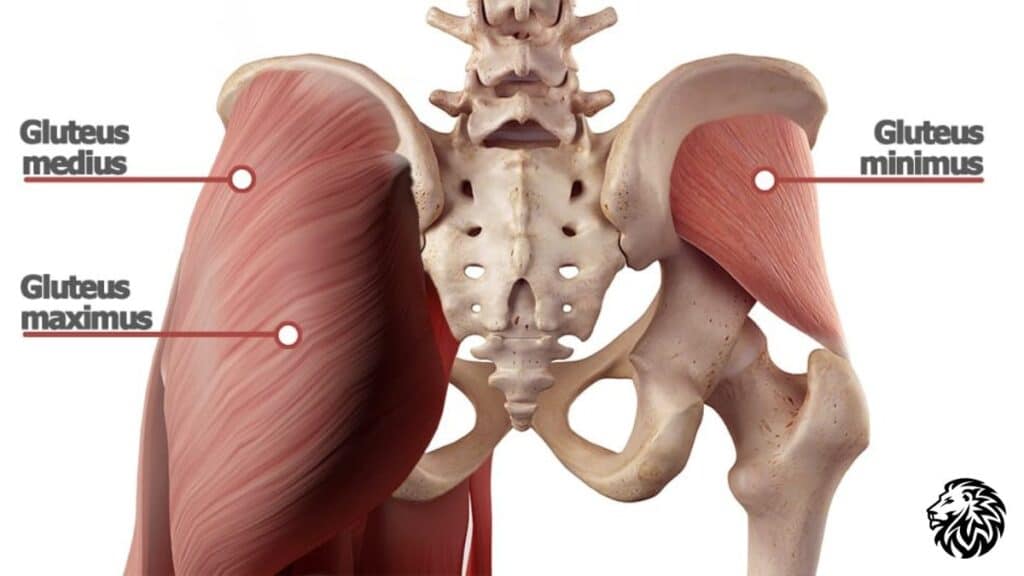
Understanding the anatomy of the glutes is crucial for effective training and development of these muscles. The gluteal region is composed of three primary muscles:
- Gluteus Maximus: This is the largest and most superficial of the three glute muscles. It’s responsible for the shape of your buttocks and is the most visible. The gluteus maximus is crucial for a range of movements, including hip extension (moving your thigh backward), external rotation (turning your leg outward), and abduction (moving your thigh away from the center of your body). It plays a key role in movements like standing up from a sitting position, climbing stairs, and squatting.
- Gluteus Medius: Located beneath the gluteus maximus and partially covered by it, the gluteus medius is primarily responsible for hip abduction. It also assists in hip internal and external rotation. This muscle is crucial for stabilizing the pelvis during walking or any activity that involves lifting one leg. Strengthening the gluteus medius can help in improving balance and reducing the risk of injuries, especially in the hips and knees.
- Gluteus Minimus: This is the smallest and deepest of the gluteal muscles. Like the gluteus medius, it aids in hip abduction and stabilization of the pelvis. It also plays a role in internal and external rotation of the thigh. Strengthening the gluteus minimus is important for maintaining hip stability, especially in movements that involve single-leg support.
In addition to these primary muscles, there are other muscles in the region that support the function of the glutes, such as the tensor fasciae latae and the deep rotator muscles of the hip.
Effective glute training should involve exercises that target all three of these muscles to ensure balanced development and functionality. This is why a varied workout routine that includes exercises like squats, lunges, hip thrusts, and others is essential for comprehensive glute development. Understanding the anatomy and function of these muscles can help in better targeting them during workouts and improving the effectiveness of your glute training regimen.
