Your quads, those muscles at the front of your thighs, aren’t just there for show. They’re like the superheroes of your legs. Think of every time you walk your dog, dash for a bus, or take on a flight of stairs – that’s your quads working overtime to keep you moving with ease.
In the world of sports, think of them as the MVPs. Picture a sprinter getting that explosive start, a soccer player shooting that game-winning goal, or a gym enthusiast nailing a heavy squat. Yup, that’s the magic of strong quads. They don’t just help you outdo yourself in sports but also have your back (or should we say, your legs?) by lowering your injury risks.
So, how about we give these superheroes the training they deserve? Dive in with us as we explore five awesome exercises to make your quads even stronger, ensuring you’re always on the move, stable, and showing off some impressive leg power.
Anatomy of the Quadriceps

The quadriceps femoris, commonly known as the quadriceps or quads, is a group of large muscles located at the front of the thigh. These muscles are primarily responsible for extending the knee and play a fundamental role in movements like walking, running, and jumping. Here’s a quick breakdown of the four major muscles that comprise the quadriceps group:
- Rectus Femoris: This muscle originates from the pelvis and extends down the middle of the thigh. Unique among the quadriceps muscles, the rectus femoris is involved in both hip flexion and knee extension.
- Vastus Lateralis: Located on the outer side of the thigh, this muscle is the largest of the quad muscles. It’s crucial for providing stability and strength during activities that require powerful knee extension.
- Vastus Medialis: This teardrop-shaped muscle can be found on the inner part of the thigh. It is particularly important in stabilizing the patella (knee cap) and ensuring proper knee alignment during movement.
- Vastus Intermedius: Situated beneath the rectus femoris, this muscle lies deep in the center of the thigh. It plays a more subtle yet essential role in knee extension alongside its counterparts.
Understanding the specific roles and locations of these muscles is fundamental for targeted strengthening and to gain a comprehensive idea of how they work in unison to support our daily movements and athletic endeavors.
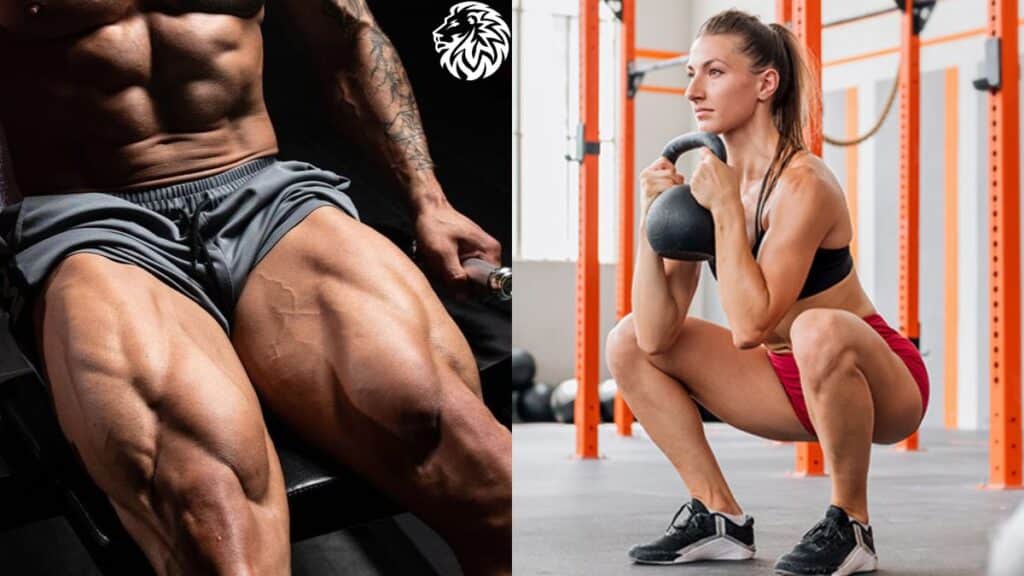
