The biceps, popularly known as the ‘guns’ in the fitness world, are one of the most admired and showcased muscles in the human body. But beyond aesthetics, these muscles play crucial roles in our daily activities. Located on the front part of the upper arm, the biceps comprise two primary muscle groups: the biceps brachii, with its long and short heads, and the underlying brachialis. Their primary functions involve elbow flexion and forearm supination, which in simpler terms means bending the elbow and rotating the forearm to turn the palm upwards. Think of every time you pick up a grocery bag, twist a door handle, or even just flex your arm – you’re putting those biceps to work.
Yet, for many fitness enthusiasts and athletes, simply having functional biceps isn’t enough. The desire for sculpted, strong, and larger biceps often drives individuals to the gym, looking for the best ways to train these muscles. While general arm exercises can benefit the biceps, targeted training is the secret sauce for rapid and pronounced muscle growth. A purposeful and focused approach not only ensures that the muscle fibers are activated optimally but also reduces the risk of imbalances or injuries.
In this article, we will unravel the techniques, exercises, and principles that can guide you towards achieving those impressive bicep gains, marrying both function and form. Whether you’re just beginning your fitness journey or looking to level up, understanding and applying the right strategies can make all the difference in your biceps training.
Understanding Bicep Anatomy
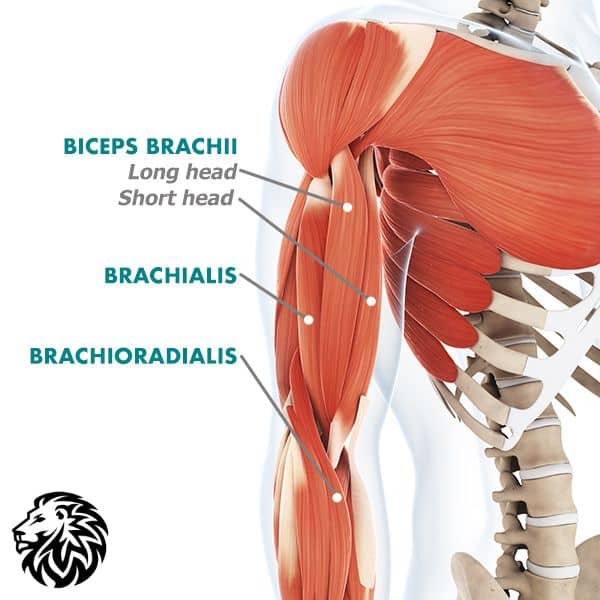
When one flexes their arm, it’s the bicep muscle that often gets the admiration, but the anatomy of this region is a bit more intricate than it appears on the surface. Let’s delve into the architecture of the biceps and the surrounding muscles to truly grasp how they contribute to arm development.
1. The Two Primary Heads: Long Head and Short Head
- Long Head: Originating from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, the long head is what gives the bicep its peak. When bodybuilders flex their arm, the height you see in the bicep muscle is mainly thanks to the long head. It’s positioned on the outer part of the arm and plays a pivotal role in both elbow flexion and shoulder movement.
- Short Head: The short head begins from the coracoid process of the scapula. It lies on the inner side of the arm and provides the bicep its width. Unlike the long head, the short head is more involved in elbow flexion and less so in shoulder movements.
Both heads come together to insert into the radial tuberosity, allowing for coordinated movement. When we talk about “bicep curls,” both these heads work synergistically. However, the angle of the exercise and grip can emphasize one head more than the other.
2. The Role of the Brachialis and Brachioradialis
- Brachialis: Positioned beneath the biceps brachii, the brachialis is often the unsung hero of the arm muscles. It originates from the lower half of the anterior surface of the humerus and inserts into the ulna. Unlike the biceps brachii, the brachialis is purely an elbow flexor. Its development can push the biceps up, creating an illusion of a larger bicep. Hence, while not visible like the biceps, a well-developed brachialis contributes significantly to the overall size of the upper arm.
- Brachioradialis: This muscle originates from the lower two-thirds of the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus and inserts into the distal radius. While technically part of the forearm, the brachioradialis plays a role in elbow flexion, especially when the forearm is in a mid-position between pronation and supination (like during a hammer curl). Developing the brachioradialis can enhance the overall appearance of the arm, giving it a more complete and balanced look.
