In today’s world, weight loss is a pressing issue for many individuals, and as a result, countless solutions have emerged to help people achieve their goals. Among the various methods, dietary supplements like Garcinia cambogia have gained significant attention. Marketed as a “natural” weight loss supplement, the tropical fruit extract has intrigued those seeking an easier path to weight loss. But how effective and safe is this supplement? Let’s examine the evidence, safety concerns, and alternative methods for achieving sustainable health goals.
What is Garcinia Cambogia?
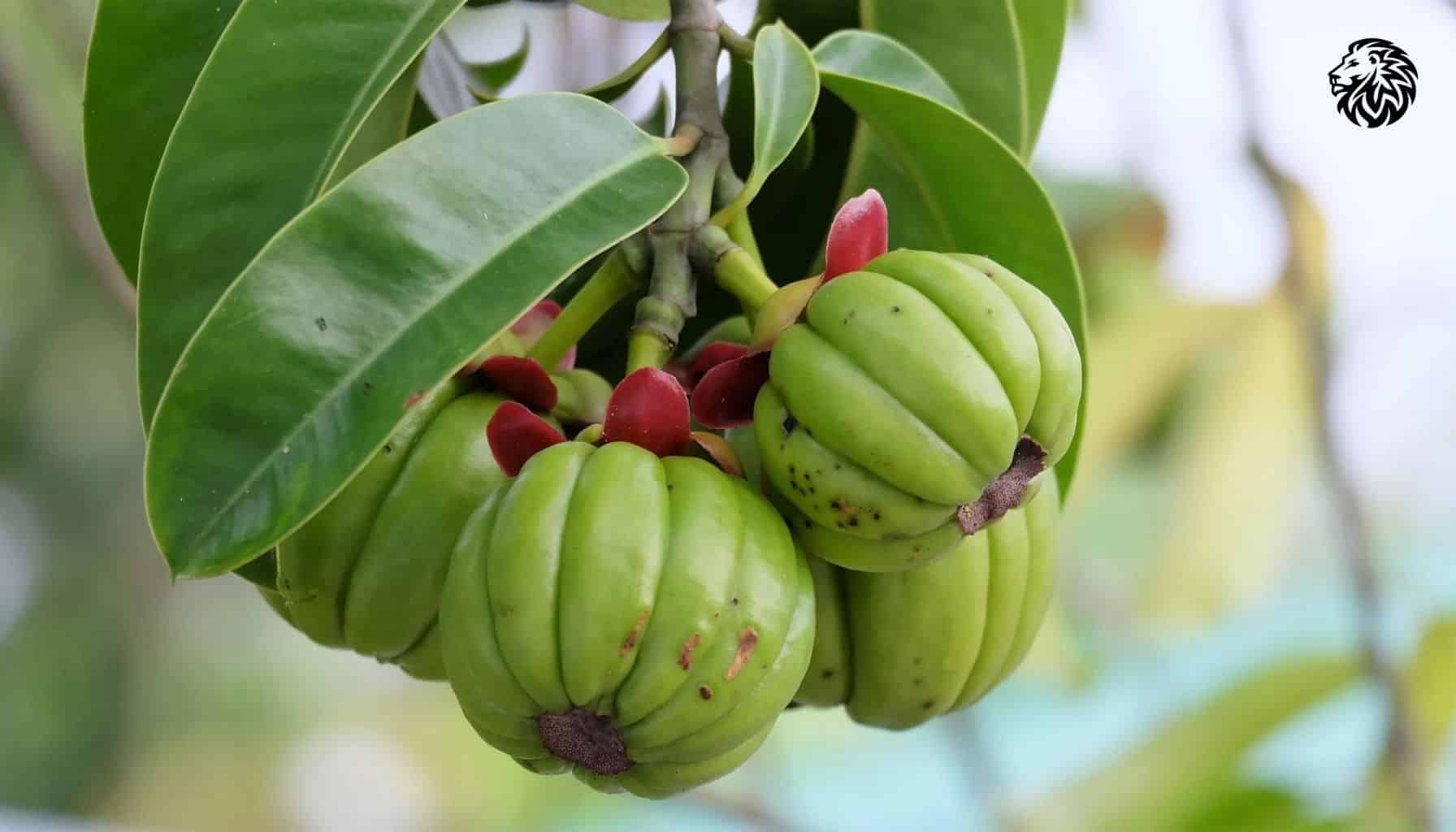
Garcinia cambogia, a fruit native to Southeast Asia, looks like a small, green pumpkin. It has been used for centuries in traditional cooking for its sour flavor. The rind of the fruit contains a compound known as hydroxycitric acid (HCA), which is marketed as the active ingredient responsible for purported weight loss benefits. The supplement industry claims that HCA helps in two main ways: it may suppress appetite and block the body from storing fat by inhibiting an enzyme called citrate lyase, which converts excess carbohydrates into fat.
