The hamstring muscles, located at the back of the thigh, are pivotal in performing a wide range of motions, from walking and running to jumping and squatting. Strong hamstrings not only enhance athletic performance but also play a crucial role in preventing leg and lower back injuries. They balance the strength of the quadriceps, helping to maintain proper posture and alignment, which is vital for everyday activities.
Dumbbell exercises for the hamstrings offer a unique set of benefits. Dumbbells provide the versatility to perform a wide range of movements that target the hamstrings from different angles. They allow for unilateral training, which helps in correcting muscle imbalances between the legs. Moreover, using dumbbells can improve overall balance and coordination, as they require more stabilization compared to machines or barbells. This aspect of training with dumbbells is particularly beneficial for functional strength and injury prevention. Additionally, dumbbell exercises can be easily adapted for all fitness levels, making them an excellent choice for anyone looking to strengthen their hamstrings.
Understanding Your Hamstrings
Anatomy of the Hamstring Muscles
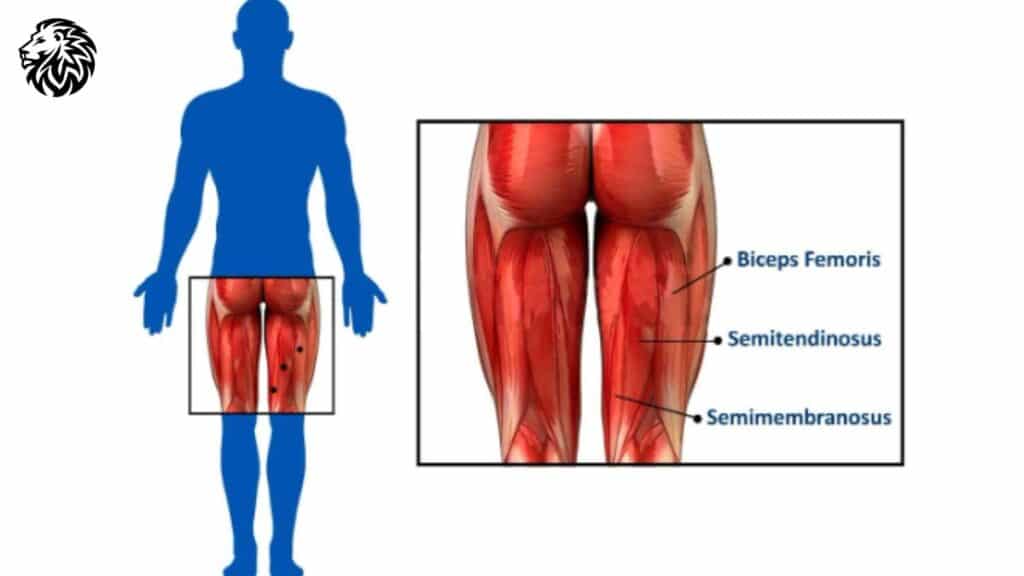
The hamstring group is comprised of three primary muscles: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. These muscles span the back of the thigh, originating from the pelvis and attaching to the lower leg bones. Each muscle plays a distinct role but collectively, they are responsible for two major joint actions – bending (flexing) the knee and extending the hip. Understanding the anatomy of these muscles is key to effectively targeting them during exercises.
Role of Hamstrings in Daily Activities and Sports
Hamstrings are integral in our daily movements. When you walk, the hamstrings work in concert with other muscles to stabilize the hips, bend the knees, and propel the body forward. During activities such as running or jumping, they provide power and speed. In sports, well-developed hamstrings contribute to agility, quick directional changes, and explosive movements. They also play a crucial role in maintaining balance and posture. Weak or tight hamstrings, on the other hand, can lead to lower body injuries and impact overall mobility. This highlights the importance of having strong and flexible hamstrings not just for athletes but for everyone engaging in everyday physical activities.