While the biceps brachii is central to arm aesthetics, the combined development of the brachialis and brachioradialis ensures optimal strength and a fuller appearance. Understanding the anatomy is crucial; it helps design an exercise regimen that targets all these muscles, ensuring balanced growth and reducing the risk of injuries.
Principles for Fast Muscle Growth

Muscle growth, scientifically known as hypertrophy, is driven by specific physiological principles. When looking to boost the size and strength of any muscle group, including the biceps, understanding and employing these principles can optimize results. Here’s a closer look at these key tenets:
1. Progressive Overload: Increasing Resistance Over Time
- What is it? Progressive overload refers to the process of gradually increasing the weight or resistance in your workouts over time.
- Why is it important? Muscles adapt to the stresses you place on them. If the stress remains constant, so does the muscle size and strength. By progressively increasing the resistance, you challenge the muscles, causing microscopic damage that, when repaired, results in muscle growth.
- How to apply it: Start with a weight that allows you to perform exercises with proper form for a given number of reps. Once you can comfortably exceed your target reps, increase the weight. For instance, if you start curling 20 pounds for 10 reps and eventually can do 12-15 reps with ease, it’s time to move up in weight.
2. Muscle Time Under Tension (TUT): The Importance of the Contraction Duration
- What is it? Time under tension refers to the amount of time a muscle is under strain during a set.
- Why is it important? Research has shown that the longer a muscle remains under tension (within reason), the more muscle fibers are activated and broken down. This results in a stronger stimulus for muscle growth during the recovery process.
- How to apply it: Instead of rushing through reps, focus on controlled movements. For instance, take 2 seconds to lift (concentric phase) and 3-4 seconds to lower (eccentric phase) the weight. This technique not only enhances muscle growth potential but also reduces the risk of injury.