The 7 Best Glute Growing Exercises for a Bigger Booty
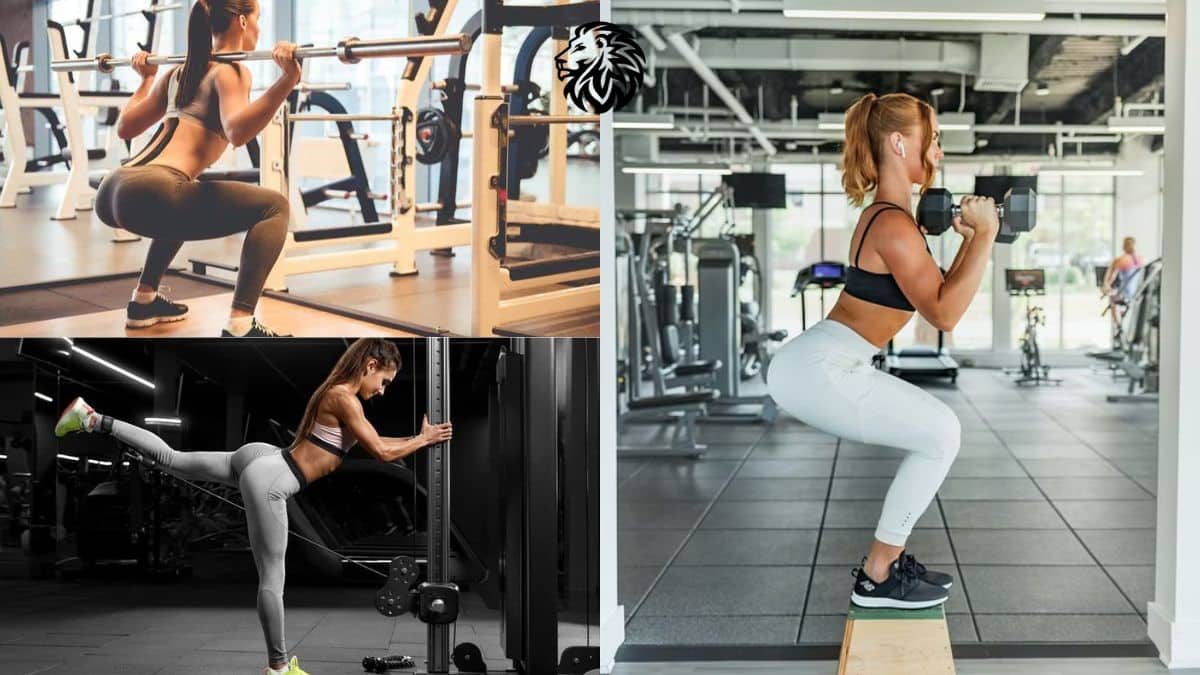
Exercise #1: Squats

Description of the Squat Movement:
Squats are a fundamental exercise that primarily targets the glutes, quadriceps, hamstrings, and core. The basic movement involves standing with your feet shoulder-width apart, bending your knees and lowering your body as if sitting back into a chair, keeping your back straight and chest up, and then pushing back up to the starting position. Proper form is key to prevent injury and maximize effectiveness.
Variations of Squats:
- Bodyweight Squats: These are the simplest form, requiring no equipment. They’re ideal for beginners or as part of a warm-up routine.
- Barbell Squats: Typically performed with a barbell placed on the upper back (back squat). This variation allows for the addition of significant weight, leading to greater strength and muscle gains.
- Dumbbell Squats: Holding a dumbbell in each hand at your sides or a single dumbbell in front of your chest (goblet squat) adds resistance while also challenging your stabilizer muscles.
- Sumo Squats: With a wider stance and toes pointed outwards, sumo squats place more emphasis on the inner thighs and glutes compared to traditional squats.
Benefits for Glute Growth:
Squats are incredibly effective for building glute muscles due to the extensive activation these muscles receive during the movement. Here are some key benefits:
- Comprehensive Muscle Engagement: Squats not only work the glutes but also engage the entire lower body and core, leading to improved overall muscle tone and functional strength.
- Adaptability for Strength Gains: With various squat variations, you can continuously challenge your glutes by increasing resistance or changing the squat style.
- Improved Muscle Hypertrophy: Regular squatting, especially with added weight, stimulates muscle growth (hypertrophy) in the glutes, contributing to a larger and firmer booty.
- Enhanced Functional Strength: Squats mimic natural movement patterns, improving your ability to perform daily activities and reducing the risk of injury.
- Versatility: Squats can be performed anywhere, with or without equipment, making them a convenient exercise for people of all fitness levels.
Incorporating these different squat variations into your workout routine can significantly contribute to the development of strong, well-shaped glutes. Remember to focus on proper form and gradually increase intensity to ensure continual progress and prevent injury.
