A strong and well-defined chest is not only aesthetically pleasing but also crucial for overall upper body strength and function. The chest muscles, primarily the pectoralis major and minor, are responsible for pushing, pressing, and stabilizing the shoulder joint. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the 7 best chest exercises for maximum strength, including variations and tips for proper execution. By incorporating these exercises into your fitness routine, you can unleash your pectoral power and enhance your overall upper body performance.
Key Takeaways
- Incorporate the 7 best chest exercises: Boost your upper body strength by regularly performing barbell bench press, dumbbell chest press, push-ups, chest flyes, chest dips, pullovers, and Hammer Strength chest press.
- Prioritize proper form and technique: Ensure maximum strength gains and injury prevention by using correct form and progressively increasing weight or resistance for each exercise.
- Train chest muscles 1-2 times per week: Allow adequate rest and recovery between sessions to optimize muscle growth and prevent overtraining.
- Experiment with exercise variations: Target different areas of the chest and prevent muscle imbalances by incorporating variations of each exercise into your fitness routine.
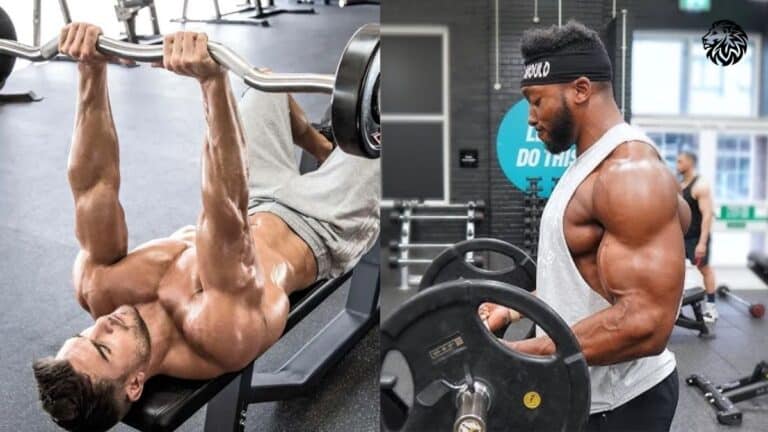
Barbell Bench Press
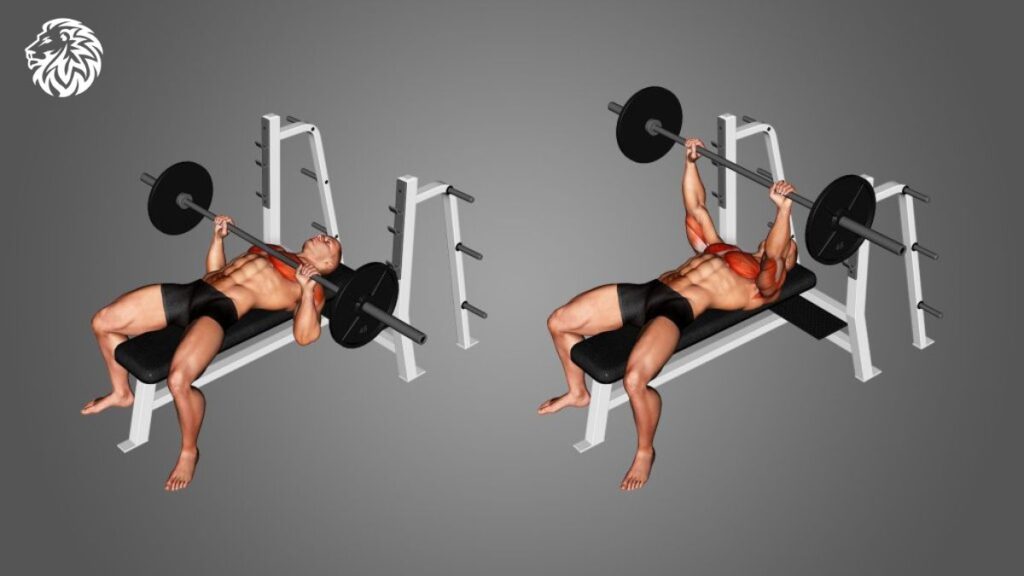
The barbell bench press is the cornerstone of chest training. The barbell bench press targeting the pectoralis major, triceps, and anterior deltoids. To perform this exercise correctly:
- Lie on a flat bench with your feet firmly on the ground.