Preparing for Your Workout
Importance of Warming Up
Before diving into any exercise routine, especially one involving weights, a proper warm-up is crucial. Warming up prepares your body for the increased physical demands of the workout, helping to enhance performance and reduce the risk of injury. It increases blood flow to the muscles, raises body temperature, and improves flexibility, all of which are important for effective and safe hamstring training. A good warm-up should include light aerobic activity, like jogging or cycling for 5-10 minutes, followed by dynamic stretches that mimic the exercises you will be performing. This approach ensures that your hamstrings and surrounding muscles are adequately prepared for the workout ahead.
Safety Tips When Using Dumbbells
When incorporating dumbbells into your hamstring workout, safety should be a top priority. Here are some key tips to keep in mind:
- Choose the Right Weight: Start with a weight that you can lift for 10-12 reps with good form. If you’re struggling to complete the reps, the weight is too heavy.
- Maintain Proper Form: Always prioritize form over the amount of weight you’re lifting. Poor form not only reduces the effectiveness of the exercise but also significantly increases the risk of injury.
- Controlled Movements: Perform each exercise with controlled, steady movements. Avoid using momentum to lift the weight, as this can lead to muscle strains.
- Stable Positioning: Ensure you have a stable stance or position before starting an exercise. This might mean planting your feet firmly on the ground or ensuring a bench is stable.
- Breathing: Remember to breathe regularly during your exercises. Exhale during the exertion phase and inhale during the easier phase.
- Listen to Your Body: If you feel pain (other than typical muscle fatigue) or discomfort, stop the exercise. It’s important to differentiate between pushing your limits and causing potential harm.
By adhering to these safety guidelines, you can enjoy a productive and injury-free workout, maximizing the benefits for your hamstrings and overall health.
Dumbbell Exercises for Hamstrings
