Low-carb diets have soared in popularity as a go-to strategy for weight loss, championed by numerous health enthusiasts, nutritionists, and success stories. At their core, these diets focus on minimizing carbohydrate intake while emphasizing proteins and fats, based on the premise that reducing carbs leads to a decrease in insulin levels, ultimately facilitating fat burning and weight loss.
Despite the widespread acclaim, a significant number of individuals find themselves grappling with a perplexing dilemma: they adhere to a low-carb regimen but don’t see the expected decrease in the scale numbers. This issue can be both frustrating and demotivating, especially when the efforts seem aligned with the diet’s principles.
The aim of this article is to explore this conundrum by delving into 9 possible reasons why a low-carb diet might not be yielding the desired weight loss results. These insights will help readers understand the nuances of low-carb diets and how to optimize them for effective weight loss, ensuring that their dietary efforts are not in vain.
9 Reasons Why You Are Not Losing Weight on a Low-Carb Diet
1. Misunderstanding Low-Carb Principles

Understanding What a Low-Carb Diet Truly Involves
A low-carb diet fundamentally involves reducing the intake of carbohydrates, typically focusing on a daily carb intake significantly lower than the standard dietary recommendations. This reduction often means limiting foods like bread, pasta, sugar, and some fruits, while emphasizing proteins, healthy fats, and vegetables. The idea is to shift the body’s metabolism from relying on carbs for energy to burning fats, a state known as ketosis.
Common Misconceptions About Low-Carb Diets
- All Carbs are Bad: One prevalent misconception is the blanket vilification of all carbohydrates. It’s important to distinguish between different types of carbs – refined carbs (like white bread and pastries) versus complex carbs (like vegetables and whole grains). While refined carbs are limited in a low-carb diet, nutrient-rich, complex carbs are often included in moderation.
- Unlimited Fat and Protein Intake: Another misunderstanding is the assumption that you can consume unlimited amounts of fat and protein. While low-carb diets do allow for more of these macronutrients, caloric intake and balance still matter for weight loss.
- Instant Results: Many people expect rapid weight loss, not realizing that sustainable weight loss is often gradual. Initial weight loss on a low-carb diet is frequently due to water loss, not necessarily fat loss.
- No Need for Exercise: There’s a myth that diet alone is sufficient for weight loss. Exercise remains an essential component of overall health and aids in creating a calorie deficit, which is crucial for weight loss.
- The Same Approach Works for Everyone: Low-carb diets aren’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Individual responses can vary significantly based on factors like metabolism, age, and activity level.
- Neglecting Nutritional Balance: Some people focus solely on carb reduction, ignoring the importance of a well-rounded diet that includes a variety of nutrients.
By addressing these misconceptions and understanding what a low-carb diet genuinely entails, individuals can better align their eating habits with the principles of effective and healthy weight loss.
2. Inadequate Protein Intake
The Role of Protein in Weight Loss and Muscle Maintenance
Protein plays a crucial role in weight loss and the maintenance of muscle mass, especially in the context of a low-carb diet. It’s not just about the calories; protein has a higher thermic effect compared to fats and carbs, meaning the body uses more energy to digest and metabolize it. This can boost metabolic rate and increase calorie burning. Additionally, protein is vital for preserving muscle mass, particularly important during weight loss to prevent the body from burning muscle for energy.
Proteins also contribute to satiety, helping to curb appetite and reduce overall calorie intake. A diet adequate in protein can thus be a powerful ally in managing hunger and promoting a healthy weight.
Ensuring Sufficient Protein Intake on a Low-Carb Diet
- Choose High-Quality Protein Sources: Opt for lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based sources like legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods provide essential amino acids and are generally low in carbohydrates.
- Incorporate Protein in Every Meal: Aim to include a source of protein in every meal to ensure a steady intake throughout the day. This not only helps in muscle maintenance but also keeps you full and satisfied, reducing the likelihood of snacking on high-carb foods.
- Be Mindful of Portions: While it’s important to eat enough protein, overconsumption can lead to excess calorie intake. Understanding appropriate portion sizes can help maintain the right balance.