3. Importance of Rest and Recovery: How Muscles Actually Grow During Rest
- What is it? Rest and recovery refer to the period post-workout where muscles repair and grow.
- Why is it important? Contrary to what some believe, muscles don’t grow during the workout itself. Instead, exercise creates microscopic tears in muscle fibers. It’s during rest that the body repairs these tears, building the muscles back thicker and stronger.
- How to apply it:
- Post-Workout Nutrition: Consume protein-rich foods or shakes post-workout to provide the building blocks (amino acids) for muscle repair.
- Sleep: Ensure you’re getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep. During deep sleep, growth hormone is released, which plays a vital role in muscle growth.
- Rest Days: While it’s tempting to train hard daily, muscles need time to recover. For beginners, it’s typically recommended to wait 48-72 hours before working the same muscle group again.
Incorporating these principles into your bicep training regimen, or any muscle group for that matter, can greatly enhance your results. While consistency is key, understanding the science behind muscle growth ensures that your efforts yield the maximum payoff.
Effective Bicep Exercises
Achieving impressive bicep growth requires more than just standard curls. Here’s an exploration of some of the most effective bicep exercises, each targeting the muscle from slightly different angles and utilizing various mechanics.
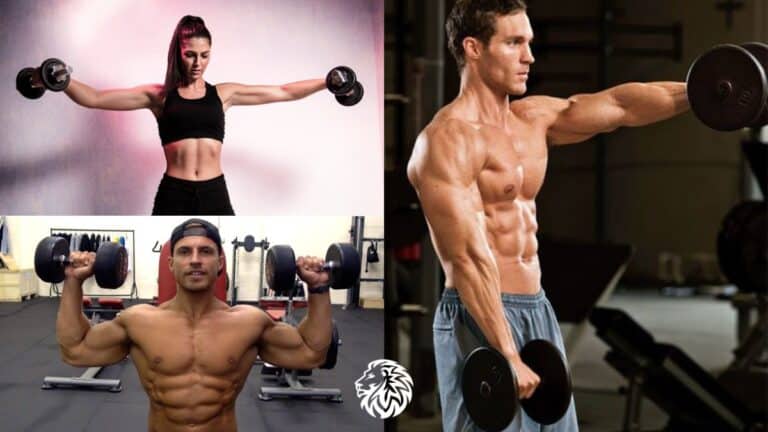
1. Standing and Seated Dumbbell Curls
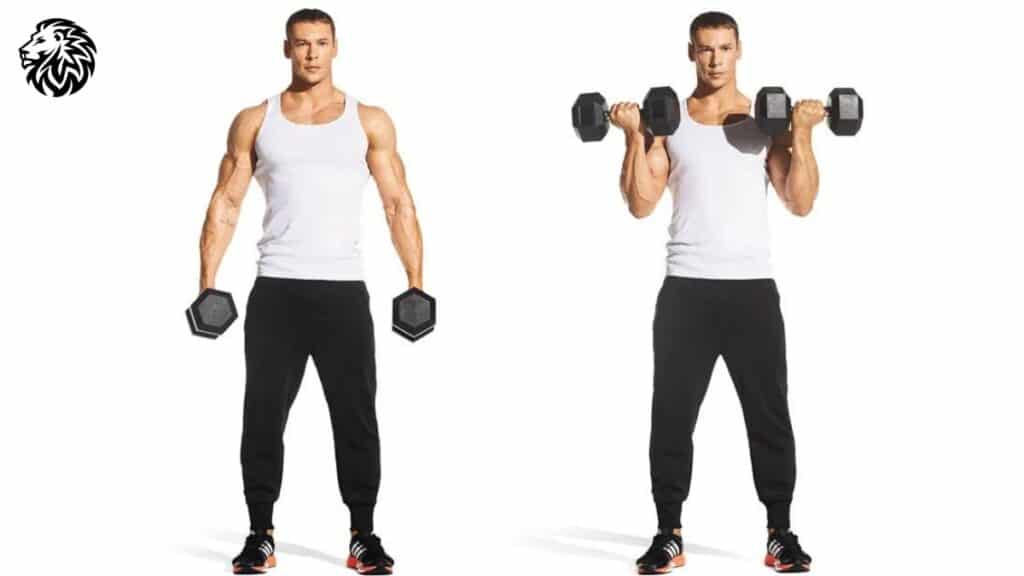

- How to: Holding a dumbbell in each hand by your sides, with palms facing forward, curl the weights towards your shoulders while keeping the elbows stationary. Lower back to the start. This can also be done while seated on a bench.
- Why it’s effective: Both standing and seated variations isolate the biceps, with the seated version limiting the use of momentum.
2. Barbell Curls (and its variations)
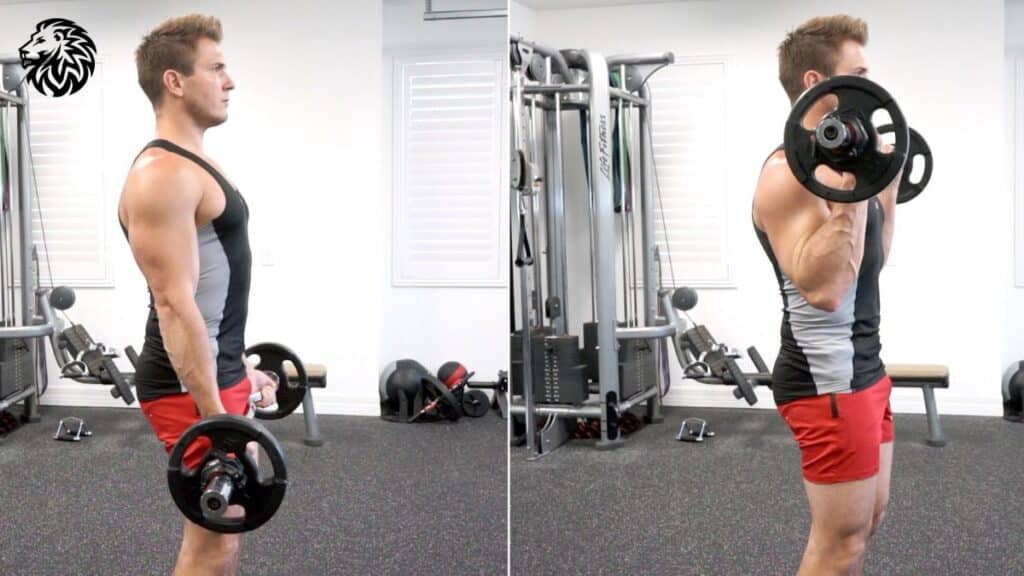

- How to: Hold a barbell with an underhand grip, hands shoulder-width apart. Curl the weight towards your shoulders while keeping your elbows locked by your sides.