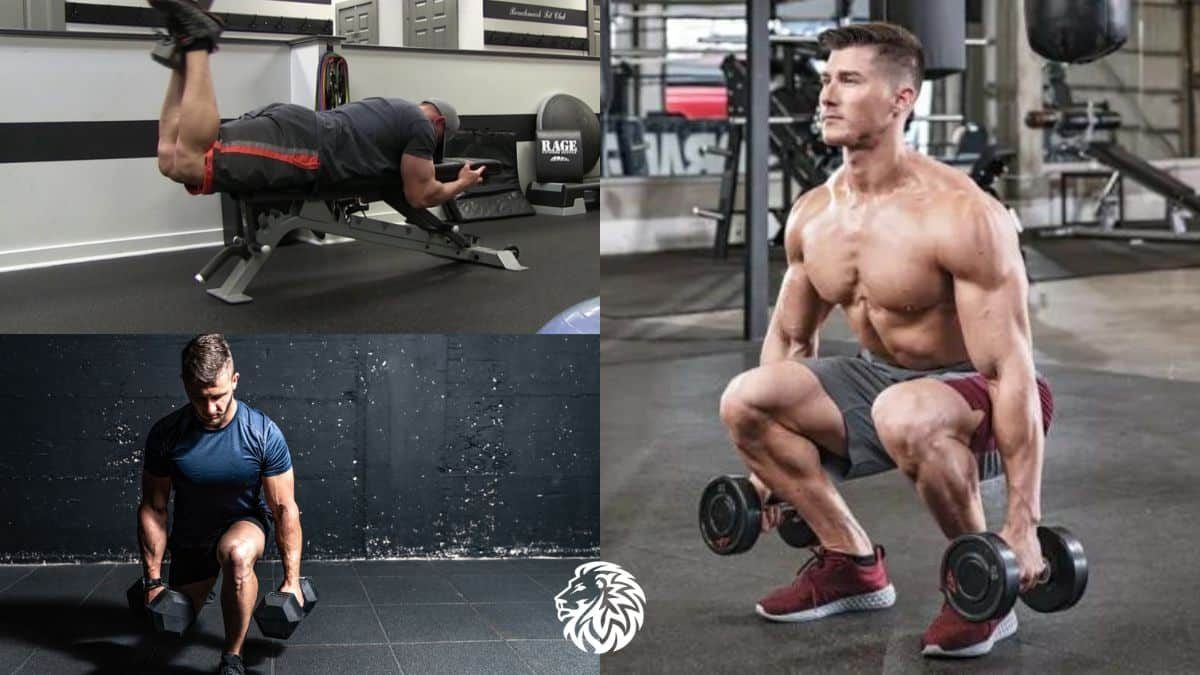
Exercise 1: Dumbbell Deadlifts
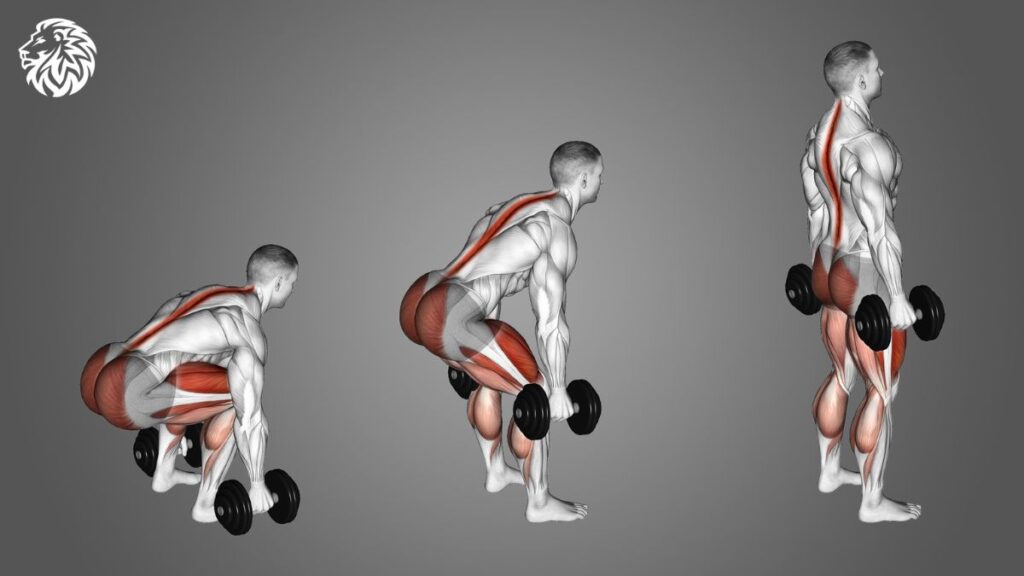

The dumbbell deadlift is a highly effective exercise for strengthening the hamstrings, along with the glutes and lower back. It mimics the motion of picking up a heavy object from the ground, making it functional and practical.
Description and Step-by-Step Guide
- Starting Position: Stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand in front of your thighs. Your palms should be facing your body.
- The Descent: Hinge at your hips and slightly bend your knees as you lower the dumbbells towards the ground. Keep your back flat and chest up. The dumbbells should travel close to your legs.
- The Bottom Position: Go down as far as your flexibility allows without rounding your back. You should feel a stretch in your hamstrings.
- The Ascent: Engage your hamstrings and glutes to return to the starting position. Keep the core engaged and exhale as you lift.
- Repeat: Perform the desired number of repetitions, maintaining control and form throughout the exercise.
Tips for Proper Form
- Keep Your Back Straight: Maintaining a neutral spine is crucial to prevent injury. Avoid rounding your back during the movement.
- Move Through Your Hips: The motion should be a hip hinge, not a squat. Think about pushing your hips back and then forward.
- Neck Alignment: Keep your neck in a neutral position, aligned with your spine. Avoid looking up or down excessively.
- Engage Your Core: A tight core will help stabilize your spine and improve the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Don’t Rush: Perform the movement in a controlled manner. Rushing through the exercise can lead to poor form and reduced effectiveness.
- Avoid Locking Your Knees: Keep a slight bend in the knees throughout the movement to maintain tension in the hamstrings and protect your joints.
- Weight Distribution: Keep the weight on your heels to engage the hamstrings and glutes more effectively.
By following these steps and tips, the dumbbell deadlift can be a cornerstone exercise in your hamstring strengthening routine.