Exercise 1: Squats
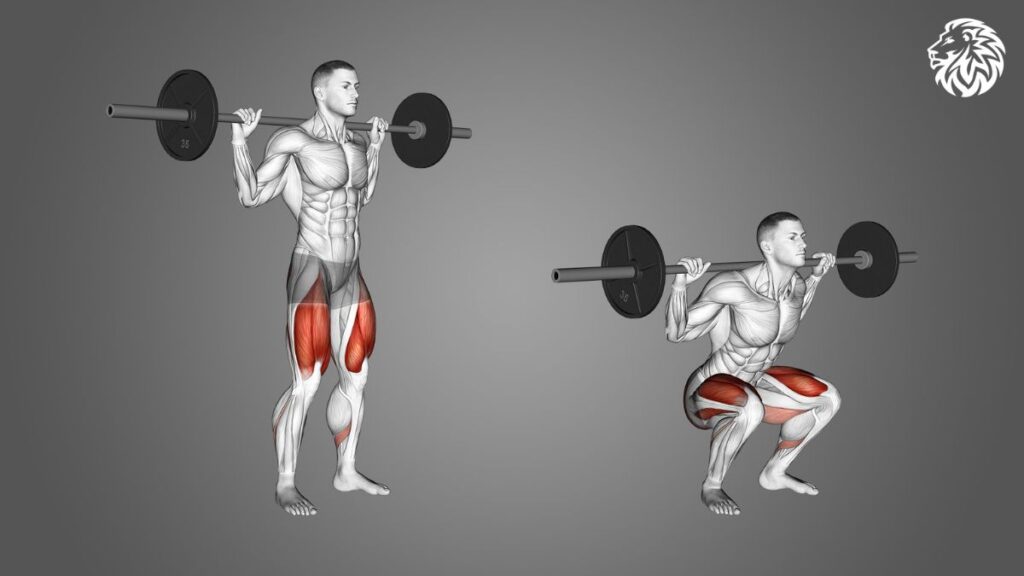
Description and Benefits: Squats are often dubbed the “king of exercises” because of their comprehensive benefits. This compound movement engages multiple muscle groups, with the quadriceps being at the forefront.
- Whole Body Engagement: Beyond the quads, squats also target the hamstrings, glutes, lower back, and core, making it a full-body exercise.
- Functional Fitness: The squat mimics everyday movements, such as sitting in a chair or picking up an object from the ground. Strengthening through squats can improve daily life functionality.
- Bone Density: Weight-bearing exercises like squats can improve bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Caloric Burn: Due to the engagement of large muscle groups, squats can lead to a significant caloric burn, aiding in weight management.
Proper Form and Technique:
- Starting Position: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Your toes can be pointed slightly outward. Keep your spine neutral, chest up, and shoulders relaxed.
- Descending: Begin by pushing your hips back as if sitting in a chair. As you descend, ensure your knees are tracking over your toes but not going past them. Keep your chest up and back straight.
- Depth: Aim to go as low as your mobility allows, ideally until your thighs are parallel to the ground or lower. Ensure your heels stay firmly planted.
- Ascending: Push through your heels to return to the starting position. Engage your quads and glutes as you rise.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Knees Caving In: This can put undue stress on the ligaments of the knee. Ensure your knees are tracking over your toes.
- Lifting Heels: Rising onto the balls of your feet can strain the knee. Keep your heels grounded.
- Rounding the Back: A rounded back can lead to spinal injuries. Maintain a neutral spine by engaging the core and keeping the chest up.
- Not Going Low Enough: Partial squats do not fully engage the quads or glutes. Aim for depth while maintaining form.
- Overextending at the Top: Locking out too aggressively or hyperextending the back at the top of the movement can be harmful. Finish the movement with a controlled stance.
Incorporating squats into your routine with proper technique will ensure maximum benefit and minimized risk of injury.
