Quadricep Exercises
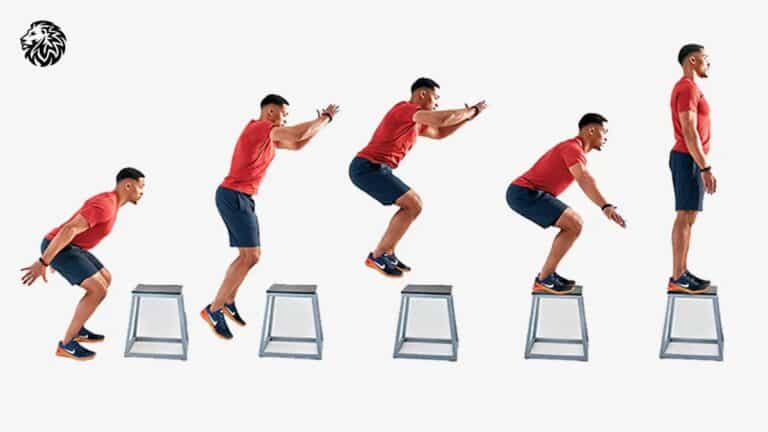
Learn how to do box jumps with proper form, build strength, improve agility, and maximize your workouts...
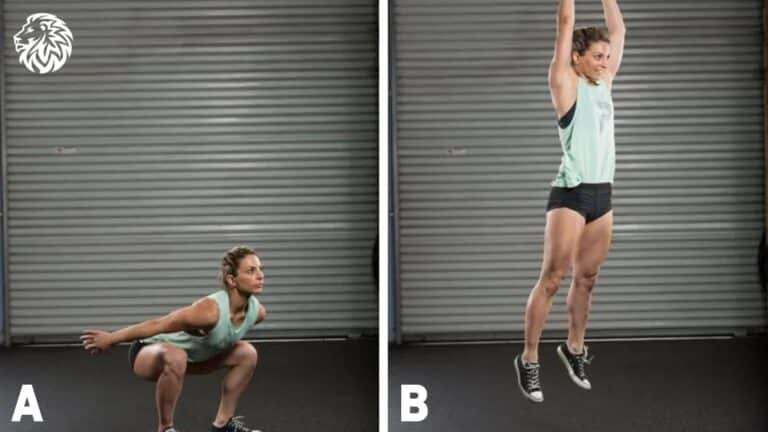
Boost lower-body strength and endurance with jump squats. Learn proper form, muscle engagement, benefits,...
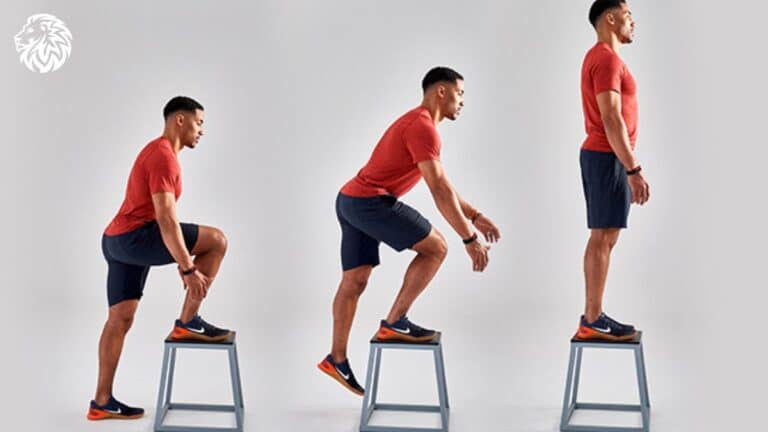
Learn how to do step-ups with proper form, target key muscles, and maximize benefits. Get tips, variations,...