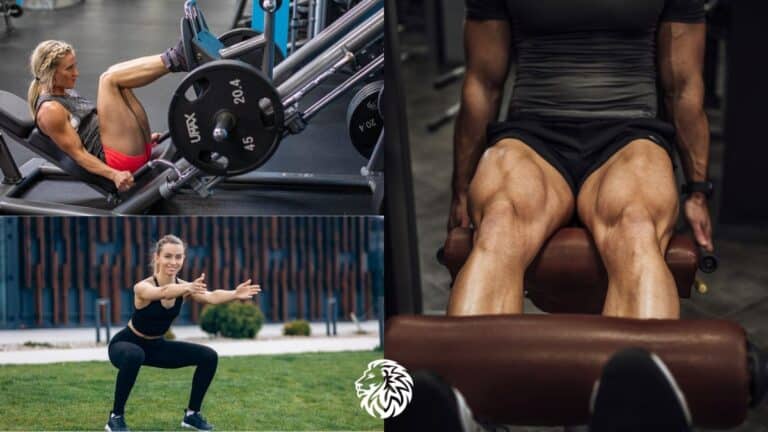
Exercise 2: Dumbbell Lunges

Dumbbell lunges are a versatile exercise that target the hamstrings, along with the quadriceps, glutes, and calves. They are excellent for improving balance, coordination, and unilateral strength (strength on each side of the body).
Description and Step-by-Step Guide
- Starting Position: Stand upright with your feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand by your sides.
- Lunge Forward: Step forward with one leg, lowering your hips until both knees are bent at about a 90-degree angle. The front knee should be directly above your ankle, and the back knee should hover just above the ground.
- The Ascent: Push through the heel of your front foot to return to the starting position.
- Alternate Legs: Repeat the movement, stepping forward with the opposite leg.
- Continuation: Continue alternating legs for the desired number of repetitions.
Variations for Different Difficulty Levels
- Beginner:
- Bodyweight Lunges: Start with bodyweight lunges to master the form before adding weights.
- Static Lunges: Instead of stepping forward each time, stay in a lunge position and perform several repetitions before switching legs.
- Intermediate:
- Walking Lunges: Instead of returning to the starting position, continue moving forward with each lunge, walking across the room.
- Reverse Lunges: Step backward into the lunge rather than forward, which can be easier on the knees.
- Advanced:
- Elevated Lunges: Place your rear foot on an elevated surface like a step or bench for a deeper lunge and increased difficulty.
- Lunge with Bicep Curl: Add a bicep curl with the dumbbells as you lunge to incorporate upper body work.
- Jump Lunges: Add a jump to switch legs in the air for a plyometric, cardio-intensive version.
Remember, the key to effective lunges is control and stability. Make sure to keep your core engaged, and focus on a smooth, controlled movement rather than speed.
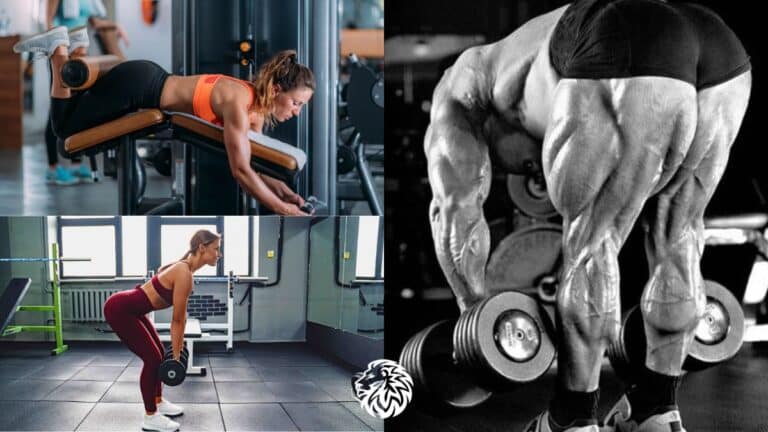
Exercise 3: Dumbbell Stiff-Legged Deadlift
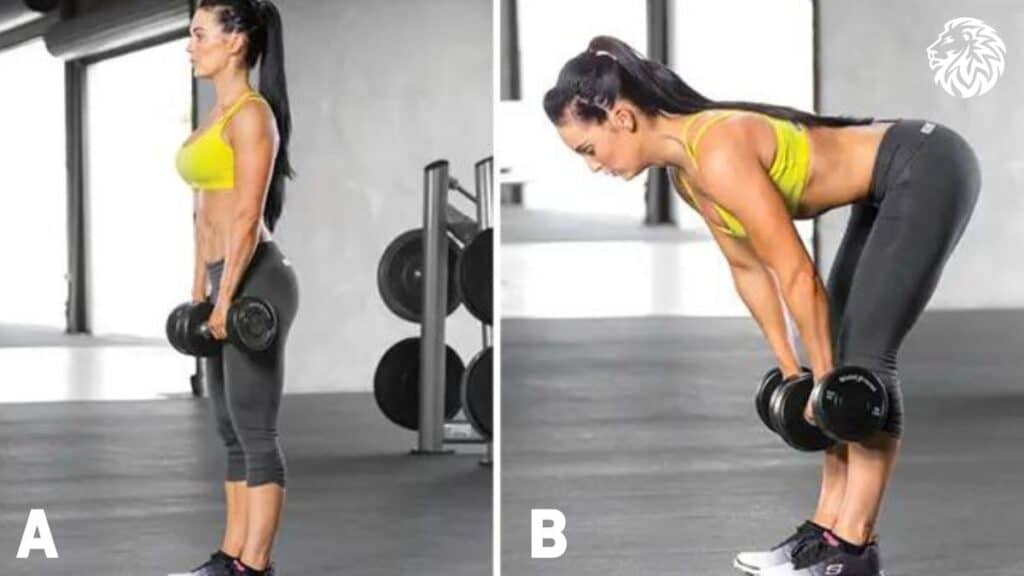