Though the concept seems promising, the scientific community has not reached a consensus on how or whether Garcinia cambogia actually works to reduce weight. Several theories exist, such as its potential to increase serotonin levels to suppress appetite or its impact on enzymes that break down carbohydrates. However, conclusive evidence remains elusive.

The Scientific Evidence
Numerous studies have been conducted to investigate whether Garcinia cambogia genuinely aids in weight loss. The results are mixed at best. A 2011 meta-analysis reviewed 12 studies that met strict scientific criteria and concluded that while some trials indicated a small, short-term weight loss effect, the results were hardly significant. Another review in 2015, which included 17 trials involving both animals and humans, also found minimal benefits. Interestingly, some of the larger trials found no meaningful difference in weight loss between participants who took Garcinia cambogia and those who took a placebo.
One of the most notable trials involved 135 participants, where both the group taking Garcinia cambogia and the placebo group lost significant weight. This outcome led researchers to suggest that external factors like support and encouragement, not the supplement itself, were more likely responsible for the weight loss.
In summary, while Garcinia cambogia might offer some short-term benefits, the effects are generally minimal and often hard to isolate from other factors like diet and exercise. As a weight-loss solution, the supplement does not live up to the “miracle” status often promoted in marketing.

Safety Concerns
One of the most significant concerns surrounding Garcinia cambogia is its safety. Although the supplement is marketed as “natural,” that doesn’t necessarily mean it’s safe. Herbal remedies like Garcinia cambogia are regulated as food products in many countries, including the United States. This means they don’t undergo the rigorous testing that pharmaceuticals do, leaving questions about their safety unanswered.
There have been documented cases of liver damage linked to Garcinia cambogia. In one instance, a woman developed severe liver failure after taking 1,000 milligrams of the supplement daily for just two weeks. She ultimately required a liver transplant. Another case involved a woman who experienced high liver function tests and coagulation issues after just one week of use. Fortunately, her condition improved once she stopped taking the supplement.
Beyond liver damage, other reported side effects include stomach upset, dry mouth, headaches, dizziness, and diarrhea. Importantly, anyone with pre-existing conditions such as heart disease or diabetes should consult a healthcare provider before taking Garcinia cambogia, as the supplement may interfere with medications or worsen certain conditions. Additionally, it is not recommended for use by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
One of the potential effects of Garcinia cambogia on blood sugar levels also raises concerns. While some studies in rats have shown a decrease in blood glucose absorption, these effects have not been consistently replicated in humans. For example, a small human study found no significant reduction in blood glucose levels in people with diabetes, further undermining claims that Garcinia cambogia could benefit those managing diabetes. In fact, some research has suggested that the supplement could increase fasting blood sugar levels, making it potentially harmful for people with blood sugar control issues.
The Appeal of Weight Loss Supplements
The desire for a quick fix to weight loss is understandable. For many people, losing weight can be a challenging, lifelong battle. The promises of weight loss supplements like Garcinia cambogia—easy fat burning, reduced appetite, and rapid results—are highly tempting, especially in a world where we’re constantly bombarded with images of thin, fit individuals as the ideal.
However, relying on supplements can lead to disappointment and even health risks. As noted, the scientific evidence for Garcinia cambogia‘s effectiveness is weak, and there are real safety concerns associated with its use. Moreover, weight loss supplements are not subject to the same regulations as pharmaceutical drugs, making their content and potential side effects uncertain.

Lifestyle Changes: The Proven Path to Health
While it can be frustrating to hear, the most reliable, safe, and effective way to lose weight remains through lifestyle changes. Diet, exercise, and stress management have long been proven to improve health and lead to sustainable weight loss.
A balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is a key factor in maintaining a healthy weight. Increasing physical activity, even in small amounts, can make a big difference over time. Exercise helps to burn calories and boosts metabolism, and regular movement can improve mood and energy levels.
Beyond diet and exercise, managing stress and getting adequate sleep are also critical components of a healthy lifestyle. Stress can lead to overeating or poor food choices, and lack of sleep has been shown to increase hunger hormones, making weight loss even more challenging.
The appeal of short-term solutions like weight loss supplements is strong, but they often come with risks and rarely lead to long-lasting results. Rather than turning to Garcinia cambogia or other similar supplements, it’s better to focus on sustainable, long-term changes.
The Bottom Line
Garcinia cambogia may not live up to its weight-loss hype, and its use carries potential risks, including serious side effects like liver damage. While the idea of taking a pill to lose weight is appealing, the reality is that lifestyle changes—healthy eating, exercise, and stress management—are the best ways to achieve lasting health and well-being.
Before starting any new supplement, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider, especially for individuals with existing health conditions. Natural does not always mean safe, and the risks associated with Garcinia cambogia should not be overlooked.
In conclusion, while Garcinia cambogia and other weight loss supplements offer the allure of an easy fix, the evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited. The best approach to long-term health remains making sustainable changes to your lifestyle, focusing on balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and mindful living. By making these choices, you’ll not only see results but also improve your overall well-being for the long haul.
Frequently Asked Questions About Garcinia Cambogia
What is Garcinia Cambogia?
Garcinia Cambogia is a tropical fruit from Southeast Asia, often used as a weight-loss supplement due to its active ingredient, hydroxycitric acid (HCA), which is claimed to reduce fat storage and suppress appetite.
Does Garcinia Cambogia help with weight loss?
The evidence supporting Garcinia Cambogia‘s effectiveness for weight loss is weak. Some studies show small, short-term weight loss benefits, but overall, the results are inconclusive and often attributed to lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, rather than the supplement itself.
Is Garcinia Cambogia safe to use?
While some people may tolerate Garcinia Cambogia well at recommended dosages, there are reports of serious side effects, including liver damage. Other common side effects include stomach upset, dry mouth, headaches, and dizziness.
Can Garcinia Cambogia cause liver damage?
Yes, there have been documented cases of liver damage linked to Garcinia Cambogia, including severe cases that required liver transplants. Users should exercise caution and consult a healthcare provider before use.
How does Garcinia Cambogia work?
Garcinia Cambogia‘s active ingredient, HCA, is believed to inhibit an enzyme called citrate lyase, which helps the body store fat from excess carbohydrates. However, its actual effectiveness in humans remains unproven.
Can Garcinia Cambogia lower blood sugar levels?
Studies on Garcinia Cambogia and blood sugar control have been inconsistent. While some animal studies showed reduced glucose absorption, human studies have not consistently demonstrated these effects, making it unreliable for managing blood sugar levels.
Does Garcinia Cambogia interact with medications?
Yes, Garcinia Cambogia may interact with medications, especially diabetes drugs, antidepressants, statins, and blood thinners. Consult a healthcare provider before using the supplement if you are on medication.
Who should avoid taking Garcinia Cambogia?
Garcinia Cambogia is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, people with liver disease, diabetes, or heart conditions, and those taking medications that may interact with the supplement.
Are there any long-term benefits to using Garcinia Cambogia?
There is no strong evidence suggesting long-term benefits from using Garcinia Cambogia. Sustainable weight loss is more effectively achieved through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
Should I use Garcinia Cambogia for weight loss?
Given the minimal proven benefits and the potential risks, it is advisable to focus on healthier, long-term weight management strategies, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, rather than relying on supplements like Garcinia Cambogia.
References
- WebMD. (n.d.). Garcinia cambogia for weight loss. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/vitamins-and-supplements/garcinia-cambogia-weight-loss
- Hébert, M. F., Ma, X., Naraharisetti, S. B., Krudys, K. M., Umans, J. G., Hankins, G. D. V., … & Easterling, T. R. (2014). Garcinia cambogia and liver function: A systematic review of its weight loss benefits and potential liver toxicity. National Institutes of Health. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4053034/
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (2020, August). Garcinia cambogia. NCCIH. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/garcinia-cambogia
- Villines, Z. (2017, August 17). What is garcinia cambogia? Does it work? Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318030