- Grasp the barbell with a grip slightly wider than shoulder-width.
- Lower the barbell to your mid-chest, keeping your elbows at a 45-degree angle.
- Push the barbell back up until your arms are fully extended.
Variations: Incline barbell bench press, decline barbell bench press
Dumbbell Chest Press
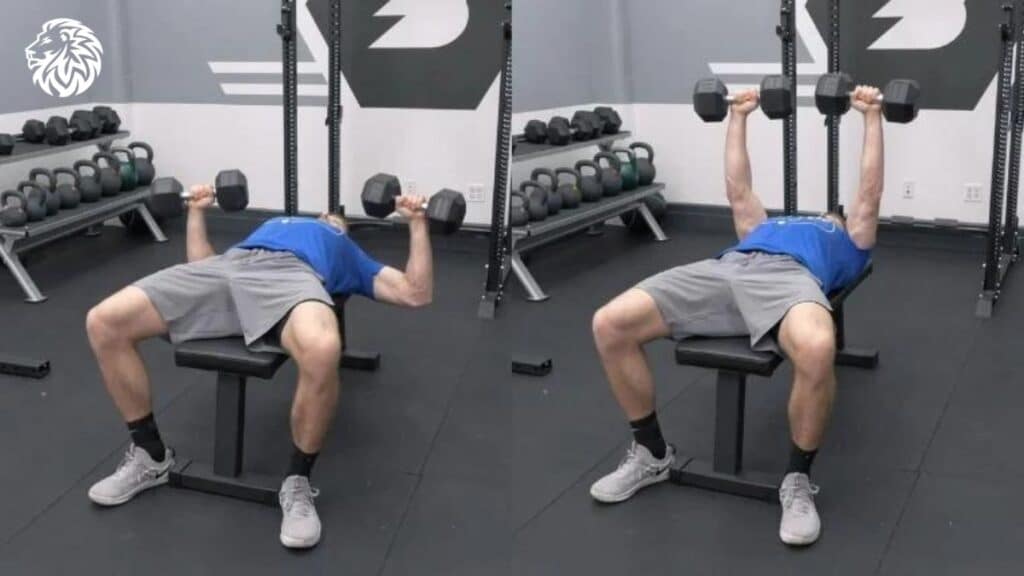

The dumbbell chest press is a versatile alternative to the barbell bench press. It allows for a greater range of motion and better chest activation.
- Lie on a flat bench with a dumbbell in each hand.
- Position the dumbbells at shoulder level with your palms facing forward.
- Press the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended.
- Lower the dumbbells back to the starting position, keeping your elbows at a 45-degree angle.
Variations: Incline dumbbell chest press, decline dumbbell chest press
Push-Ups
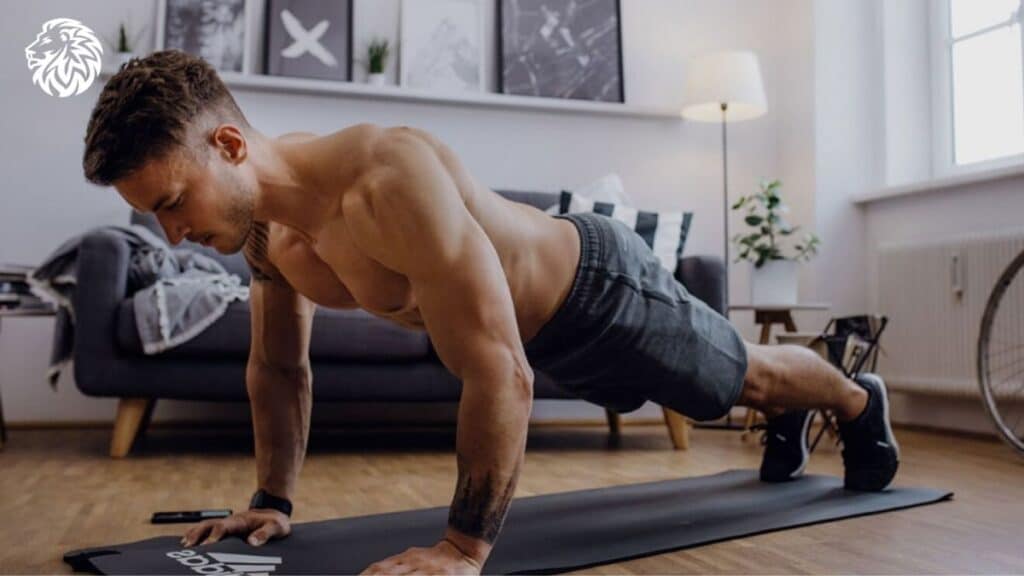

Push-ups are a bodyweight exercise that effectively targets the chest, triceps, and anterior deltoids.