The stiff-legged deadlift is a powerful exercise for isolating the hamstrings. It also engages the lower back and glutes, making it a comprehensive lower body workout.
Detailed Instructions
- Starting Position: Stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand in front of your hips, palms facing your thighs.
- Hinging at the Hips: With a slight bend in your knees, hinge forward at your hips, lowering the dumbbells towards the floor. Keep your back straight and your neck in line with your spine.
- Lowering the Weight: Lower the dumbbells as far as your hamstring flexibility allows without rounding your back. You should feel a stretch in your hamstrings.
- The Lift: Engage your hamstrings and glutes to lift your torso back up to the starting position. Keep your core engaged and exhale as you rise.
- Repeat: Continue for the desired number of repetitions, maintaining a slow and controlled movement throughout.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Rounding the Back: This is a common mistake and can lead to injury. Keep your spine neutral throughout the movement.
- Locking the Knees: While the legs are straighter than a traditional deadlift, avoid locking the knees. Maintain a slight bend to keep tension on the hamstrings and off the knee joints.
- Looking Up or Down: This can strain your neck. Keep your neck in a neutral position, in line with your spine.
- Going Too Low: If your flexibility doesn’t allow you to lower the weights to the ground without rounding your back, only go as far as you can while maintaining proper form.
- Using Too Much Weight: This can compromise form and lead to injury. Start with a lighter weight to ensure you can perform the exercise correctly and safely.
- Rushing the Movement: Perform the exercise with control, especially when lowering the weights. Rapid movements can decrease the effectiveness of the exercise and increase the risk of injury.
Focusing on form and controlled movements will ensure you get the most out of the stiff-legged deadlift while minimizing the risk of injury.