Exercise #2: Lunges

How to Properly Perform Lunges:
Lunges are a versatile lower body exercise that target the glutes, quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves. To perform a basic lunge:
- Starting Position: Stand with your feet hip-width apart. Keep your upper body straight, shoulders relaxed, and chin up.
- The Lunge: Step forward with one leg, lowering your hips until both knees are bent at about a 90-degree angle. Ensure that your front knee is directly above your ankle and not pushed out too far. The other knee should not touch the floor.
- Return to Start: Keep the weight in your heels as you push back up to the starting position.
Variations of Lunges:
- Walking Lunges: These involve stepping forward into a lunge, then stepping the back foot forward into another lunge, essentially ‘walking’ forward.
- Reverse Lunges: Instead of stepping forward, you step backward into the lunge. This variation can be easier on the knees and places more emphasis on the glutes.
- Curtsy Lunges: These involve stepping back and across behind the front leg, similar to a curtsy. This variation targets the gluteus medius and minimus for more rounded glute development.
Impact on the Glutes and Lower Body:
Lunges are exceptionally beneficial for building and toning the glutes and lower body:
- Targeted Glute Activation: Lunges specifically engage the gluteal muscles, especially when taking longer steps. The different variations allow you to hit the glutes from multiple angles for comprehensive development.
- Lower Body Strength and Symmetry: They work each leg individually, which helps in correcting muscle imbalances and strengthening both sides of the body equally.
- Improved Balance and Coordination: Lunges require and thus improve balance and coordination, essential for functional fitness and everyday activities.
- Flexibility and Mobility Enhancement: Regularly performing lunges can increase hip flexor flexibility, benefiting overall mobility.
- Versatility and Adaptability: Like squats, lunges can be performed anywhere and easily modified to increase intensity, such as by adding weights or increasing repetitions.
Incorporating these lunge variations into your workout routine can lead to significant improvements in glute size, shape, and overall lower body strength. As always, focus on maintaining good form to maximize benefits and minimize the risk of injury.
Exercise #3: Hip Thrusts

Step-by-Step Guide to Performing Hip Thrusts:
Hip thrusts are a powerful exercise specifically targeting the glutes. They are known for their effectiveness in building glute strength and size.
- Starting Position: Sit on the ground with a bench directly behind you. Have a padded barbell or weight across your hips (for beginners, start without weight to master the form).
- Setup: Lean against the bench so that it is across your upper back. Your feet should be planted flat on the ground, about shoulder-width apart. Ensure your knees are bent and your feet are close enough to your butt.
- The Movement: Drive through your heels, extending your hips vertically. Your body should form a straight line from your shoulders to your knees at the top of the movement. Ensure your chin is tucked and neck neutral.
- Squeeze and Hold: At the top of the thrust, squeeze your glutes hard for a moment.
- Return to Start: Lower your hips back down to the starting position in a controlled movement.
Variations of Hip Thrusts:
- Single-Leg Hip Thrust: Performed similarly to the standard hip thrust but with one leg lifted off the ground. This increases the challenge and targets each glute independently.
- Barbell Hip Thrust: Adds more resistance to the exercise and is ideal for intermediate to advanced individuals. The barbell is placed across the hips with added weights as needed.
Importance for Glute Activation and Strength:
Hip thrusts are especially beneficial for the following reasons:
- Direct Glute Targeting: Hip thrusts involve a powerful hip extension movement that directly targets the gluteus maximus, the largest muscle in the gluteal region.
- Maximal Muscle Activation: This exercise allows for a greater range of motion in the hips, which leads to maximal glute activation, especially at the top of the movement where the glutes are fully contracted.
- Strength and Size Gains: Regularly including hip thrusts in your routine can lead to significant increases in both the strength and size of the glute muscles.
- Improved Performance: Strong glutes are essential for explosive movements, stability, and overall athletic performance.
- Lower Back Health: By strengthening the glutes, hip thrusts can also help in reducing or preventing lower back pain, a common issue arising from weak gluteal muscles.
