A plant-based diet, which is focused on whole, minimally processed plant foods, is bursting with nutrient-dense, fiber-rich foods that support general health and wellbeing. These foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
A surge in plant-based diet popularity stems from health, environmental, and ethical motivations. Ample research suggests that such diets lower chronic disease risk, aid weight management, and promote longevity. Environmentally speaking, plant-based diets slash carbon footprints and foster sustainable food production. Ethically, they support animal welfare and curb animal exploitation.
Despite plant-based diets’ benefits, some misconceptions linger – particularly around building muscle. Concerns range from protein intake to nutrient deficiencies, but with the right knowledge and strategies, it’s entirely possible to gain muscle mass while maintaining a plant-based diet. This article tackles 12 common reasons for struggling to gain muscle on a plant-based diet and offers actionable solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Optimize protein intake: Consume diverse plant-based protein sources and ensure adequate essential amino acids for effective muscle growth.
- Prioritize sleep and stress management: Boost muscle recovery and hormonal balance by improving sleep quality and incorporating stress-reduction techniques.
- Caloric intake and meal timing: Create a caloric surplus by incorporating calorie-dense plant-based foods, and optimize pre- and post-workout nutrition.
- Stay consistent and realistic: Maintain a consistent routine in diet and training, while setting achievable goals and expectations for muscle growth.
1. Inadequate protein intake
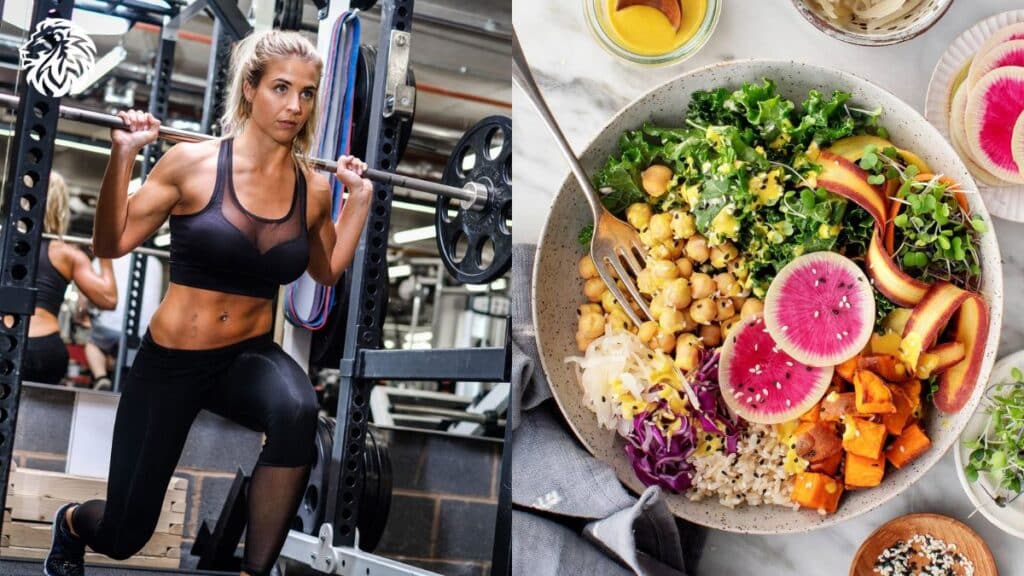
Importance of protein for muscle growth
As the building blocks for muscle tissue, amino acids in protein play a crucial role in muscle growth. Strength training damages muscle fibers on a microscopic scale; the body repairs and rebuilds through protein synthesis, leading to stronger, larger muscles.
Plant-based protein sources
Contrary to popular belief, many plant-based foods boast high protein content, including legumes (lentils, chickpeas, black beans), whole grains (quinoa, brown rice, barley), soy products (tofu, tempeh, edamame), and nuts and seeds (almonds, chia seeds, pumpkin seeds). Meeting protein needs is entirely achievable through a well-planned plant-based diet.