Exercise 4: Dumbbell Hamstring Curl
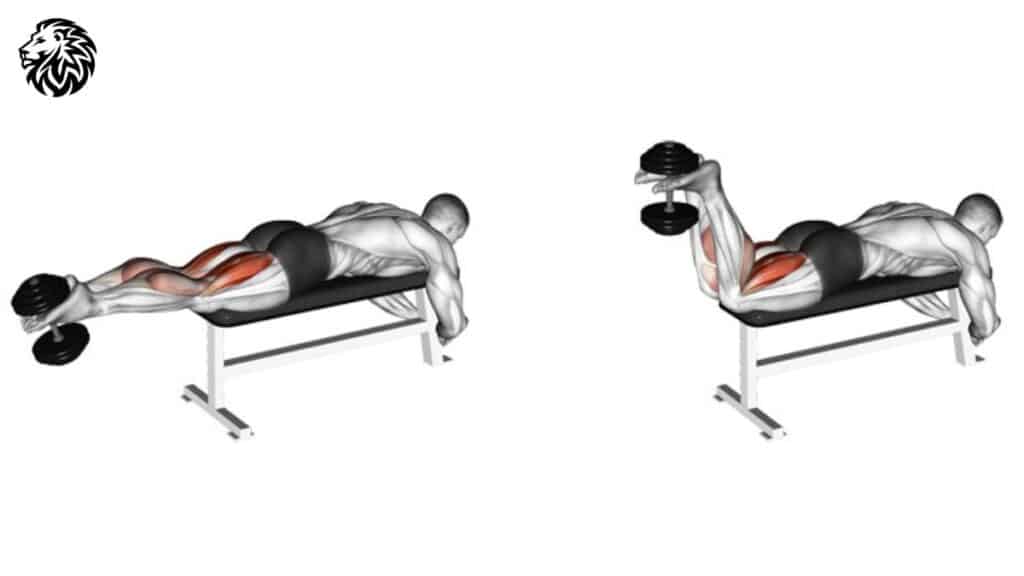
The dumbbell hamstring curl primarily targets the hamstrings, and it’s a great exercise for isolating these muscles. It can be a bit challenging to perform with dumbbells, but with the right technique, it can be highly effective.
How to Perform Effectively
- Starting Position: Lie flat on your stomach on a bench, with your legs extended. Place a dumbbell between your feet – you might need to hold it in place with your feet.
- Lifting the Weight: Bend your knees and curl your legs up towards your buttocks, lifting the dumbbell as you do so. Keep the movement controlled, focusing on using your hamstrings.
- Top Position: Lift the dumbbell as far as you comfortably can, ideally getting your heels close to your buttocks.
- Lowering the Weight: Slowly lower the dumbbell back to the starting position, fully extending your legs.
- Repeat: Continue for the desired number of repetitions, maintaining a slow and controlled movement throughout.
Adjustments for Beginners and Advanced Individuals
- Beginners:
- Lower Weight: Start with a lighter dumbbell to get used to the movement.
- Bodyweight Curls: If holding a dumbbell is too challenging, try performing the exercise without weight, focusing on the hamstring contraction.
- Assisted Curls: You can also perform this exercise lying on the floor and pushing your feet against a wall for stability as you curl.
- Advanced:
- Increase Weight: Use a heavier dumbbell as your strength improves.
- Single-Leg Curls: Perform the exercise with one leg at a time for increased intensity and to address any muscle imbalances.
- Stability Ball Curls: While not a dumbbell exercise, using a stability ball to perform hamstring curls can add an extra challenge to your routine.
Remember, the key to effective hamstring curls is to maintain control and focus on the hamstring muscle throughout the movement. Avoid using momentum to lift the weight, as this can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise and increase the risk of injury.
Integrating Hamstring Exercises into Your Routine
Creating a Balanced Workout Plan
A well-rounded fitness routine should include exercises that target all major muscle groups, ensuring balanced development and reducing the risk of injury. When integrating hamstring exercises:
- Frequency: Aim to train your hamstrings 2-3 times per week. This allows for adequate recovery while promoting muscle growth and strength.
- Variety: Include different hamstring exercises in your routine to target the muscles from various angles and to prevent boredom.
- Progression: Gradually increase the intensity of your workouts by adding more weight, increasing repetitions, or incorporating more challenging variations of exercises.