- Variations: Close-grip, wide-grip, and EZ-bar curls.
- Why it’s effective: Barbell curls allow for heavier lifting, targeting both the bicep heads but emphasizing different portions based on the grip used.
3. Hammer Curls
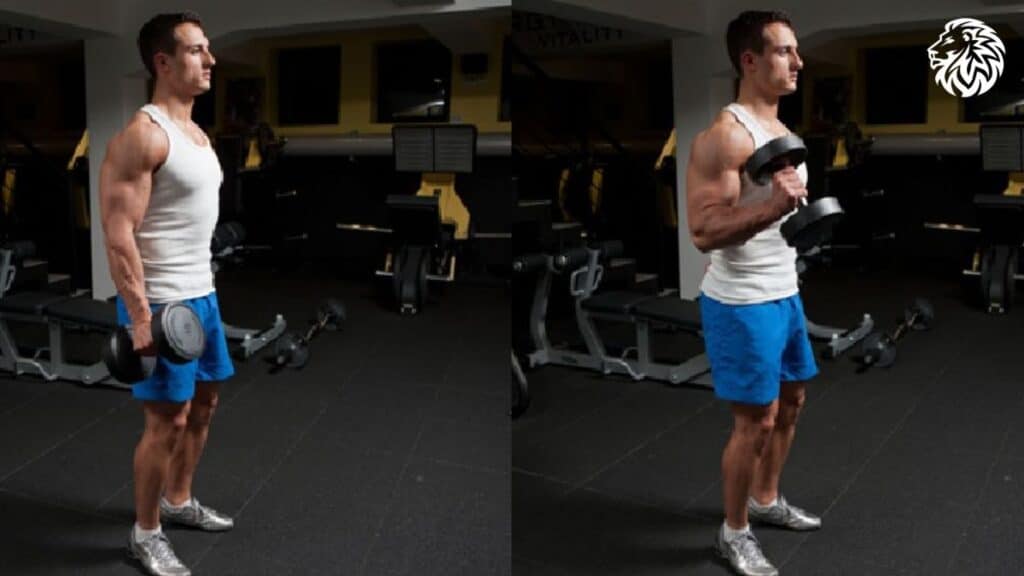

- How to: With a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing your torso, curl the weights as you would in a traditional curl.
- Why it’s effective: Hammer curls target the brachialis and the brachioradialis, enhancing the overall thickness of the arm.
4. Preacher Curls
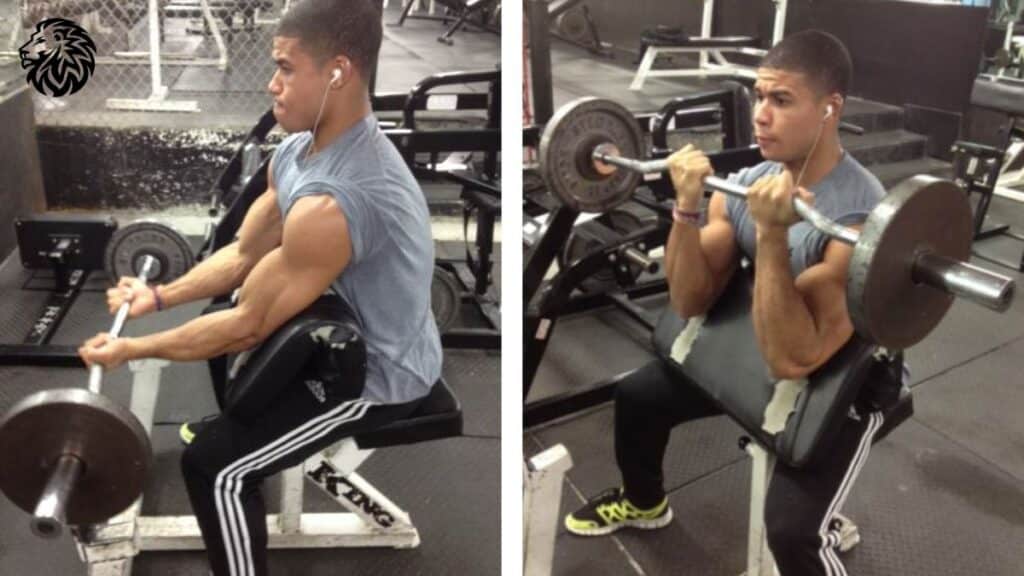

- How to: Using a preacher bench and either a barbell or dumbbell, position your arms on the pad and curl upwards.