Exercise 2: Lunges
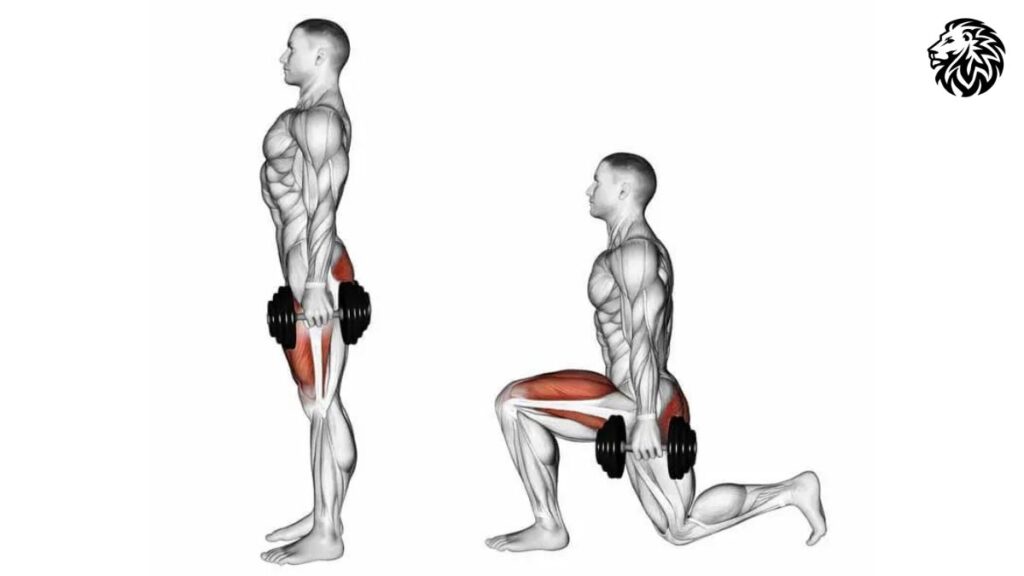
Description and Benefits: Lunges are a versatile lower body exercise that primarily targets the quadriceps while also engaging the hamstrings, glutes, and calf muscles.
- Balance and Stability: Lunges require coordination, helping improve balance and stability.
- Unilateral Exercise: As a single-leg exercise, lunges are great for identifying and rectifying strength imbalances between legs.
- Flexibility: Regular lunging can improve hip flexibility, beneficial for various daily activities and athletic movements.
- Joint Health: When done correctly, lunges can help improve knee joint health and stability.
Variations:
- Forward Lunges: From a standing position, step one foot forward and lower your body until both knees are bent at about a 90-degree angle. Push off the front foot to return to the starting position.
- Reverse Lunges: Instead of stepping forward, step backward and lower your body. This variation places less strain on the knees and emphasizes the glutes and hamstrings.
- Walking Lunges: This dynamic version combines forward lunges in a walking motion, alternating legs. Each step forward is followed by a lunge.
Proper Form and Technique:
- Stance: Begin with feet hip-width apart. When lunging, ensure the forward foot remains flat on the ground, and the back foot’s ball is grounded.
- Knee Position: The front knee should be aligned with the foot, not extending past the toes. The back knee should hover just above the ground.
- Upright Torso: Keep your torso upright, avoiding any forward lean. Engage the core for stability.
- Shoulder Position: Shoulders should be relaxed and aligned over the hips. Avoid rounding or hunching forward.
- Hand Position: Hands can be on the hips, held out to the sides for balance, or clasped in front of the chest.
For all lunge variations, maintaining alignment and balance is crucial. A controlled motion, focusing on the descent as much as the ascent, will ensure maximum muscle engagement and protection from injury. Incorporating the various lunge types can bring diversity to your workout, challenging the muscles in different ways.