Recommendations for Sets and Repetitions For hamstring development:
- Beginners: Start with 2-3 sets of 10-12 repetitions per exercise. Focus on mastering the form before increasing weight or intensity.
- Intermediate to Advanced: Aim for 3-4 sets of 8-10 repetitions with a heavier weight. The last few reps should be challenging but still maintainable with good form.
- Endurance and Toning: If the goal is muscular endurance and toning rather than bulk, aim for higher repetitions (12-15) with a lighter weight.
Combining Hamstring Exercises with Other Muscle Groups
To create a balanced routine, pair hamstring exercises with workouts targeting other muscle groups:
- Leg Days: Combine hamstring exercises with those targeting quads, calves, and glutes. For example, pair dumbbell lunges (quads and glutes) with stiff-legged deadlifts (hamstrings).
- Push-Pull-Legs Split: Incorporate hamstring-focused exercises on your leg days, alongside other lower body exercises.
- Full-Body Workouts: Include one hamstring exercise in your full-body routine, ensuring you also work on upper body and core in the same session.
- Super-Set with Antagonistic Muscles: Pair hamstring exercises (like dumbbell deadlifts) with exercises for the opposing muscle group (like quadriceps) for a balanced approach.
Remember, recovery is just as important as the workout itself. Ensure you are getting adequate rest, nutrition, and hydration to support muscle growth and overall health.
Advanced Techniques and Variations
Incorporating advanced techniques and variations into your hamstring workouts can enhance muscle growth, strength, and endurance. These methods challenge your muscles in new ways, leading to continued progress and preventing plateaus.
- Drop Sets: After completing a set of a hamstring exercise at your usual weight, immediately reduce the weight and continue doing more reps until failure. This technique increases muscle endurance and fatigue, leading to greater strength gains.
- Supersets: Perform two different hamstring exercises back-to-back with no rest in between. For example, you could do a set of dumbbell deadlifts followed immediately by dumbbell hamstring curls. This approach maximizes muscle fatigue and can improve muscular endurance and hypertrophy.
- Eccentric Training: Focus on the lowering phase of your hamstring exercises. For example, take 3-5 seconds to lower the weight during a stiff-legged deadlift. This type of training emphasizes the eccentric, or lengthening, part of the muscle contraction, leading to increased muscle strength and size.
- Paused Reps: At the most challenging part of the exercise (e.g., the bottom of a dumbbell lunge), pause and hold for a few seconds before completing the movement. This increases time under tension, a key factor in muscle growth and strength.
- Single-Leg Variations: Performing exercises on one leg, such as single-leg deadlifts, not only increases the intensity but also improves balance and addresses muscular imbalances between legs.
- Tempo Variations: Change the speed of your repetitions. For example, perform the concentric (lifting) phase quickly and the eccentric (lowering) phase slowly. Playing with different tempos can stimulate muscle growth in different ways.
- Pyramid Sets: Start with a lighter weight and higher reps, gradually increase the weight and decrease the reps in each subsequent set, and then reverse the pattern.
- Isometric Holds: Include exercises where you hold a position under tension for a period, like holding the bottom position of a lunge.
- Circuit Training: Combine several hamstring exercises into a circuit, performing each for a set time or number of reps with minimal rest in between. This enhances cardiovascular fitness while also improving muscular endurance.
When incorporating these advanced techniques, it’s crucial to listen to your body and avoid overtraining. Make sure you’re comfortable with the basic exercises and have a solid foundation of strength before progressing to these more challenging variations.
Post-Workout Care
Importance of Stretching and Cooling Down
After a rigorous hamstring workout, a proper cool-down and stretching session are crucial for several reasons. Cooling down helps to gradually lower the heart rate and prevent blood pooling, which can occur if you stop exercising suddenly. Stretching post-workout aids in reducing muscle soreness, improving flexibility, and decreasing the risk of injury. It also helps to relax the muscles that have been intensely worked, leading to better muscle recovery and growth.
Hamstring-Specific Stretches
- Standing Hamstring Stretch: Stand and cross one foot in front of the other. Bend at the waist and reach your hands towards your toes. Hold for 15-30 seconds and switch legs.