- Consider Protein Quality: Focus on the quality of the protein. For instance, choosing grass-fed meat over grain-fed can provide additional health benefits, such as more omega-3 fatty acids.
- Use Protein Supplements if Necessary: In some cases, especially for vegetarians or those with high protein requirements, protein supplements like whey or plant-based protein powders can be beneficial. They provide a convenient and low-carb way to increase protein intake.
- Track Your Protein Intake: Especially when starting out, keeping track of how much protein you consume can be helpful. It ensures you’re meeting your needs without overdoing it.
By prioritizing protein intake and choosing the right sources, individuals on a low-carb diet can enhance their weight loss efforts and maintain muscle mass, leading to a healthier and more toned physique.
3. Overconsumption of High-Calorie Foods

Identifying High-Calorie, Low-Carb Foods That Might Lead to Weight Gain
A common pitfall in low-carb diets is the inadvertent overconsumption of high-calorie foods. While these foods may be low in carbs, their high calorie content can easily offset the calorie deficit required for weight loss. Examples include:
- Nuts and Seeds: Although healthy, nuts and seeds are very calorie-dense. A small handful can contain a significant amount of calories.
- Cheeses and Full-Fat Dairy: These are often staples in a low-carb diet but can be high in calories, especially if consumed in large quantities.
- Oils and Fats: Olive oil, coconut oil, butter, and other fats are carb-free but extremely high in calories.
- Processed Low-Carb Foods: Many low-carb snacks and processed foods, like low-carb bars, can be high in calories due to added fats and oils.
- Fatty Cuts of Meat: While meat is low in carbs, fatty cuts can be high in calories.
Strategies for Portion Control
- Use Measuring Tools: Instead of estimating, use measuring cups, spoons, or a food scale to accurately gauge portion sizes.
- Read Nutrition Labels: Pay attention to serving sizes and calorie content per serving on packaged foods.
- Mindful Eating: Eat slowly and without distractions, as it allows you to listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
- Plate Method for Portioning: Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables, a quarter with a lean protein, and a quarter with healthy fats to balance your meal.
- Avoid Eating Out of the Package: Serve a portion on a plate or bowl instead of eating directly from the package, which can lead to overeating.
- Plan Meals in Advance: Meal planning can help control portion sizes and prevent impulsive eating of high-calorie foods.
- Drink Water Before Meals: Sometimes thirst is mistaken for hunger. Drinking water before meals can prevent overeating.
By being mindful of these high-calorie, low-carb foods and implementing portion control strategies, individuals can avoid the common trap of overeating while on a low-carb diet, thus supporting their weight loss goals.
4. Hidden Carbohydrates in Foods

Identifying Foods Surprisingly High in Carbohydrates
One of the hurdles in maintaining a successful low-carb diet is the presence of hidden carbohydrates in many foods. These are often overlooked, leading to unintentional carb intake that can hinder weight loss progress. Some common sources of hidden carbs include:
- Sauces and Condiments: Ketchup, BBQ sauce, and salad dressings often contain added sugars and can be high in carbs.
- Processed Meats: Deli meats, sausages, and hot dogs can have added sugars and fillers that increase their carb content.
- Dairy Products: While cheese is generally low in carbs, milk and yogurts, especially flavored ones, can have a significant carb count.
- Vegetables and Fruits: Not all are low in carbs. For example, starchy vegetables like potatoes and sweet corn, and fruits like bananas and grapes, are high in carbohydrates.
- Nuts and Seeds: Some, like cashews, have higher carb counts than others.
- “Low-Carb” Products: These can sometimes be misleading, as they may contain sugar alcohols or other ingredients that impact blood sugar levels.
Tips for Recognizing and Avoiding Hidden Carbs
- Read Nutrition Labels Carefully: Always check the carb content on food labels, paying close attention to serving sizes.
- Beware of Sugar Alcohols and Artificial Sweeteners: These can sometimes affect blood sugar levels and are often found in processed low-carb foods.
- Cook More at Home: Preparing your own meals allows for better control over ingredients and carb counts.