Exercise 3: Leg Press
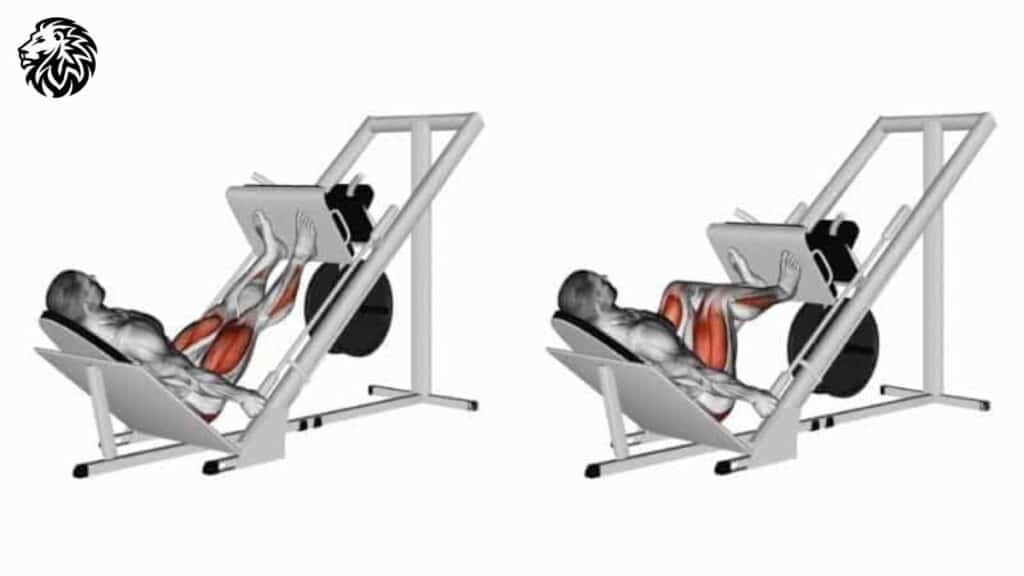
Description and Benefits: The leg press is a popular weight-training exercise that primarily targets the quadriceps, while also engaging the hamstrings, glutes, and calves.
- Strength Building: As a machine-based exercise, it allows users to lift heavy weights in a controlled environment, promoting hypertrophy and strength in the lower body muscles.
- Safety: Given its fixed path of motion, the leg press is often considered safer than free weights for those new to resistance training or recovering from certain injuries.
- Adjustability: Many leg press machines are adjustable, allowing users to change the angle and positioning, targeting the muscles differently.
How to Safely Use Leg Press Machines:
- Adjustment: Ensure the seat and sled are adjusted to your height and limb length. Your legs should form a 90-degree angle or slightly less at the starting position.
- Weight Selection: Start with a lighter weight to warm up and ensure proper form. Gradually increase weight as needed.
- Secure Position: Use the handles on the sides to stabilize your upper body. Do not pull on them to aid in the pressing motion.
- Safety Latches: Familiarize yourself with the safety latches and ensure they are accessible in case you need to stop mid-rep.
Proper Form and Technique:
- Foot Placement: Place your feet shoulder-width apart on the sled. Position can vary slightly up or down based on preference and which part of the quad you want to emphasize.
- Full Range of Motion: Begin by bending your knees and bringing the weight toward you, then push the sled away without locking your knees at the top.
- Knee Tracking: Ensure your knees are tracking over your feet and not caving inward.
- Neutral Spine: Maintain contact with the backrest, ensuring a neutral spine. Avoid arching or rounding your back.
- Breathing: Exhale as you push the weight away and inhale as you return to the starting position.
While the leg press is often considered safe, proper form is still crucial to prevent injuries and get the most benefit from the exercise. Always prioritize form over the amount of weight being used, and don’t hesitate to ask a trainer or gym staff for guidance if you’re unfamiliar with the machine.