How to ensure sufficient protein intake on a plant-based diet
To ensure adequate protein intake, consume protein-rich foods daily and pay attention to portion sizes. Plant-based protein powders (e.g., pea or brown rice protein) offer a convenient option, especially for strength trainers.
2. Not consuming enough calories
Caloric needs for muscle growth
To build muscle, consume more calories than you burn. This caloric surplus furnishes the body with energy for synthesizing new muscle tissue. Plant-based diets often underestimate caloric needs since plant foods generally contain fewer calories than animal-based alternatives.
Plant-based foods with high caloric density
Incorporating calorie-dense plant-based foods like avocados, nuts and seeds, nut butters, dried fruits, whole grains, and plant-based oils can help achieve a caloric surplus. Moderate consumption of these foods can substantially increase daily caloric intake without overwhelming food volume.
Strategies for increasing caloric intake
Increase caloric intake by opting for larger portions, more frequent meals, or snacks. Adding calorie-dense ingredients, such as nuts and seeds, to meals and smoothies also helps. Track food intake with a diary or app to identify areas needing improvement.
3. Lack of essential amino acids

Importance of essential amino acids
Essential amino acids are dietary necessities since the body can’t synthesize them. They play vital roles in various processes, including muscle protein synthesis. A balanced diet, rich in essential amino acids, is crucial for muscle growth support.
Plant-based sources of essential amino acids
Although most animal-based proteins contain all nine essential amino acids, plant-based sources may have lower content of one or more. However, many plant-based foods, such as quinoa, soy products, chia seeds, and buckwheat, are rich in essential amino acids. Consuming diverse plant-based protein sources daily ensures an adequate intake of essential amino acids.
Complementary protein sources and meal planning
By combining different plant-based protein sources, a complete amino acid profile can be achieved. This approach, called complementary protein, involves consuming two or more plant-based protein sources that, when combined, provide all essential amino acids. Examples of complementary protein pairings include rice and beans, hummus and whole-grain pita, and peanut butter with whole-grain bread. Planning meals with complementary protein sources can support muscle growth on a plant-based diet.
4. Inadequate nutrient intake
Nutrients critical for muscle growth
Aside from protein, other nutrients play critical roles in muscle growth and overall health. These include vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D, calcium, iron, and zinc. A deficiency in any of these nutrients can hinder muscle growth and recovery.
Plant-based sources of important nutrients
There are plenty of plant-based sources for the nutrients necessary for muscle growth. Some examples include:
- Vitamin D: fortified plant-based milk, mushrooms exposed to sunlight
- Calcium: leafy greens, fortified plant-based milk, tofu, almonds
- Iron: legumes, whole grains, leafy greens, dried fruit
- Zinc: legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds
Ensuring a well-rounded diet
To guarantee sufficient essential nutrient intake, one must strive for a diverse and harmonious diet, brimming with an array of plant-based delicacies. Daily consumption of fruits, veggies, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds is key. Concerned about meeting nutrient requirements? Enlist the expertise of a registered dietitian or nutritionist for tailor-made advice on fine-tuning a plant-based diet for muscle growth.
5. Insufficient strength training

Importance of strength training for muscle growth
Strength training is crucial for stimulating muscle growth, as it places stress on the muscles, causing micro-tears in the muscle fibers. The body then repairs and rebuilds these fibers, resulting in increased muscle size and strength. Without consistent and effective strength training, it can be challenging to gain muscle mass, regardless of diet.
Common mistakes in strength training
Some common mistakes in strength training that can hinder muscle growth include:
- Inadequate training frequency or intensity: Failing to train consistently or not pushing oneself hard enough during workouts.
- Poor exercise technique: Incorrect form increases the risk of injury and reduces the effectiveness of the exercise.
- Lack of progression: Not challenging the muscles with increased weight or intensity over time, leading to a plateau in muscle growth.
