Due to their capacity to promote weight loss, muscle growth, and general health improvement, high-protein diets have grown in popularity in recent years. A high-protein diet raises questions about its safety and potential side effects, as with any diet. The safety of high-protein diets will be examined in this article, along with any potential advantages and risks.
Key Takeaways
- High-protein diets can have potential benefits such as increased muscle mass, improved satiety, better weight loss outcomes, and improved heart health.
- High-protein diets can also have potential risks such as kidney damage, dehydration, increased risk of certain cancers, nutrient deficiencies, and increased risk of osteoporosis.
- To ensure a safe and balanced high-protein diet, it’s important to choose high-quality protein sources, balance macronutrient intake, monitor kidney function if necessary, and consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to the diet.
- Good sources of protein include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds, while good sources of carbohydrates and fats include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
What Is a High-Protein Diet?
A high-protein diet is a way of eating that places a focus on eating foods high in protein, like meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts. The diet typically entails decreasing the intake of carbohydrates and fats while increasing the proportion of protein in the diet.
In addition to helping the body build and repair tissues, produce hormones and enzymes, and support the immune system, protein is an essential macronutrient. A diet rich in protein has a number of potential advantages, including the promotion of weight loss, the reduction of hunger and appetite, the preservation of muscle mass during weight loss, and the improvement of metabolic health.
Benefits of High-Protein Diets
High-protein diets can have several potential benefits for some individuals, including:
- Weight loss: Protein has been shown to increase satiety and reduce hunger, which may lead to a decrease in overall food intake and weight loss.
- Preservation of muscle mass: When losing weight, the body may break down muscle for energy. Consuming a diet high in protein may help preserve muscle mass during weight loss.
- Improved body composition: High-protein diets may help reduce body fat and increase muscle mass, which can improve overall body composition.
- Improved bone health: Protein is important for building and maintaining strong bones.
- Better metabolic health: High-protein diets may help improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control, which can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
- Reduced risk of heart disease: Some research suggests that high-protein diets may help improve blood lipid profiles and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Increased satiety: Protein is more satiating than carbohydrates or fat, which can help individuals feel fuller for longer periods and reduce snacking between meals.
Risks of High-Protein Diets
While high-protein diets may have potential benefits for some individuals, there are also potential risks and drawbacks that should be considered. These include:
- Kidney damage: Consuming high levels of protein over a prolonged period can increase the workload of the kidneys, which can lead to kidney damage and other renal issues.
- Dehydration: High-protein diets can increase water loss through urine, leading to dehydration.
- Nutrient deficiency risk: Avoiding certain food groups, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in favor of protein-rich foods, can lead to nutrient deficiencies.
- Increased risk of chronic disease: According to some research, high-protein diets, especially those rich in animal-based proteins, may raise the risk of developing chronic illnesses like cancer and heart disease.
- Bad breath: High-protein diets can lead to bad breath due to the production of ammonia and other compounds during protein metabolism.
- Digestive issues: Eating a lot of protein can cause constipation, bloating, and diarrhea.
- Weight gain: Consuming too much protein can lead to weight gain if calorie intake exceeds energy expenditure.
It’s important to note that individual needs and tolerances may vary, and a high-protein diet may be appropriate for some individuals under the guidance of a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
Your needs for protein are influenced by a number of variables, including your age, sex, weight, and level of activity. In general, 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight is advised daily. However, to support muscle growth and repair, athletes and bodybuilders might require more protein.