Exercise 4: Step-Ups
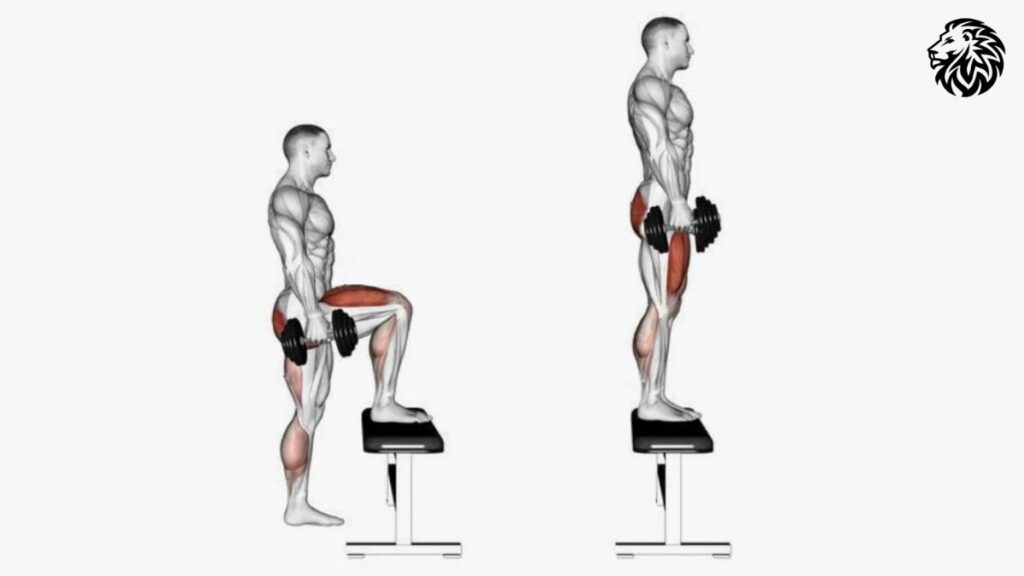
Description and Benefits: Step-ups are a functional exercise that simulates real-life movements, making them particularly beneficial for improving daily mobility and athletic performance.
- Functional Strength: Enhances the ability to climb stairs or hike, translating to better overall mobility.
- Balance and Stability: Challenges unilateral leg strength and balance, helping rectify leg imbalances and improve coordination.
- Versatility: Can be easily modified for intensity and can be performed virtually anywhere, from the gym to home.
How to Increase Intensity:
- Weights: Holding dumbbells in each hand or using a barbell on your shoulders will add resistance, making the exercise more challenging.
- Increased Height: Using a taller platform or bench will demand a greater range of motion and engage the quads more intensively.
- Variations: Introduce step-up variations, like lateral step-ups or step-ups with a knee raise at the top, to engage different muscle groups and add complexity.
Proper Form and Technique:
- Platform Positioning: Stand facing a bench or platform. Ensure it’s sturdy and won’t slide during the exercise.
- Foot Placement: Place one foot fully onto the center of the bench. The entire foot should be on the platform, not hanging off.
- Upright Posture: Keep your chest lifted, shoulders back, and look straight ahead. This ensures a neutral spine throughout the movement.
- Engage the Leading Leg: Drive through the heel of the foot on the bench, engaging the quads and glutes, to lift your body up. Try not to push off too much with the trailing leg.
- Controlled Descent: Lower yourself back to the ground with control, rather than simply dropping down. This eccentric phase is crucial for muscle engagement and development.
- Switch Legs: Ensure an even number of reps on each leg to maintain balanced strength and development.
Remember, the focus should be on quality, not quantity. As with any exercise, performing step-ups with proper form ensures maximum muscle engagement and minimizes the risk of injury.