- Neglecting muscle groups: Focusing on specific muscle groups while neglecting others can result in imbalances and hinder overall muscle growth.
Effective strength training routines for plant-based athletes
An effective strength training routine should include exercises that target all major muscle groups, such as squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and pull-ups. Ideally, plant-based athletes should engage in strength training at least two to three times per week, progressively increasing the weight or intensity over time. Additionally, incorporating periodization, which involves varying training volume and intensity over time, can help maximize muscle growth and prevent plateaus.
6. Overtraining
Symptoms of overtraining
Overtraining occurs when an individual exercises too frequently or intensely without allowing sufficient time for rest and recovery. Symptoms of overtraining include persistent fatigue, decreased performance, mood changes, sleep disturbances, and increased susceptibility to illness or injury.
Importance of rest and recovery
Rest and recovery are essential components of a successful strength training program, as they allow the body to repair and rebuild damaged muscle tissue. Adequate rest helps prevent overtraining, ensuring consistent progress in muscle growth.
Strategies for preventing overtraining
To prevent overtraining, individuals should:
- Schedule rest days: Include at least one to two rest days per week, allowing the muscles to recover fully.
- Monitor training volume and intensity: Be mindful of the overall workload and avoid excessive increases in training volume or intensity.
- Listen to the body: Pay attention to signs of fatigue or decreased performance and adjust the training routine accordingly.
- Prioritize sleep and nutrition: Ensuring sufficient sleep and proper nutrition supports muscle recovery and helps prevent overtraining.
7. Inadequate sleep

Role of sleep in muscle recovery and growth
Sleep proves indispensable in muscle restoration and growth, as the body mends and fortifies muscle tissue during slumber. Besides, sleep is vital for hormonal equilibrium, immune functionality, and mental prowess, all contributing to triumphant strength training and general well-being.
Common sleep issues
Some common sleep issues that may negatively affect muscle growth include:
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night.
- Sleep apnea: Breathing interruptions during sleep, leading to fragmented sleep and decreased sleep quality.
- Poor sleep hygiene: Habits and environmental factors that interfere with the quality and duration of sleep.
Tips for improving sleep quality
To boost sleep quality and back muscle growth, individuals should:
- Set a consistent sleep routine: Sleeping and rising at regular hours every day aids in synchronizing the body’s internal clock.
- Foster a sleep-conducive environment: A dark, hushed, and cool bedroom encourages restorative rest.
- Curtail screen time pre-slumber: Screens’ blue light can hinder melatonin production, a sleep-regulating hormone.
- Adopt a calming bedtime ritual: Soothing activities like reading, meditating, or warm baths signal it’s time to snooze.
- Address sleep abnormalities: Persistent sleep issues warrant consultation with healthcare professionals for specialized treatment.
8. High stress levels
Impact of stress on muscle growth
Elevated stress levels can thwart muscle growth by disrupting hormonal balance, impairing immunity, and deteriorating sleep quality. Chronic stress may also sap motivation and focus, complicating maintenance of a consistent, efficient strength training regimen.
Connection between stress and cortisol levels
Cortisol, the infamous “stress hormone,” surges in response to stress. Heightened cortisol levels can undermine muscle growth by promoting muscle tissue breakdown and inhibiting protein synthesis.
Techniques for managing stress
To curb stress and bolster muscle growth, individuals should:
- Participate in regular exercise: Physical activity, including strength training, helps alleviate stress and uplift mental well-being.
- Embrace mindfulness and relaxation methods: Meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation can diminish stress levels.
- Prioritize self-indulgence: Allocating time for hobbies, socializing, and leisure fosters work-life balance and reduces stress.
- Consult professional aid: Those grappling with chronic stress can seek valuable guidance from mental health professionals.