- Use Carb-Tracking Apps: Technology can be a handy tool in keeping track of daily carb intake.
- Educate Yourself About Food Choices: Learn which foods are naturally low in carbs and which are surprisingly high.
- Choose Whole, Unprocessed Foods: These are less likely to contain hidden carbs compared to their processed counterparts.
By being vigilant about hidden carbs in foods and employing strategies to recognize and avoid them, individuals on a low-carb diet can ensure they stay on track with their carb intake, facilitating more effective weight loss.
5. Lack of Fiber and Its Effects

Understanding the Role of Fiber in Digestion and Weight Loss
Fiber plays a pivotal role in maintaining digestive health and aiding in weight loss, yet it is often neglected in low-carb diets. There are two types of fiber – soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and can help lower glucose levels and blood cholesterol. Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and aids in digestion and regularity. Both types are important for health, and a lack of them can lead to digestive issues like constipation and may hinder weight loss efforts. Fiber also adds bulk to the diet, promoting a feeling of fullness which can reduce overall calorie intake.
Incorporating High-Fiber, Low-Carb Foods into Your Diet
- Focus on Non-Starchy Vegetables: Vegetables like broccoli, spinach, kale, and cauliflower are low in carbs but high in fiber, making them ideal for a low-carb diet.
- Include Seeds and Nuts: Chia seeds, flaxseeds, almonds, and walnuts are excellent sources of fiber. However, watch the portion sizes due to their high-calorie content.
- Select Fiber-Rich Fruits: Berries like raspberries, blackberries, and strawberries offer a good balance of fiber and low net carbs.
- Use Low-Carb Whole Grains Sparingly: If your carb limit allows, whole grains like quinoa and barley can be included in small amounts.
- Incorporate Avocado: It’s not only rich in healthy fats but also a great source of fiber.
- Utilize Psyllium Husk: This is a fiber supplement that can be added to smoothies or yogurt to increase fiber intake without adding significant carbs.
- Plan Your Meals: Ensure each meal includes a source of fiber, balancing it with your overall carb intake.
- Read Labels for Fiber Content: When buying packaged foods, choose options with higher fiber content.
By being mindful of fiber intake and choosing appropriate low-carb, high-fiber foods, individuals can improve their digestive health and potentially enhance their weight loss efforts on a low-carb diet.
6. Stress and Hormonal Imbalance

Understanding the Impact of Stress and Hormones on Weight Loss
Stress and hormonal imbalances can significantly impede weight loss efforts, even in the context of a low-carb diet. Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that can lead to increased appetite and cravings for high-carb, sugary foods. It can also slow down metabolism, making it harder to lose weight. Hormonal imbalances, such as those involving thyroid hormones, insulin, and sex hormones, can also affect metabolism, appetite, and body fat distribution, making weight loss more challenging.
Techniques to Manage Stress and Balance Hormones
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise is a potent stress reliever and can help regulate hormones. Activities like yoga, walking, or strength training can be particularly beneficial.
- Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep can upset hormonal balance, increasing hunger and stress hormones. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or tai chi can reduce stress levels.
- Healthy Eating Habits: Besides low-carb, ensure your diet is balanced with sufficient protein, healthy fats, and micronutrients to support hormonal health.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can stress the body and affect hormonal balance. Drinking enough water throughout the day is essential.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both can contribute to cortisol production and disrupt sleep, so moderating their intake is advisable.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you suspect a hormonal imbalance, consult a healthcare provider. They can offer guidance and treatment options.
- Social Support and Hobbies: Engaging with friends, family, and activities you enjoy can reduce stress levels and improve your overall well-being.
By incorporating these techniques into daily life, individuals can manage stress and hormonal imbalances, potentially enhancing their ability to lose weight on a low-carb diet.