Exercise 5: Leg Extensions
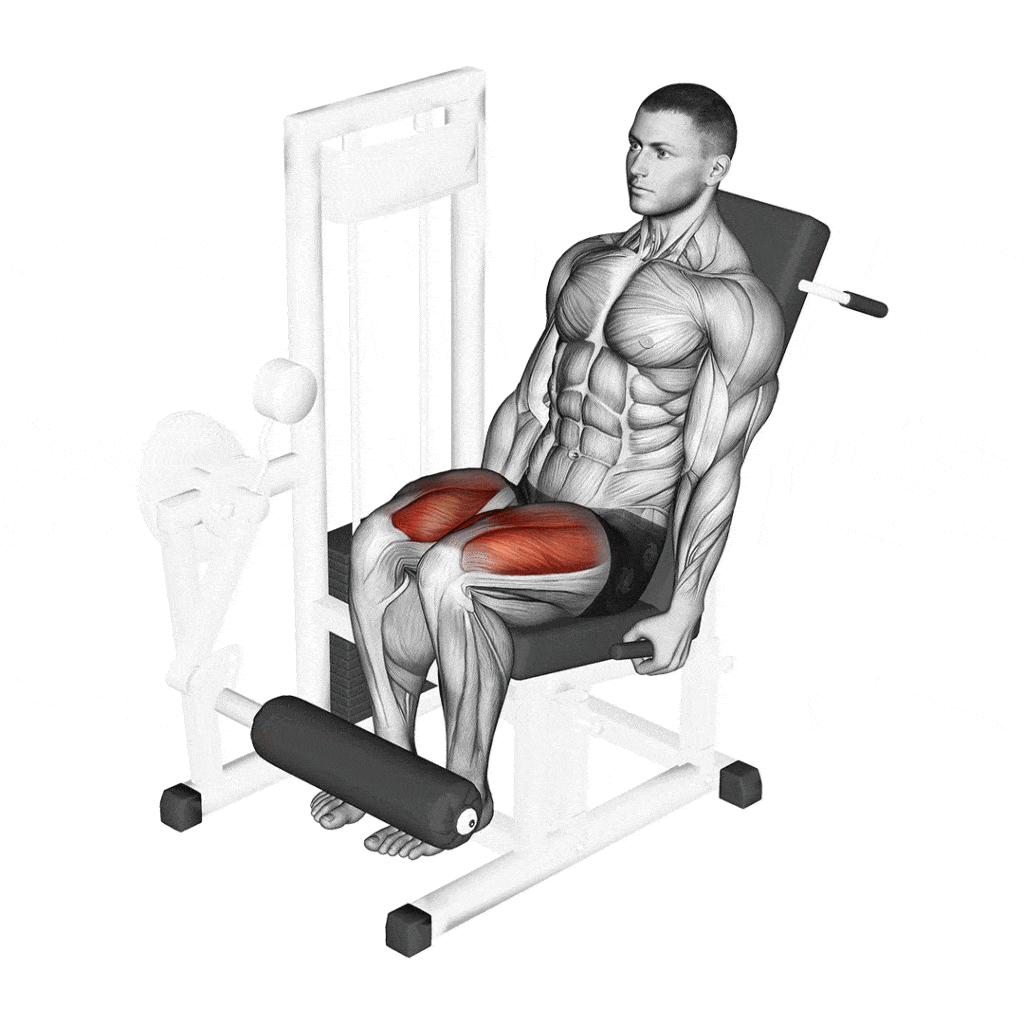
Description and Benefits: Leg extensions are an isolation exercise that specifically targets the quadriceps. Performed on a leg extension machine, this exercise allows for focused strengthening of the front thigh muscles.
- Quadriceps Isolation: Unlike compound movements, leg extensions solely target the quads, making them effective for building definition and strength in this specific muscle group.
- Rehabilitation: Often used in physiotherapy settings to help regain strength post-injury or surgery due to its controlled nature and specific targeting.
- Progress Tracking: Given the controlled environment of the machine, it’s easier to track strength progress by monitoring weight increments.
Importance of Controlled Movements to Protect the Knees: The leg extension machine places a considerable amount of force on the knee joint, especially at the peak contraction point. Using momentum or excessive weight can strain the ligaments and tendons around the knee. Therefore, controlled movements are crucial:
- Safety: Ensures that the force is applied gradually, reducing the risk of sudden strain or injury.
- Muscle Engagement: Controlled motion maximizes muscle fiber recruitment throughout the movement.