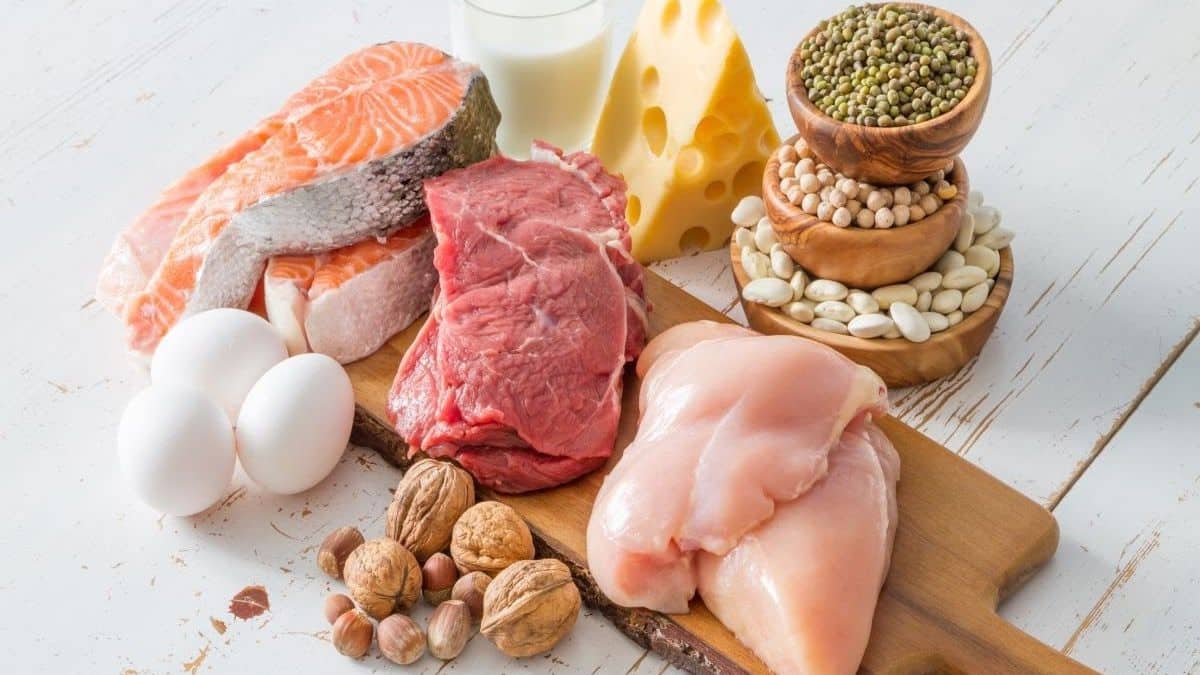
Choosing the Best Protein Sources
Protein sources vary greatly in quality. It’s crucial to pick protein sources that are rich in nutrients and of high quality. Among the best sources of protein are:
- Lean meats like beef, turkey, and chicken
- fish like mackerel, tuna, and salmon
- Eggs
- Milk, cheese, and yogurt are examples of dairy products.
- Legumes like chickpeas, lentils, and beans
- Nuts and seeds, including chia seeds, walnuts, and almonds
Avoiding Potential Risks
The following steps should be taken to minimize any risks connected to high-protein diets:
- Drink a lot of water to avoid becoming dehydrated.
- To make sure you’re getting a variety of nutrients, choose a variety of protein sources.
- Reduce your intake of processed meats because they have been linked to an increased risk of cancer and heart disease.
- Keep an eye on your kidney function if you have a history of kidney disease or other kidney problems.
Balancing Macronutrients
Despite the fact that protein is an important macronutrient, it is also important to balance your carbohydrate and fat intake. When compared to fats, which are necessary for hormone production and nutrient absorption, carbohydrates offer energy and fiber. Eat a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, as part of your diet.
Carbohydrates
The body and brain require carbohydrates for energy, and they also serve as a significant source of fiber. Among the best sources of carbohydrates are:
- Fruits such as berries, bananas, apples, and others
- Leafy greens, carrots, and sweet potatoes are examples of vegetables.
- Whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice
- Legumes like chickpeas, lentils, and beans
Fats
Hormone production, nutrient absorption, and brain health all depend on healthy fats. Among the best sources of healthy fats are:
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds, including chia seeds, walnuts, and almonds
- fatty fish, including mackerel, salmon, and tuna
- Coconut oil, olive oil, and other oils derived from plants
Conclusion
For weight loss, gaining muscle mass, and general health, high-protein diets can be secure and productive. If you have a history of kidney problems, it’s crucial to choose high-quality protein sources, balance your intake of macronutrients, and keep an eye on your kidney function. Before making any significant changes to your diet, as with any diet, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider.
FAQs
Can eating a lot of protein cause you to gain weight?
Although eating a lot of protein is frequently linked to weight loss, eating too many calories from any macronutrient can result in weight gain. You should balance your caloric intake and keep an eye on your portion sizes.
Is it safe for people with kidney disease to eat a high-protein diet?
To prevent further kidney damage, people with kidney disease or other kidney problems may need to limit their protein intake. Before making any significant dietary changes, it’s crucial to speak with a medical professional.
Are sources of protein derived from plants just as efficient as those derived from animals?
If consumed in sufficient quantities and combined with other nutrient-dense foods, plant-based protein sources can be just as effective as animal-based protein sources. The following are some excellent plant-based protein sources: quinoa, lentils, tofu, and beans.
How can I ensure that a vegetarian or vegan diet provides me with enough protein?
Nuts, seeds, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, beans, lentils, tofu, and other vegetarian and vegan products are good sources of protein. To make sure you’re getting enough protein each day, it’s crucial to pick a variety of protein sources and combine them with other nutrient-dense foods.
Does taking protein supplements pose any risks?
A balanced diet combined with moderate use of protein supplements can make them safe. However, consuming too much protein from supplements carries health risks like dehydration and kidney damage. Prior to including protein supplements in your diet, it’s critical to select high-quality options and seek medical advice.