- Why it’s effective: The support of the preacher bench isolates the biceps, eliminating any assistance from the shoulders.
5. Concentration Curls
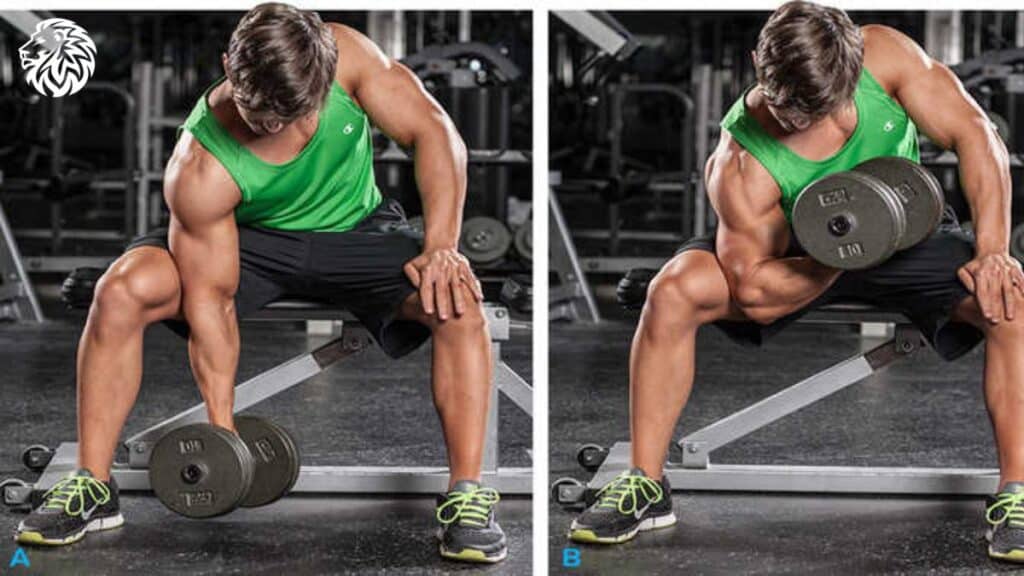

- How to: Seated on a bench, hold a dumbbell in one hand, hinging forward slightly. Place the back of your upper arm on your inner thigh, and curl the dumbbell towards your shoulder.
- Why it’s effective: This move maximally isolates the bicep, ensuring focused contraction.
6. Incline Dumbbell Curls
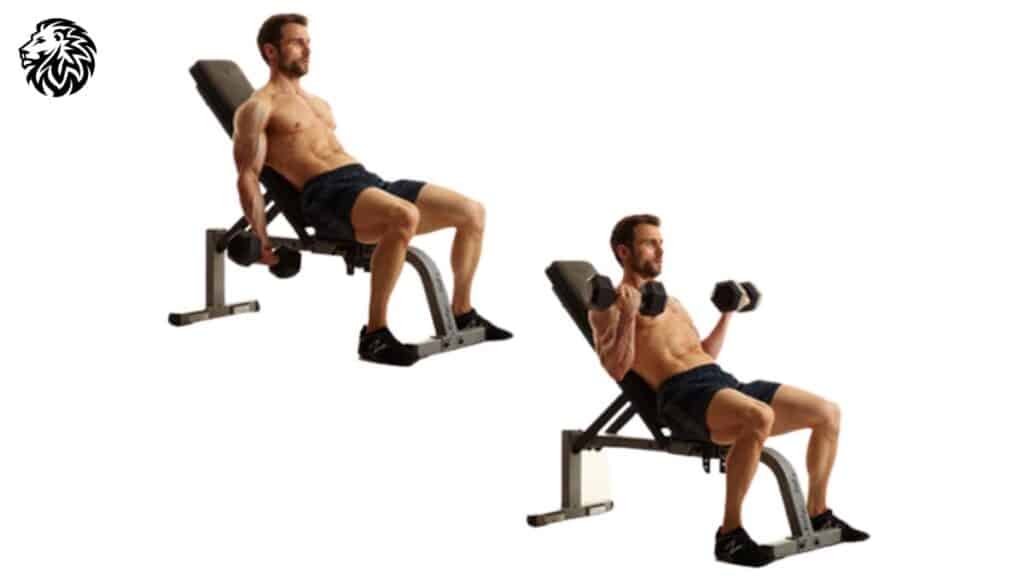

- How to: Sit on an incline bench with a dumbbell in each hand, arms extended straight down. Curl the weights while keeping the upper arms stationary.