To see the best results, it’s important to progressively increase the resistance or vary the exercises as you become stronger. This can be done by adding more weight to the barbell hip thrusts or increasing the number of repetitions or sets for the single-leg hip thrust. As with any exercise, maintaining proper form is crucial to prevent injury and ensure the effectiveness of the workout.
Exercise #4: Deadlifts

Explanation of the Deadlift Technique:
Deadlifts are a compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups, including the glutes, hamstrings, lower back, and core. The technique is critical for effectiveness and safety:
- Starting Position: Stand with your feet hip-width apart, toes pointing forward, with the barbell over the center of your feet.
- Grip and Posture: Bend at your hips and knees to reach the bar. Grip the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Your back should be straight, chest up, and shoulders slightly over the bar.
- The Lift: Drive through your heels to lift the bar. Keep the bar close to your body, and lift it by extending your hips and knees. Your hips and shoulders should rise at the same time.
- Upward Movement: As you lift, keep your back straight and head in a neutral position. Continue lifting until you are standing up straight.
- Lowering the Bar: Bend your hips back and slightly bend your knees to lower the bar to the ground, maintaining a straight back throughout the movement.
Variations of Deadlifts:
- Romanian Deadlift (RDL): This variation focuses on hip hinge movement, keeping the legs relatively straight (only slightly bent knees), emphasizing hamstring and glute activation. It’s excellent for developing the posterior chain.
- Sumo Deadlift: In this variation, you adopt a wider stance with your toes pointed out. This stance allows for more engagement of the glutes and inner thighs, along with the hamstrings and lower back.
Role in Developing the Glutes and Hamstrings:
Deadlifts play a significant role in developing lower body strength, particularly in the glutes and hamstrings:
- Comprehensive Muscle Engagement: Deadlifts engage multiple muscle groups at once, leading to improved overall strength and muscle coordination.
- Glute Activation: The upward movement of the deadlift, especially in the hip extension phase, heavily engages the glute muscles.
- Hamstring Development: The lifting and lowering phases of the deadlift significantly work the hamstrings, contributing to balanced leg development.
- Posterior Chain Strengthening: Deadlifts are essential for strengthening the posterior chain, which is crucial for better posture, improved athletic performance, and reduced risk of injuries.
- Versatility: Different variations target the muscles slightly differently, making deadlifts a versatile tool in any strength training regimen.
Incorporating deadlifts into your workout routine can lead to significant improvements in glute and hamstring strength and size. It’s crucial to practice proper form and start with a weight that is manageable to reduce the risk of injury. As you progress, you can gradually increase the weight to continue challenging your muscles.
Exercise #5: Glute Bridges

Basic Glute Bridge Form and Execution:
Glute bridges are a highly effective exercise for targeting the glute muscles. Here’s how to perform the basic glute bridge:
- Starting Position: Lie flat on your back on a mat with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Your feet should be about hip-width apart and close to your butt.
- The Lift: Push through your heels to lift your hips off the floor. Raise your hips until your knees, hips, and shoulders form a straight line.
- Squeeze and Hold: At the top of the movement, squeeze your glutes hard and hold for a moment.
- Return to Start: Lower your hips back down to the starting position in a controlled manner.
Advanced Variations:
- Weighted Glute Bridge: For added intensity, place a weighted plate or barbell across your hips. This increases resistance, further challenging your glute muscles.
- Elevated Glute Bridge: Perform the glute bridge with your feet elevated on a bench or step. This variation increases the range of motion and intensifies the exercise.
Focused Glute Activation for Better Growth:
Glute bridges are particularly effective for glute activation and growth for several reasons:
- Direct Glute Targeting: This exercise isolates the glutes, ensuring they’re receiving maximal engagement and activation.
- Reduced Lower Back Stress: Unlike some other lower body exercises, glute bridges place minimal stress on the lower back, making them suitable for individuals with back concerns.
- Enhanced Muscle Mind Connection: The controlled movement of glute bridges allows for a strong muscle-mind connection, which is vital for muscle growth and development.
- Scalability for Progress: Starting with the basic bridge and progressing to advanced variations like weighted or elevated bridges allows for continual challenge and growth.