7. Inconsistent Carb Intake
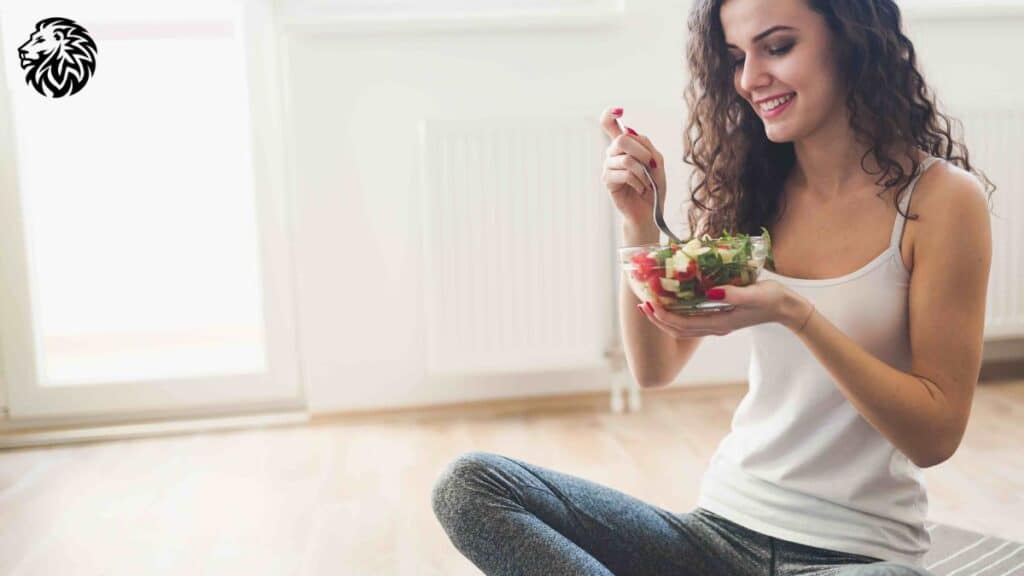

The Importance of Consistency in Low-Carb Eating
Maintaining a consistent low-carb intake is crucial for the success of a low-carb diet. Inconsistencies, such as fluctuating daily carb intake, can disrupt the body’s adaptation to burning fat for fuel and may lead to plateaus or even weight gain. Consistent carb intake helps in stabilizing blood sugar levels, reducing cravings, and maintaining a state of ketosis (if that’s the goal), all of which are essential for effective weight loss and overall health.
Methods to Track and Maintain a Consistent Low-Carb Diet
- Keep a Food Diary: Recording your daily food intake can help you monitor your carb consumption and identify any inconsistencies.
- Use Carb-Counting Apps: Many mobile apps are designed to track carb intake, making it easier to stay within your daily carb goals.
- Plan Your Meals in Advance: Meal planning ensures that you have the right foods on hand, helping to avoid impromptu high-carb meals or snacks.
- Educate Yourself on Carb Content: Knowing the carb content of common foods can help in making informed choices and maintaining consistency.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes, as larger portions can inadvertently increase carb intake.
- Read Labels Carefully: When purchasing packaged foods, read the nutrition labels to determine the carb content per serving.
- Be Consistent Across All Meals: Try to distribute your carb intake evenly throughout the day to avoid large fluctuations.
- Adjust as Needed Based on Your Body’s Response: Be attentive to how your body reacts and make adjustments to find the right balance that works for you.
By implementing these methods, individuals on a low-carb diet can maintain a consistent carb intake, thereby enhancing their chances of successful weight loss and overall health improvement.