- Why it’s effective: The incline angle stretches the biceps, particularly the long head, ensuring a full range of motion.
Tips for Proper Form and Avoiding Common Mistakes:
- Stable Elbows: Ensure your elbows remain close to your torso during curls. Avoid letting them drift forward as this can involve the front deltoids, taking the focus off the biceps.
- Limit Momentum: Use controlled movements to avoid using momentum, which can reduce the exercise’s effectiveness and increase injury risk.
- Full Range of Motion: Ensure you’re extending and flexing the arm fully in each repetition. Partial reps can limit growth potential.
- Avoid Overarching the Back: Especially during standing curls, ensure you’re not arching your back to lift the weight. This can strain the lower back.
- Focus on the Eccentric: The lowering phase (eccentric) causes significant muscle damage leading to growth. Don’t just drop the weight; lower it with control.
- Mind-Muscle Connection: Focus on the contraction of the biceps throughout the exercise. This enhances muscle fiber recruitment and optimizes growth.
By incorporating these exercises into your bicep routine and following the tips for proper form, you can ensure efficient, effective, and safe muscle growth.
Role of Workout Intensity and Volume

When it comes to muscle growth, both intensity (how hard you push during each set) and volume (the total amount of work done, typically measured as sets x reps) play crucial roles. Finding the right balance between the two can make a significant difference in hypertrophy outcomes.
1. Repetition and Set Range for Hypertrophy
Traditionally, the following ranges are advised for muscle hypertrophy:
- Repetitions: 6-12 reps per set. This range is believed to be optimal for muscle growth as it strikes a balance between muscle tension, metabolic fatigue, and time under tension.
- Sets: 3-6 sets per exercise. This can vary based on the individual’s recovery ability, the muscle group’s size, and overall workout volume.
2. Manipulating Intensity with Advanced Techniques
- Drop Sets: Start with a heavier weight and perform to near failure. Immediately reduce the weight and continue with the set to failure again. This process can be repeated multiple times. Drop sets increase the set’s intensity and overall volume in a short period.
- Supersets: This involves performing two exercises back-to-back with no rest in between. There are different types of supersets, but for biceps, an example might be pairing a bicep exercise with a tricep exercise. It’s efficient and also creates an intense pump.
- Forced Reps: With the help of a spotter, once you reach muscle failure, the spotter assists you in performing a few additional repetitions. This pushes the muscle past its fatigue point, enhancing the intensity of the set.
3. The Importance of Tracking Workouts and Progression
- Objective Measurement: Keeping a record of your workouts—weights used, sets, reps, and even how you felt—gives you an objective measure to assess progress.
- Progressive Overload: We’ve already highlighted the importance of progressive overload. Tracking ensures that you’re consistently increasing resistance or volume, driving continual muscle growth.
- Avoiding Stagnation: By monitoring your workouts, you can easily identify when you’ve plateaued and adjust your program accordingly, whether it’s by increasing intensity, changing exercises, or manipulating volume.
- Motivation: Seeing tangible progress in your records can serve as a powerful motivational tool. Noting new personal bests or realizing how much you’ve advanced over weeks and months can be highly motivating.
Intensity and volume are both pivotal in the hypertrophy equation. While it’s essential to push your muscles hard (intensity), it’s equally crucial to ensure they get enough overall work to elicit growth (volume). However, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer; individuals might respond differently to various training stimuli. It’s crucial to listen to your body, ensure adequate recovery, and be willing to adjust based on feedback and results. Tracking your workouts and regularly reflecting on your progress can provide valuable insights into what works best for you.
Nutrition for Bicep Growth
While training is the stimulus for muscle growth, nutrition is the foundation that supports and amplifies the results. The biceps, like all muscles, require specific nutrients to repair, grow, and function optimally.