- Versatility: Glute bridges can be performed anywhere, requiring minimal equipment (like a mat), making them a convenient exercise for all fitness levels.
Regularly incorporating glute bridges into your workout routine can lead to significant improvements in glute strength, size, and shape. Remember to focus on form and control, especially when adding weights or increasing the difficulty with advanced variations. This will ensure the most effective engagement of your glute muscles for optimal growth and development.
Exercise #6: Step-Ups

Proper Form for Step-Ups:
Step-ups are a functional exercise that targets the glutes, quadriceps, and hamstrings. They are performed using a bench, step, or platform.
- Starting Position: Stand in front of a bench or step. Keep your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart.
- The Step-Up: Place one foot on the bench, ensuring your foot is firmly planted. Push through the heel of the elevated foot to lift your body up onto the bench. Your trailing leg can either be lifted to the bench or just tap the bench before descending.
- The Descent: Step back down with the same foot, returning to the starting position. Control your descent rather than just dropping down.
- Switch Sides: Repeat the movement with the other leg.
Incorporating Different Heights and Weights:
- Height Variations: Using higher steps increases the intensity of the exercise, as it requires more effort to step up. This can be a progressive challenge as you get stronger.
- Adding Weights: Holding dumbbells or wearing a weighted vest can add extra resistance, making the exercise more challenging and effective for building strength.
Benefits for Glute Building and Symmetry:
Step-ups are particularly beneficial for several reasons:
- Targeted Glute Activation: The action of stepping up primarily engages the glute muscles, especially when pushing through the heel.
- Muscle Balance and Symmetry: As a unilateral exercise, step-ups are done one leg at a time, which helps in correcting muscle imbalances and promoting symmetry in muscle development.
- Functional Strength: They mimic everyday movements like climbing stairs, improving functional strength that translates to daily activities.
- Versatility: Step-ups can be modified in various ways (height, weights, speed) to suit different fitness levels and goals.
- Joint-Friendly: This exercise is low-impact, making it easier on the knees and hips compared to high-impact exercises like jumping.
Regularly including step-ups in your workout regimen can greatly enhance glute strength, size, and overall lower body symmetry. They are also effective for improving balance and coordination. As with any exercise, ensure proper form to maximize benefits and minimize the risk of injury. Gradual progression in height and weight can help in continuously challenging the muscles for ongoing development.
Exercise #7: Cable Kickbacks

Instructions for Cable Kickbacks:
Cable kickbacks are a glute-focused exercise that uses a cable machine to provide resistance, targeting the gluteus maximus for definition and shape.
- Setting Up the Cable Machine: Attach an ankle strap to the low pulley of a cable machine. Fasten the strap around one ankle.
- Starting Position: Stand facing the cable machine, holding onto the machine or a support bar for balance. Stand far enough away so that the weight is lifted off the stack, keeping tension on the cable.
- The Movement: Keeping your back straight and core engaged, slowly kick the strapped leg straight back as far as you can, focusing on using your glutes to power the movement.
- Squeeze and Hold: At the peak of the movement, squeeze your glute for a second.
- Return to Start: Slowly return your leg to the starting position, maintaining control and keeping tension on the glutes.
- Switch Sides: After completing your set, switch the strap to the other ankle and repeat.
Tips on Resistance and Posture:
- Start with Light Resistance: Begin with a weight that allows you to perform the movement with proper form. It’s more important to target the correct muscles than to use heavy weight.
- Maintain Proper Posture: Keep your spine neutral, and avoid arching your back. This ensures that your glutes are doing most of the work.
- Controlled Movements: Move in a controlled manner, both while kicking back and returning to the starting position, to maximize glute engagement.
- Steady Base: Keep the leg that’s not moving slightly bent and stable. This helps with balance and allows you to isolate the glutes on the working leg.
Targeting the Glute Muscles for Definition and Shape:
Cable kickbacks are effective for several reasons:
- Direct Glute Isolation: This exercise isolates the glutes, making it excellent for specifically targeting these muscles.
- Variable Resistance: The cable machine allows for constant tension on the glutes throughout the entire range of motion, which can lead to better muscle growth and definition.
- Versatility: You can adjust the resistance and angle of movement to vary the stimulus to the glutes, helping to shape and define them more effectively.
