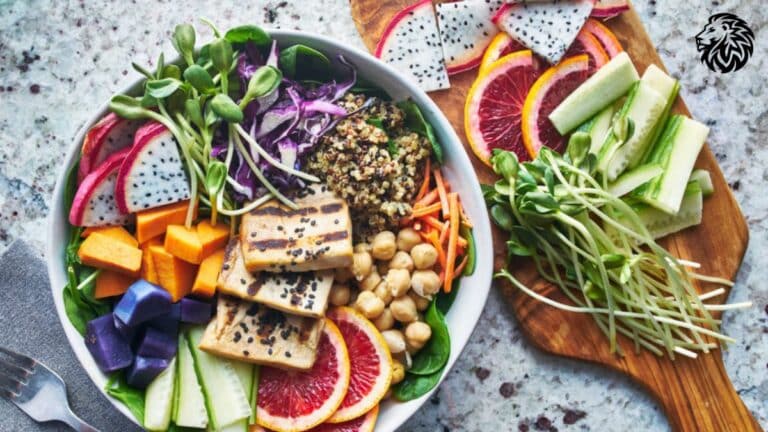
A plant-based diet, primarily focused on consuming foods derived from plants, has become a cornerstone of healthful eating and sustainable living. This dietary approach includes a wide array of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, oils, whole grains, legumes, and beans. It doesn’t necessarily mean that one is vegetarian or vegan and refrains from eating meat or dairy. Instead, one prefers more foods from plant sources in comparison to animal products.
The surge in popularity of plant-based diets in recent years is multifaceted. Health benefits, such as a lower risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer, have been well-documented in numerous scientific studies. Moreover, environmental concerns are also a significant driving force, as plant-based diets are generally considered more sustainable and eco-friendly compared to diets high in meat and dairy. This is due to lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced water usage, and lesser land required for plant-based food production.
Additionally, there’s a growing societal shift towards more ethical and humane food choices. As awareness of animal welfare issues in the meat and dairy industries increases, many people are turning to plant-based diets as a way to align their eating habits with their ethical beliefs.
In contemporary culture, the plant-based diet is no longer seen as a fringe lifestyle choice. It’s increasingly embraced by mainstream society, with supermarkets, restaurants, and even fast-food chains offering a wider range of plant-based options. This acceptance has made it easier and more appealing for people to incorporate plant-based foods into their daily lives, regardless of whether they choose to fully commit to a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle.
This article will explore ten significant benefits of adopting a plant-based diet, shedding light on why more people are making this dietary shift and how it can positively impact health, the environment, and ethical food consumption.
10 Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
1. Improved Heart Health

One of the most significant benefits of a plant-based diet is its positive impact on heart health. A growing body of research indicates that those who adhere to plant-based diets have a lower risk of developing heart disease compared to those who consume meat-heavy diets.
Mechanisms Behind Heart Health Improvement
- Low in Saturated Fat and Cholesterol: Plant-based diets are typically low in saturated fat and cholesterol. High intake of saturated fats, commonly found in animal products, is linked to increased levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol, which is a primary contributor to heart disease. Plants, on the other hand, contain no cholesterol and generally lower levels of saturated fats.
- High in Fiber and Healthy Nutrients: Plants are rich in dietary fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, which are known to support heart health. Fiber helps in reducing cholesterol levels and also aids in maintaining a healthy weight, further decreasing heart disease risk.
- Reduction in Blood Pressure: A diet high in fruits and vegetables has been shown to lower blood pressure, a key risk factor for heart disease. The potassium found in plants can help balance the negative effects of salt, which aids in keeping blood pressure in check.
Evidence from Studies
Numerous studies have provided evidence supporting the heart-healthy benefits of a plant-based diet:
- A study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that a plant-based diet was associated with a 16% lower risk of having a cardiovascular disease event and a 32% lower risk of dying from a cardiovascular disease.
- Research in the Journal of Nutrition observed that participants following a plant-based diet had lower cholesterol levels compared to those on omnivorous diets. The reduction in LDL cholesterol is particularly notable.
- The Adventist Health Study-2, a large-scale study of vegetarians and vegans, showed that vegetarians had a 34% lower risk of developing ischemic heart disease than non-vegetarians.
These studies, among others, illustrate the potential of plant-based diets in maintaining heart health and preventing heart-related illnesses. By focusing on whole, plant-based foods and reducing the intake of animal products, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and improve their overall cardiovascular health.
2. Weight Loss and Management