- Joint Health: Prevents unnecessary wear and tear on the knee joint and surrounding structures.
Proper Form and Technique:
- Seat Adjustment: Adjust the machine’s seat so your knees align with the machine’s pivot point. This ensures the force is applied correctly and minimizes undue stress on the knees.
- Pad Positioning: The pad should sit just above the ankles, comfortably resting against the lower shins.
- Back Support: Maintain full contact with the backrest. Avoid leaning forward or arching the back during the exercise.
- Controlled Movement: Initiate the movement by flexing the quads and slowly lifting the weight. At the peak, there should be a brief pause to ensure full muscle contraction. Slowly lower the weight in a controlled manner to the starting position.
- Breathing: Exhale as you lift the weight (extension) and inhale as you lower it back down.
It’s worth noting that while leg extensions are effective for targeting the quads, they shouldn’t replace compound exercises but rather complement them. Always ensure that the weight selected allows for controlled movement and doesn’t cause pain or discomfort in the knees. If unsure, seek guidance from a trainer or fitness professional.
Tips for Quadriceps Strengthening

- Importance of Warm-Up and Cool-Down:
- Prepare the Body: A good warm-up increases blood flow to the muscles, preparing them for the upcoming activity and reducing the risk of injury.
- Joint Lubrication: Warm-up exercises help lubricate the joints, especially crucial for exercises that heavily involve the knees.
- Transition: Cooling down gradually brings your heart rate back to its resting rate and aids in the removal of lactic acid, reducing post-exercise soreness.
- Recovery: Gentle cool-down exercises can speed up recovery, ensuring the muscles are ready for the next workout session.
- Stretching the Quadriceps to Prevent Injury and Improve Flexibility:
- Reduce Tightness: Regular stretching can reduce muscle tightness, which is a common culprit for injuries.
- Range of Motion: Improved flexibility can enhance the range of motion in the joints, allowing for better performance and less strain during exercises.
- Post-Workout Stretch: After a workout, when the muscles are warm, is an optimal time to stretch as it can help in lengthening and relaxing the muscles.
- Quadriceps Stretch: While standing, grab your ankle behind you, pulling it towards your glutes. Keep the knees together and push the hips forward, feeling a stretch in the front thigh.
- Listening to the Body and Avoiding Overexertion:
- Pain vs. Discomfort: While muscle discomfort or fatigue can be normal, sharp or persistent pain is a warning sign. Always differentiate between the two.
- Rest and Recovery: Muscles grow and repair during rest. Overworking without adequate rest can lead to injuries and hinder strength development.
- Hydration: Drink enough water before, during, and after exercise. Proper hydration supports muscle function and recovery.
- Progressive Overload: Increase exercise intensity, duration, or weight gradually. This approach ensures consistent progress while minimizing the risk of injury.
- Feedback: If something feels off or unusually painful, consider consulting a fitness professional or physical therapist to ensure you’re on the right track and using proper form.
Incorporating these tips can make a significant difference in safely strengthening the quadriceps and achieving long-term fitness goals. Remember, consistency paired with mindfulness is key to effective muscle building and overall health.
Conclusion
The quadriceps, as one of the body’s most powerful muscle groups, play a pivotal role in our daily activities, from simple tasks like standing and walking to more demanding actions in sports and fitness. Strengthening the quadriceps is not just about aesthetics or athletic performance; it’s about enhancing overall mobility, stability, and ensuring long-term joint health.
Incorporating the exercises outlined in this article can provide a solid foundation for building and maintaining strong quadriceps. But as with any fitness journey, consistency is key. It’s not about how much you can do in a single session, but rather about regular and mindful practice over time.
Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or someone just starting their fitness journey, let these exercises serve as a guide to a stronger, more resilient lower body. Embrace the journey, celebrate the progress, and always prioritize your body’s health and well-being. Strong quadriceps are within reach—commit to your fitness routine, and the results will follow.