- Improved Muscle Activation: The resistance from the cable provides a unique challenge to the glutes, activating the muscle fibers differently than free weights or bodyweight exercises.
Incorporating cable kickbacks into your lower body or glute-focused workout routine can significantly contribute to improved glute strength, definition, and shape. Remember to focus on form and muscle engagement rather than just moving the weight to get the most out of this exercise.
Combining Exercises for Optimal Results

Creating a balanced workout routine is essential for achieving optimal glute growth and overall fitness. Here are some tips and considerations to help you design an effective routine:
- Incorporate a Variety of Exercises: Include a mix of the exercises we’ve discussed (squats, lunges, hip thrusts, deadlifts, glute bridges, step-ups, cable kickbacks) in your routine. This variety ensures all areas of the glutes are targeted and helps prevent boredom.
- Balance with Other Muscle Groups: While focusing on glutes is important, ensure you’re also working other muscle groups for overall body strength and balance. Include exercises for the upper body, core, and other parts of the lower body.
- Create a Weekly Plan: Depending on your fitness level and goals, you might work on your glutes 2-3 times per week, ensuring there’s at least one day of rest in between these workouts for recovery.
Importance of Progressive Overload and Consistency:
- Progressive Overload: To continue making gains, gradually increase the intensity of your workouts. This can be done by adding more weight, increasing reps or sets, or making exercises more challenging.
- Consistency is Key: Regular workouts are essential for muscle growth and development. Stick to your workout schedule and be patient, as results take time.
Advice on Rest and Recovery:
- Rest Days: Incorporate rest days into your routine. Muscles need time to repair and grow, and this happens during rest periods.
- Quality Sleep: Prioritize good sleep, as it is crucial for recovery and muscle growth. Aim for 7-9 hours per night.
- Nutrition: Fuel your body with a balanced diet rich in protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates. Proper nutrition supports muscle growth and recovery.
- Hydration: Stay hydrated before, during, and after workouts. Water is essential for overall health and aids in the recovery process.
- Active Recovery: On rest days, consider light activities like walking, yoga, or stretching to improve circulation and aid in muscle recovery.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any signs of overtraining or fatigue. If you feel excessively sore or tired, you may need to take an extra day off or reduce the intensity of your workouts.
Combining these elements into your fitness routine can lead to significant improvements in glute strength and size, as well as overall health and fitness. Remember that everyone’s body responds differently to exercise, so it’s important to tailor your routine to your individual needs and goals.
Conclusion
In this guide, we explored the seven best exercises for growing and strengthening your glutes: squats, lunges, hip thrusts, deadlifts, glute bridges, step-ups, and cable kickbacks. Each of these exercises offers unique benefits and targets the glutes in different ways, ensuring a comprehensive approach to glute development.
- Squats are foundational for overall lower body strength, particularly targeting the glutes and thighs.
- Lunges offer versatility and balance, working each leg individually for symmetrical muscle development.
- Hip Thrusts provide direct glute activation, crucial for building size and strength in the glute muscles.
- Deadlifts engage the entire posterior chain, which includes the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back.
- Glute Bridges are excellent for focused glute activation and are especially beneficial for those with lower back issues.
- Step-Ups enhance functional strength and are great for improving muscle balance and coordination.
- Cable Kickbacks isolate and sculpt the glutes, offering a unique way to shape and tone.
Remember, achieving the desired results requires dedication and patience. Consistency in your workout routine is key, as is progressively challenging your muscles through increased intensity or variations of these exercises. The journey to stronger, well-developed glutes isn’t just about the workouts; it’s a lifestyle that includes proper rest, recovery, and, importantly, nutrition.
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in muscle growth and recovery. A balanced diet rich in protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates will fuel your workouts and aid in the repair and growth of muscle tissue. Stay hydrated, get enough sleep, and listen to your body’s needs.
The road to a bigger, stronger booty is a combination of targeted exercise, good nutrition, and the right mindset. Stay motivated, be patient with your progress, and remember that every step you take is a move towards your fitness goals. With determination and the right approach, you’ll not only enhance your physical appearance but also improve your overall health and well-being.