- Start in a plank position with your hands shoulder-width apart.
- Lower your body, bending your elbows until your chest nearly touches the ground.
- Push your body back up to the starting position, maintaining a straight line from head to toe.
Variations: Wide-grip push-ups, diamond push-ups, elevated push-ups
Chest Flyes
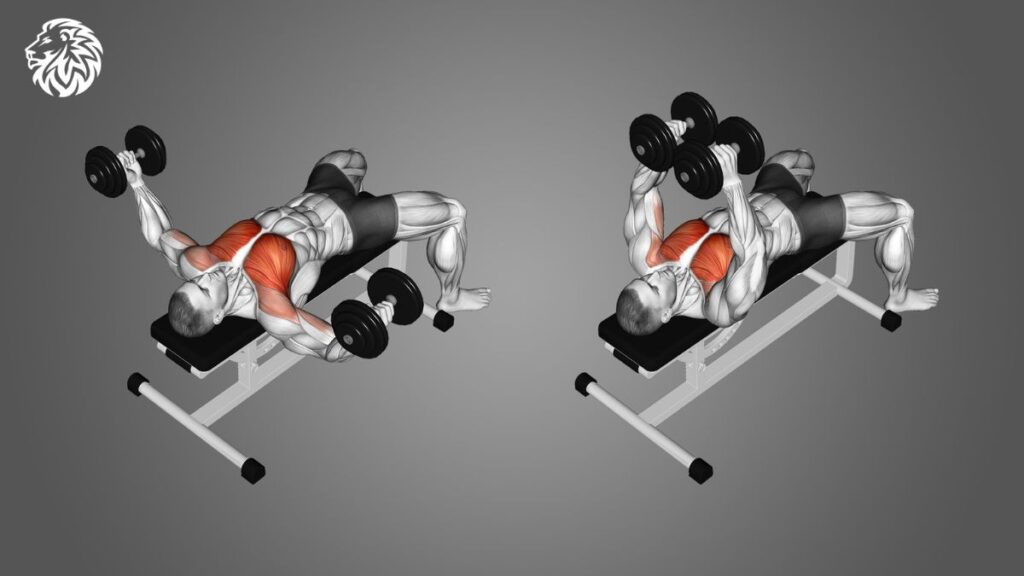
Chest flyes isolate the pectoral muscles, providing a great stretch and contraction.
- Lie on a flat bench with a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing inward.
- Extend your arms above your chest, maintaining a slight bend in your elbows.
- Slowly lower the dumbbells out to the sides, feeling a stretch in your chest.
- Bring the dumbbells back to the starting position, squeezing your chest muscles.
Variations: Incline chest flyes, decline chest flyes, cable chest flyes
Chest Dips
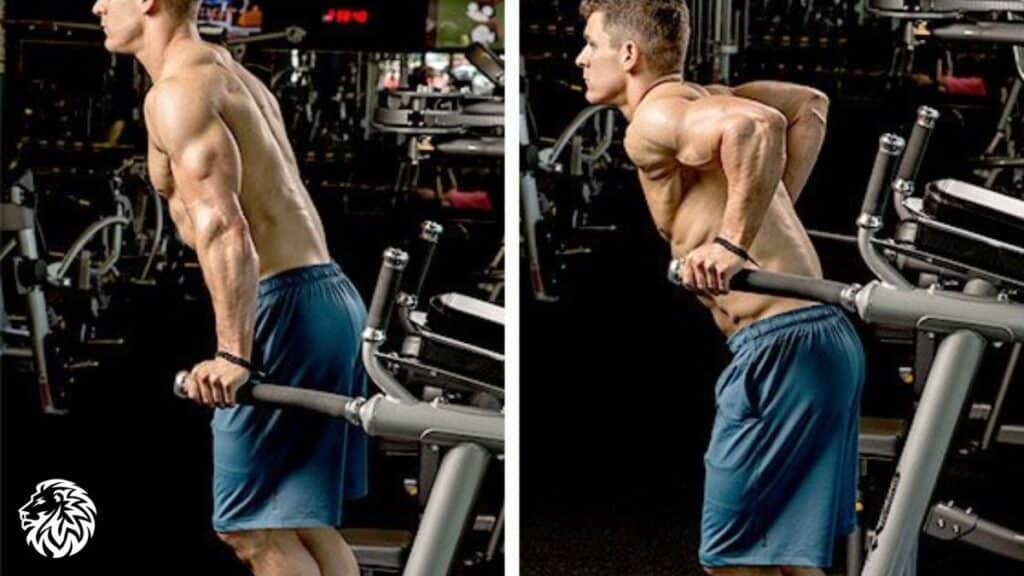

Chest dips target the lower chest, triceps, and anterior deltoids.