8. Neglecting Physical Activity
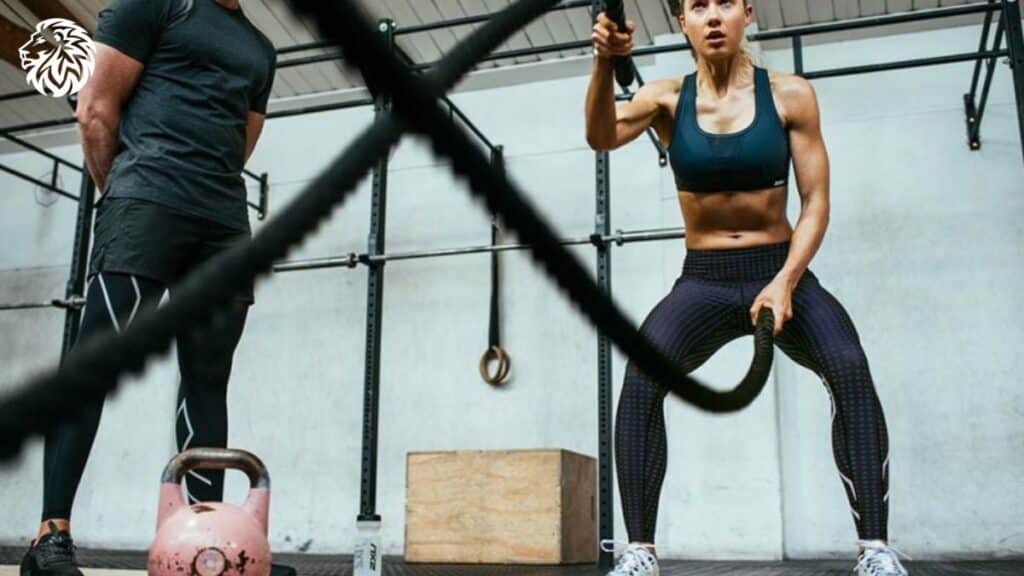

Understanding the Role of Exercise in Complementing a Low-Carb Diet
Physical activity is a critical component of any weight loss plan, including a low-carb diet. Exercise not only helps burn calories but also builds muscle mass, which can increase metabolism. Additionally, regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, which is particularly beneficial in a low-carb diet aimed at stabilizing blood sugar levels. Exercise also enhances mood and energy levels, providing a psychological boost to maintain dietary efforts.
Recommended Types of Physical Activity for Those on a Low-Carb Diet
- Cardiovascular Exercises: Activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling help burn fat and improve heart health. These can be particularly effective when done at a moderate intensity for a longer duration.
- Strength Training: Lifting weights or using resistance bands helps build muscle, which can be beneficial since muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, even at rest.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of high-intensity exercise followed by rest periods can be highly effective for fat burning. HIIT can also be adapted to a variety of fitness levels and can be done with minimal equipment.
- Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Practices like yoga or Pilates not only improve flexibility and balance but can also reduce stress, which is beneficial for weight loss.
- Consistency is Key: Regularity in exercise is more important than intensity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week, as recommended by health guidelines.
- Listen to Your Body: On a low-carb diet, some might experience a temporary decrease in energy levels during workouts. It’s important to listen to your body and adjust the intensity of workouts accordingly.
- Stay Hydrated and Well-Nourished: Ensure you’re hydrating adequately and consuming enough electrolytes, especially if engaging in more intense or prolonged physical activity.
By incorporating a balanced mix of physical activities into a low-carb lifestyle, individuals can significantly enhance their weight loss efforts, improve overall fitness, and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
9. Medical Conditions and Medications
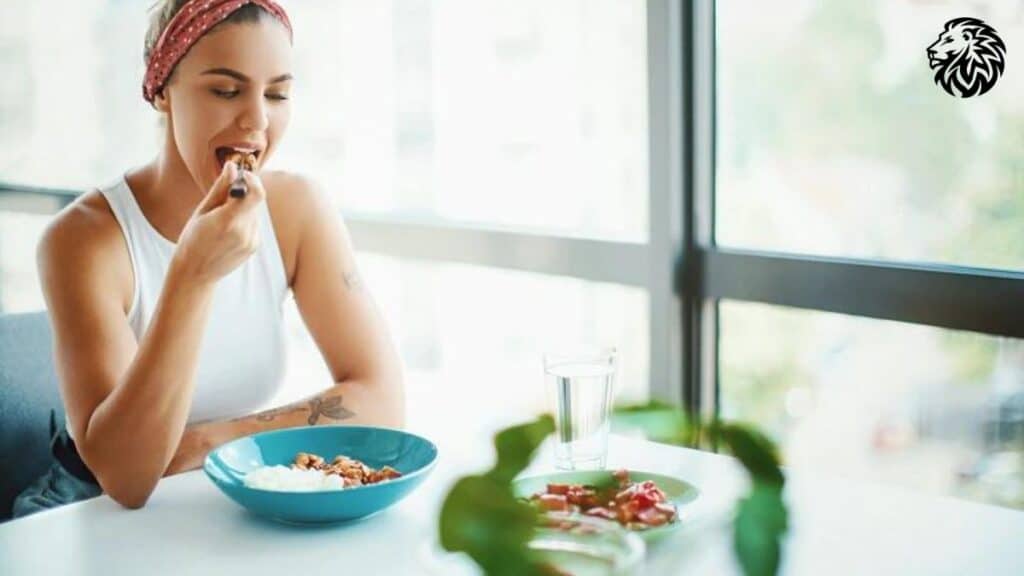

Understanding the Influence of Medical Conditions and Medications on Weight Loss
Certain medical conditions and medications can have a profound impact on weight loss, often making it more challenging. Understanding these factors is crucial for those struggling to lose weight despite adhering to a low-carb diet.