- Seated Hamstring Stretch: Sit on the ground with one leg extended and the other bent with the foot resting against the inner thigh of the extended leg. Lean forward from your hips towards the foot of the extended leg. Hold for 15-30 seconds and switch sides.
- Lying Hamstring Stretch: Lie on your back, lift one leg, and gently pull it towards you, keeping it straight. Hold for 15-30 seconds and switch legs.
Tips for Muscle Recovery
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after your workout to aid in recovery and overall health.
- Proper Nutrition: Consume a balanced meal with a good mix of protein, carbohydrates, and fats after your workout. Protein is particularly important for muscle repair and growth.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough quality sleep, as this is when most muscle recovery and growth occur.
- Active Recovery: Engage in light, low-impact activities such as walking, yoga, or swimming on your rest days. This can help improve circulation and facilitate muscle repair without overstraining the muscles.
- Foam Rolling: Use a foam roller for self-myofascial release to help alleviate muscle tightness and improve flexibility.
- Rest: Allow adequate time between workouts for your muscles to recover. Overtraining can lead to injury and hinder progress.
Implementing these post-workout care practices can significantly improve your recovery and contribute to better overall fitness and muscle health.
Conclusion
In summary, this article has provided a comprehensive guide to the best dumbbell exercises for strengthening and toning the hamstrings. We’ve explored the anatomy and importance of the hamstring muscles in both daily activities and sports. The exercises detailed—Dumbbell Deadlifts, Dumbbell Lunges, Stiff-Legged Deadlifts, and Hamstring Curls—offer a range of techniques for effectively targeting these crucial muscles. By incorporating variations and advanced techniques, individuals at all fitness levels can challenge their hamstrings and continue to see progress.
Additionally, we emphasized the significance of a proper warm-up and safety tips for using dumbbells, ensuring that workouts are not only effective but also safe. Integrating these exercises into a balanced workout plan, with appropriate sets and repetitions, is key to achieving the best results. Furthermore, the importance of post-workout care, including stretching, cooling down, and tips for muscle recovery, cannot be overstated.
Consistency is paramount in any fitness regimen. Regularly incorporating these hamstring exercises into your routine will lead to improved muscle strength, flexibility, and overall lower body health. As with any fitness journey, patience and perseverance are crucial. Stay committed, listen to your body, and gradually increase the intensity of your workouts for sustainable and impressive results. Remember, the journey to stronger hamstrings is a marathon, not a sprint, and the rewards are well worth the effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I train my hamstrings?
You should train your hamstrings 2 – 3 times a week. At least 48 hours of rest between sessions is recommended for optimal muscle growth and recovery.
Can I use other equipment for hamstring exercises?
Absolutely! You can incorporate various equipment like resistance bands, barbells, or even machines for hamstring training, but dumbbells offer a versatile and accessible choice.
Are there other exercises I can do to improve hamstring strength and flexibility?
Yes, incorporating exercises such as leg curls, good mornings, and various stretches can help target your hamstrings and improve their overall function.
How many sets and repetitions should I perform for each exercise?
A general guideline is to perform 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions for each exercise, focusing on proper form and gradually increasing weight or reps over time.
Can I perform these exercises at home?
Yes, these dumbbell exercises can be easily performed at home, provided you have access to dumbbells and a bench or sturdy surface for the Bulgarian split squat and hamstring curl.
References and Further Reading
- SET FOR SET. (n.d.). Dumbbell Hamstring Exercises. Retrieved from https://www.setforset.com/blogs/news/dumbbell-hamstring-exercises
- Muscle & Fitness. (n.d.). 30-Minute Dumbbell Workout to Build Your Hamstrings. Retrieved from https://www.muscleandfitness.com/workouts/leg-exercises/30-minute-dumbbell-workout-build-your-hamstrings/
- Greatist. (n.d.). Hamstring Exercises. Retrieved from https://greatist.com/fitness/hamstring-exercises