- Position yourself between parallel dip bars, gripping the bars with your palms facing inward.
- Lower your body by bending your elbows, leaning slightly forward.
- Push yourself back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms.
Variation: Weighted chest dips
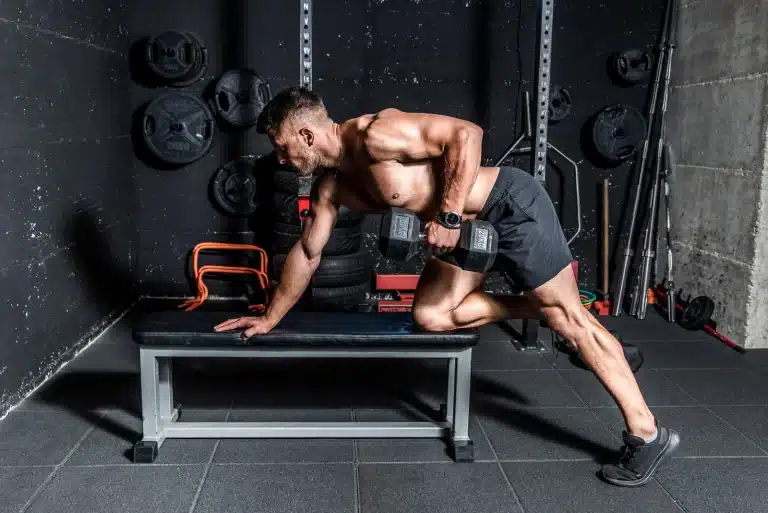
Pullovers
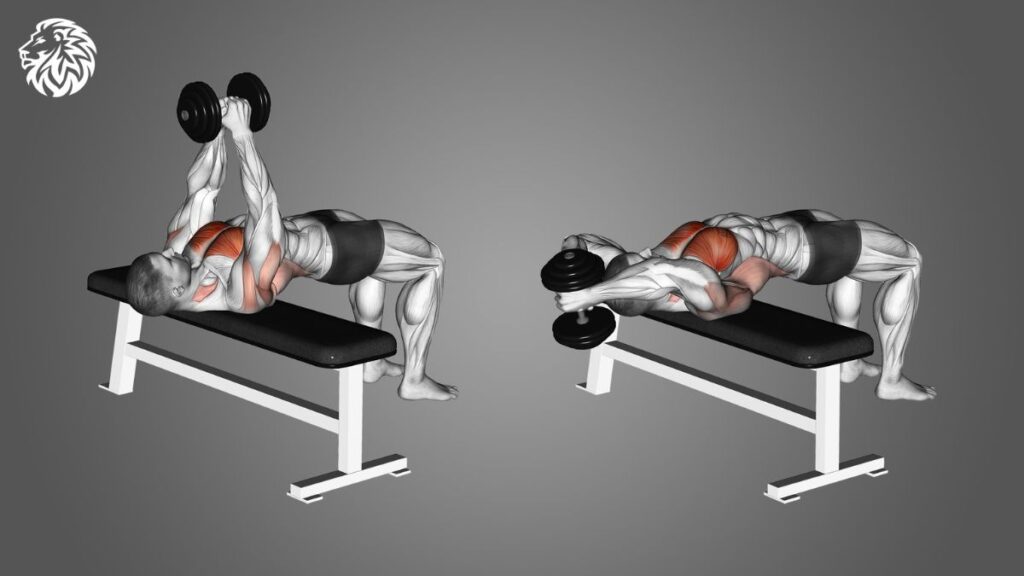
Pullovers target the upper chest, lats, and serratus anterior.
- Lie on a flat bench with a dumbbell or barbell in both hands, arms extended above your chest.