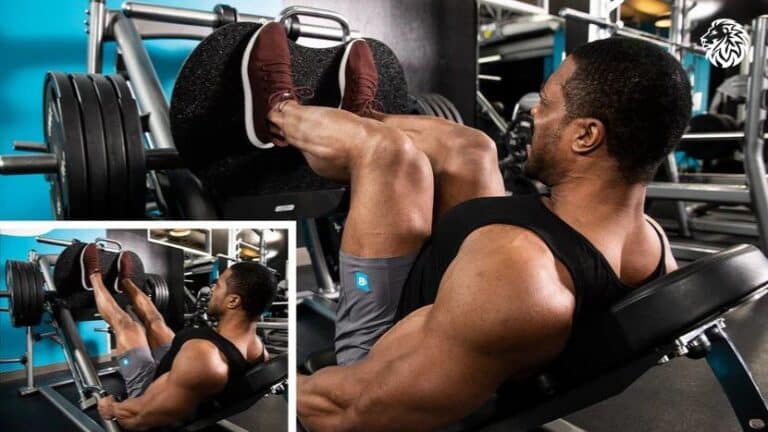
Learn how to perform the leg press with proper form, target key muscles, and optimize your workouts for...
Learn how to do hack squats with proper form, target key muscles, and enhance your lower body strength...
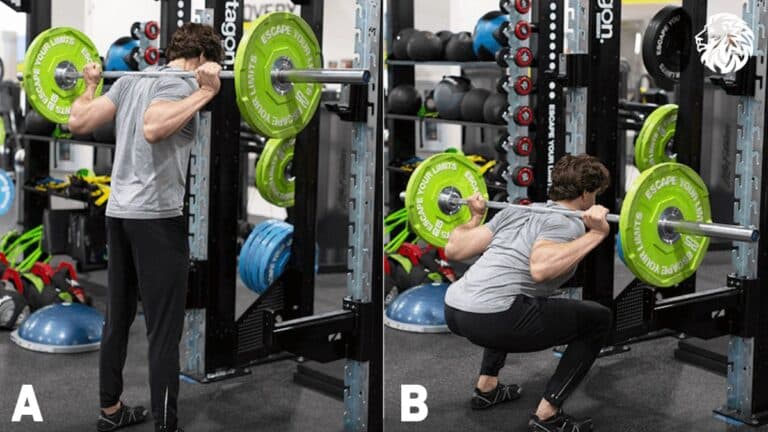
Learn how to do squats with proper form, target key muscles, avoid mistakes, and maximize results in...
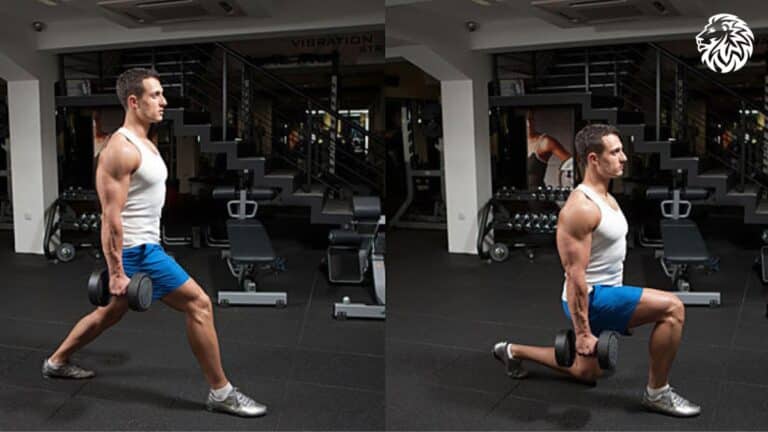
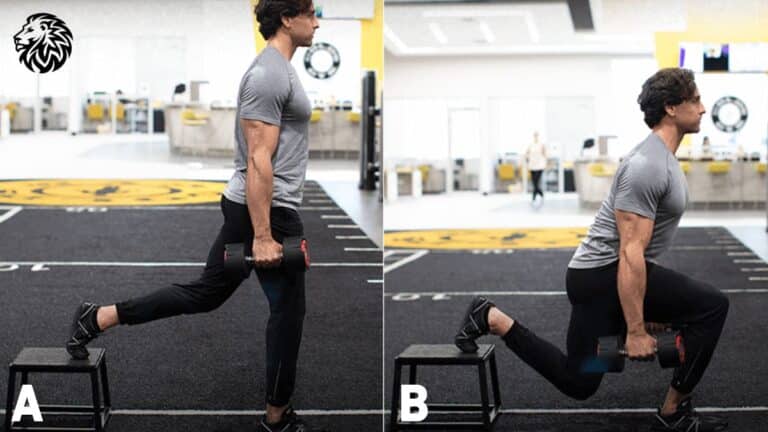
Learn how to do lunges correctly with step-by-step instructions, benefits, tips, and rep recommendations...