1. The Role of Protein in Muscle Recovery and Growth
- Muscle Repair: Intense training causes microscopic tears in muscle fibers. Proteins, broken down into amino acids, are the building blocks that repair these tears, leading to muscle growth.
- Amino Acid Pool: Consuming adequate protein ensures a steady supply of amino acids in the bloodstream, which muscles can readily use for repair and growth.
- Recommendations: For muscle growth, a general recommendation is to consume between 1.2 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. Sources can include lean meats, dairy, eggs, legumes, and plant-based proteins.
2. Importance of Hydration
- Muscle Function: Muscles are approximately 70% water. Proper hydration is crucial for optimal muscle function, contraction, and overall performance in the gym.
- Nutrient Transport: Water aids in the transportation of nutrients, including the proteins and carbohydrates muscles need for recovery and growth.
- Recommendations: While individual needs can vary, aiming for at least 3 liters (for men) and 2.2 liters (for women) per day is a general guideline, with needs increasing with exercise intensity and duration.
3. Vitamins and Minerals that Support Muscle Health
- Vitamin D: Supports muscle function and is involved in protein synthesis. A deficiency can impair muscle growth.
- Magnesium: Crucial for muscle contraction, energy production, and protein synthesis.
- Zinc: Plays a role in protein synthesis and hormone regulation, which can impact muscle growth.
- Calcium: Essential for muscle contraction.
- Iron: Vital for transporting oxygen to muscles, supporting energy production and endurance.
- Recommendations: Aim to get these nutrients from whole food sources like leafy greens, dairy, nuts, seeds, lean meats, and legumes. If deficiencies are suspected, consider consulting a healthcare professional.
4. Considering Supplements
- Creatine: One of the most researched and supported supplements for muscle growth. It helps regenerate ATP (the primary energy molecule) during high-intensity activities, potentially increasing workout performance and muscle gains.
- BCAAs (Branched-Chain Amino Acids): Comprising leucine, isoleucine, and valine, BCAAs can support muscle recovery, reduce muscle soreness, and potentially aid in muscle growth. However, if one is already consuming adequate protein, supplemental BCAAs might be redundant.
- Beta-Alanine: This amino acid can buffer acid in muscles, potentially increasing performance during high-intensity activities.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Can reduce muscle soreness and inflammation, potentially aiding in recovery.
- Recommendations: Before introducing any supplement into your regimen, it’s essential to do thorough research, understand potential side effects, and, if possible, consult with a healthcare professional.
Building impressive biceps or any muscle group requires more than just targeted exercise; it needs a comprehensive approach that incorporates proper nutrition and supplementation. By ensuring that the body has the necessary nutrients to repair and grow muscle tissue, you lay the groundwork for optimal results. Remember, training provides the stimulus, but growth occurs outside the gym, supported by what you feed your body.
Conclusion
Muscle growth, especially in prominent areas like the biceps, is a journey that requires more than just lifting weights. It’s an intricate dance of stress and recovery, fueled by the right nutrients and amplified by knowledge and consistency.
Consistency is Key: Whether you’re a novice or a seasoned athlete, consistency remains the cornerstone of success. Muscle growth is a cumulative process. It’s the daily dedication to your regimen, showing up even on days when motivation wanes, that leads to significant progress over time.
Fueling Growth with Nutrition: Just as a car needs the right fuel to run optimally, your muscles need the correct nutrition to recover and grow. The emphasis on protein, hydration, and essential vitamins and minerals isn’t just theoretical; it’s a practical necessity for those serious about muscle growth.
Rest as a Growth Catalyst: While the excitement of training can sometimes overshadow the importance of rest, it’s during these periods of downtime that muscles repair and grow. Respect your body’s signals. Adequate sleep and allowing muscles to recover between workouts isn’t laziness; it’s a strategic move towards bigger biceps and overall muscle health.
Stay Curious and Adaptable: As you progress, you’ll learn more about your body and how it responds to various stimuli. Embrace this learning process. If something isn’t yielding results, be willing to adapt and adjust. Engage with new research, experiment (safely) with your routines, and always keep the bigger picture in mind.
Your journey to impressive biceps and a stronger self is a blend of discipline, knowledge, and patience. Celebrate every milestone, no matter how small, and remember that every curl, every meal, and every night’s rest is a step towards your goal. Keep pushing, keep learning, and relish the journey.