- Slowly lower the weight behind your head, keeping your arms extended and elbows slightly bent.
- Return the weight to the starting position, using your chest and lats to control the movement.
Variation: Cable pullovers
Hammer Strength Chest Press
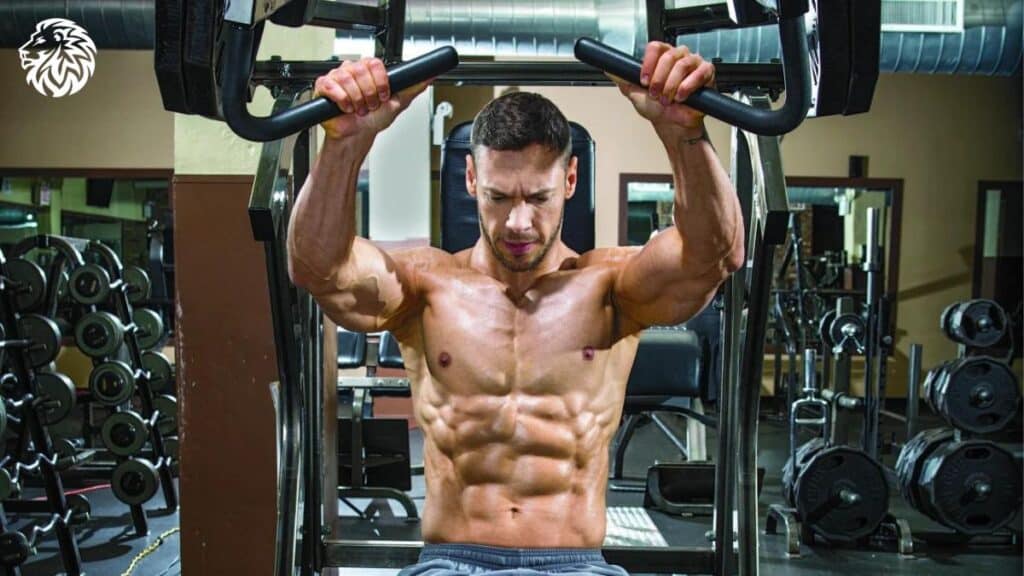

Hammer Strength machines provide a controlled range of motion and targeted muscle activation, making them an excellent addition to your chest workout.
- Adjust the seat height and weight on the Hammer Strength chest press machine.
- Sit down with your back firmly against the pad, gripping the handles with palms facing down.
- Press the handles forward until your arms are fully extended.
- Slowly return to the starting position, maintaining tension in your chest muscles.
Variation: Hammer Strength incline chest press
Conclusion
Incorporating these 7 best chest exercises into your fitness routine will help you build maximum strength and a well-defined, powerful chest. Remember to use proper form, progressively increase the weight or resistance, and vary your exercises to keep challenging your muscles and prevent plateaus. With dedication and consistency, you’ll unlock your pectoral potential and enhance your upper body performance.
FAQs
How often should I train my chest for maximum strength?
For optimal results, train your chest 1-2 times per week, allowing for adequate rest and recovery between sessions.
Can I perform all 7 chest exercises in one workout?
Yes, you can perform all 7 exercises in one workout. However, consider your current fitness level and adjust the volume accordingly to prevent overtraining.
How many sets and reps should I do for each exercise?
For maximum strength, aim for 3-5 sets of 4-6 reps per exercise, using a challenging weight that allows you to maintain proper form.
Can beginners perform these chest exercises?
Yes, beginners can perform these exercises. Start with lighter weights and focus on proper form. As your strength and technique improve, gradually increase the weight and intensity.
Is it necessary to use variations of each exercise?
Using variations of each exercise can help target different areas of the chest and prevent muscle imbalances. Experiment with different variations to find the ones that work best for you and your goals.
References:
- Schoenfeld, B. J., & Grgic, J. (2020). Effects of different repetition durations on bench press power output. Journal of strength and conditioning research, 34(4), 920-924.
- Welsch, E. A., Bird, M., & Mayhew, J. L. (2005). Electromyographic activity of the pectoralis major and anterior deltoid muscles during three upper-body lifts. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research, 19(2), 449-452.
- Trebs, A. A., Brandenburg, J. P., & Pitney, W. A. (2010). An electromyography analysis of 3 muscles surrounding the shoulder joint during the performance of a chest press exercise at several angles. Journal of strength and conditioning research, 24(7), 1925-1930.