Medical Conditions That Can Affect Weight Loss
- Thyroid Disorders: Conditions like hypothyroidism can slow down metabolism, making weight loss difficult.
- Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes: These conditions can affect how your body uses insulin and processes glucose, impacting weight management.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This hormonal disorder can lead to weight gain and make losing weight more challenging.
- Cushing’s Syndrome: A condition that results in overproduction of cortisol, the stress hormone, which can lead to weight gain, especially in the abdominal area.
- Other Hormonal Imbalances: Imbalances in hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and progesterone can affect body weight and composition.
The Impact of Medications on Weight
Certain medications can contribute to weight gain or make it harder to lose weight. These include:
- Antidepressants
- Antipsychotics
- Steroid Hormones
- Some Antihypertensives
- Insulin and Certain Diabetes Medications
Advice on Consulting Healthcare Professionals
- Seek Medical Advice: If you suspect a medical condition or believe your medication might be affecting your weight loss efforts, consult a healthcare professional.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular health check-ups can help identify any underlying conditions early.
- Discuss Medication Alternatives: If your medication is contributing to weight gain, ask your doctor about possible alternatives.
- Tailored Approach: Work with your healthcare provider to develop a weight loss plan that takes into account your medical conditions and medication.
- Be Open About Your Diet: Inform your healthcare provider about your low-carb diet, as this can impact the management of certain medical conditions and the effectiveness of medications.
Understanding and addressing these medical and medication-related factors, with the guidance of healthcare professionals, is crucial for achieving weight loss goals, particularly for those on a low-carb diet.
Conclusion
In this exploration of the challenges faced on a low-carb diet, we’ve uncovered key insights that can make a significant difference in your weight loss journey. To recap:
- Misunderstanding Low-Carb Principles: Grasping the true essence of a low-carb diet is foundational.
- Inadequate Protein Intake: Adequate protein is crucial for satiety and maintaining muscle mass.
- Overconsumption of High-Calorie Foods: Awareness of calorie-rich, low-carb foods is vital to avoid inadvertent overeating.
- Hidden Carbohydrates in Foods: Being alert to unexpected sources of carbs can prevent setbacks.
- Lack of Fiber and Its Effects: Incorporating fiber-rich foods aids in digestion and weight control.
- Stress and Hormonal Imbalance: Managing stress and hormonal health is integral to successful weight loss.
- Neglecting Physical Activity: Exercise is a key complement to dietary efforts.
- Inconsistent Carb Intake: Consistency in carb intake is crucial for maintaining metabolic balance and effectiveness.
- Medical Conditions and Medications: Acknowledging and managing medical factors is essential for personalized weight loss strategies.
As you navigate your low-carb diet, remember that weight loss and health are profoundly personal journeys. Factors like genetics, lifestyle, and personal preferences play a significant role in shaping your path. It’s important to stay informed, mindful, and flexible, adjusting your approach as you learn more about your body’s unique needs and responses.
If your progress stalls or if you encounter challenges, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from nutrition and healthcare professionals. They can provide personalized advice and support, tailored to your individual circumstances.
In closing, be patient with yourself and remember that every step forward, no matter how small, is a move towards a healthier, more balanced you.