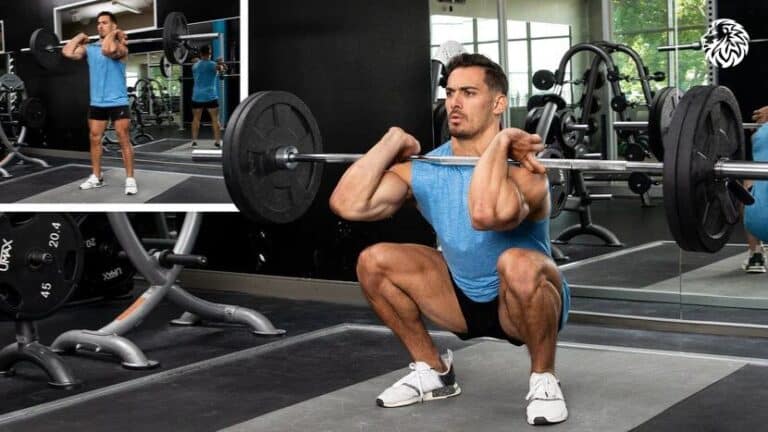
Learn how to do front squats with proper form, target muscles, benefits, tips, and variations to enhance...
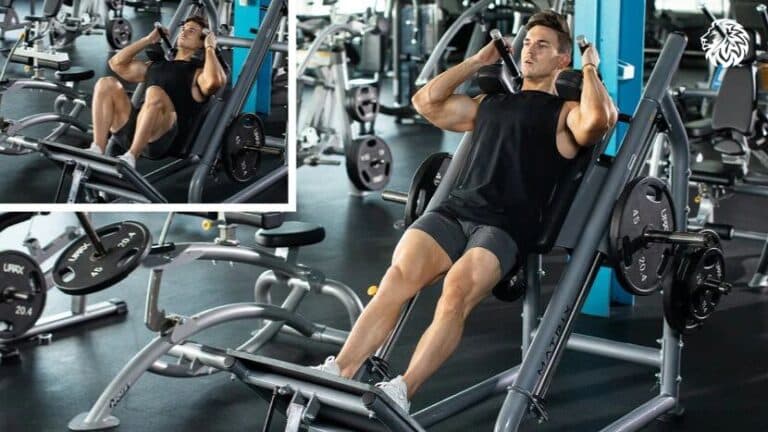
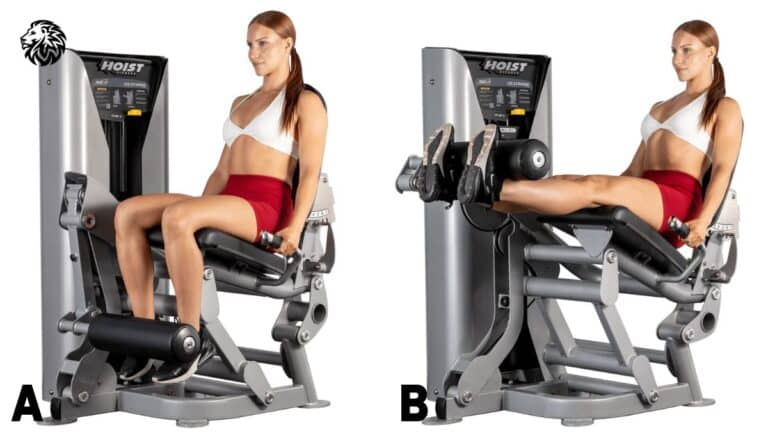
Learn how to do leg extensions with proper form, target key muscles, avoid mistakes, and enhance your...
Learn how to do Bulgarian split squats with proper form, target key muscles, and boost strength, balance,...