9. Poor meal timing

Importance of nutrient timing for muscle growth
Nutrient timing refers to the strategic consumption of nutrients, particularly protein and carbohydrates, around exercise to optimize muscle growth and recovery. Proper meal timing can ensure that the body has the necessary fuel for strength training and supports muscle recovery and growth post-workout.
Optimal pre- and post-workout nutrition
Pre-workout nutrition supplies energy (usually from carbohydrates) for training sessions and protein for muscle protein synthesis. A balanced meal or snack consumed 1-3 hours before working out can include a banana with peanut butter or a fruit, greens, and plant-based protein powder smoothie.
Post-workout nutrition replenishes glycogen stores and offers protein for muscle repair and growth. Within 30 minutes to 2 hours after exercise, a meal or snack combining carbohydrates and protein is ideal—examples: a tofu-vegetable stir-fry with brown rice or a plant-based protein powder shake with carbohydrates like bananas or oats.
Strategies for effective meal timing
To optimize meal timing for muscle growth, individuals should:
- Plan meals and snacks around workout times: Ensure pre- and post-workout nutrition is accounted for in daily meal planning.
- Listen to the body: Pay attention to hunger cues and energy levels, adjusting meal timing as needed to support optimal performance and recovery.
- Be prepared: Have pre- and post-workout snacks ready to consume when needed, such as protein bars or shakes, to avoid missed opportunities for muscle growth.
10. Lack of consistency
Importance of consistency in diet and training
Consistency in both diet and training is crucial for achieving muscle growth on a plant-based diet. Without adhering to a regular strength training routine and maintaining a well-balanced diet, it becomes challenging to see progress in muscle mass.
Common reasons for inconsistency
Some common reasons for inconsistency in diet and training include:
- Lack of planning: Failing to establish a regular training schedule or plan meals in advance.
- Loss of motivation: Difficulty maintaining motivation to consistently engage in strength training or adhere to a plant-based diet.
- Life events or disruptions: Changes in routine or personal circumstances can make it challenging to maintain consistency.
Tips for maintaining a consistent routine
To maintain consistency in diet and training, individuals should:
- Set realistic goals: Establish clear, achievable goals for strength training and dietary habits to stay motivated and focused.
- Plan and track: Plan workout routines and meals in advance, using tools such as workout logs and meal planning apps to stay organized and accountable.
- Create a support system: Connect with like-minded individuals, such as workout partners or online communities, for encouragement and shared experiences.
- Be flexible and adaptable: Acknowledge that setbacks and disruptions will happen, and be prepared to adapt and refocus on established goals.
11. Unrealistic expectations

Factors influencing muscle growth rate
Various factors influence the rate at which individuals gain muscle mass, including genetics, age, training history, and hormonal balance. Due to these factors, some people may experience slower or faster muscle growth than others, even when following the same training and nutrition regimen.
Differences between individual responses
Individual responses to strength training and nutrition can vary widely, making it important to recognize that what works for one person may not necessarily work for another. Comparing one’s progress to that of others can lead to unrealistic expectations and discouragement.
Setting realistic goals and expectations
To set realistic goals and expectations for muscle growth, individuals should:
- Understand their unique genetic potential and limitations.
- Monitor progress using personal benchmarks, such as increases in strength or muscle circumference, rather than comparing themselves to others.
- Be patient and persistent, recognizing that muscle growth takes time and consistent effort.
Conclusion
There are various reasons one might not gain muscle mass on a plant-based diet, including inadequate protein and calorie intake, poor nutrient timing, insufficient strength training, and high stress levels, among others.
Addressing these issues is essential for optimizing muscle growth on a plant-based diet. By ensuring proper nutrition, effective strength training, and a balanced lifestyle, individuals can overcome these obstacles and achieve their fitness goals.
Gaining muscle mass on a plant-based diet is entirely possible with the right approach and commitment. By staying informed, planning, and maintaining consistency in both diet and training, individuals can successfully build muscle while enjoying the numerous health, environmental, and ethical benefits of a plant-based lifestyle.