Plant-based diets have gained recognition not only for their health benefits but also as an effective approach for weight loss and management. The fundamental principles of this diet, focusing on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts, contribute to a nutrient-rich yet lower calorie intake, which is conducive to weight loss and maintaining a healthy weight.
How Plant-Based Diets Aid in Weight Loss
- Lower Calorie Density: Plant-based foods typically have fewer calories for the same volume of food compared to meat and dairy products. This means you can eat larger portions, feel fuller, and still consume fewer calories.
- High Fiber Content: Foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are high in dietary fiber, which promotes satiety. Feeling full and satisfied can reduce overall calorie intake and curb overeating.
- Improved Metabolism: Some studies suggest that plant-based diets can boost metabolism, leading to an increased calorie burn even at rest.
- Reduction of Unhealthy Fats: A diet high in plant-based foods naturally reduces the intake of unhealthy fats found in meat and dairy products, which are often linked to weight gain.
Testimonials and Case Studies
- Case Study 1: A study published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine reviewed 12 diet trials and found that people on vegetarian diets lost around 4.4 pounds more on average than those who followed non-vegetarian diets over an 18-week period.
- Case Study 2: Another study in Nutrition & Diabetes reported significant weight loss in overweight individuals who followed a plant-based diet for six months, without any major changes to exercise or portion sizes.
- Personal Testimonial: Kevin, a 35-year-old man, shared his experience in a health magazine, describing how switching to a plant-based diet helped him lose 20 pounds in three months. He noted feeling more energized and less hungry throughout the day.
- Celebrity Testimonial: A famous actress credited her plant-based diet for her rapid post-pregnancy weight loss, highlighting how the diet not only helped her shed pounds but also improved her overall energy and skin health.
These examples demonstrate that a plant-based diet can be an effective strategy for weight loss and long-term weight management. By focusing on nutrient-rich, lower-calorie plant foods, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy weight without feeling deprived or hungry.
3. Lower Risk of Certain Cancers

Adopting a plant-based diet has been linked to a reduced risk of certain types of cancer, a benefit that is drawing increasing attention in the medical community. The relationship between diet and cancer prevention has been a subject of extensive research, with plant-based diets frequently emerging as a protective factor against various cancers.
Research Linking Plant-Based Diets to Reduced Cancer Risk
- A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that a higher intake of fruits and vegetables was associated with a lower risk of developing certain types of cancer, particularly those related to the digestive system.
- The World Cancer Research Fund and the American Institute for Cancer Research recommend a plant-based diet, emphasizing the consumption of a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes for cancer prevention.
- Research in the International Journal of Cancer indicated that dietary patterns featuring plant-based foods are linked with a decreased risk of colorectal cancer.
Mechanisms by Which Plant-Based Diets May Protect Against Cancer
- High in Phytochemicals and Antioxidants: Plant-based foods are rich in phytochemicals and antioxidants that protect cells from damage that could lead to cancer. These compounds can neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the body.
- Fiber Intake: High fiber intake, typical in plant-based diets, is known to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer. Fiber aids in digestive health and ensures regular bowel movements, which helps in the elimination of carcinogens from the digestive tract.
- Reduced Consumption of Carcinogenic Compounds: Meat, especially processed and red meat, has been classified as a carcinogen by the World Health Organization. Plant-based diets naturally eliminate or reduce the intake of these potential carcinogens.
- Hormonal Balance: Some cancers, like breast cancer, are influenced by hormonal levels in the body. Plant-based diets, which are typically lower in fat and higher in fiber, can influence hormone levels and potentially reduce the risk of hormone-related cancers.
- Healthy Weight Management: Obesity is a well-known risk factor for several types of cancer. Plant-based diets are effective for weight management, thus indirectly contributing to cancer risk reduction.
In summary, the adoption of a plant-based diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can play a significant role in reducing the risk of certain cancers. The diet’s natural composition, high in protective nutrients and low in potentially harmful substances, establishes it as a beneficial choice for those looking to reduce their cancer risk.
4. Diabetes Prevention and Control

The role of a plant-based diet in preventing and controlling diabetes has garnered significant attention from the medical community and the public alike. Scientific evidence suggests that such diets can be highly effective in both preventing the onset of diabetes and managing existing conditions.
How Plant-Based Diets Aid in Diabetes Prevention and Control
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Plant-based diets are often rich in whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, which can improve insulin sensitivity. Better insulin sensitivity means the body can more effectively use the insulin it produces, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Lowering Blood Sugar Levels: Foods in a plant-based diet typically have lower glycemic indices. This means they cause a slower and lower rise in blood sugar levels, which is beneficial for diabetes management.
- Weight Management: Excess weight is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Plant-based diets are helpful for weight loss and maintenance, thereby reducing the risk of developing diabetes.
- Reduced Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is linked to the onset of type 2 diabetes. The antioxidants and phytochemicals in plant-based foods help reduce inflammation in the body.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Neal Barnard, president of the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine and a renowned advocate for plant-based diets, has conducted extensive research showing the effectiveness of plant-based diets in diabetes prevention and control. He notes that a diet high in vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains can prevent and even reverse type 2 diabetes.
- The American Diabetes Association acknowledges the benefits of a plant-based diet, stating that such diets can be particularly beneficial for people with diabetes due to their potential to improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Personal Stories
- John’s Journey: John, a 58-year-old man diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, shared in an interview how switching to a plant-based diet dramatically improved his blood sugar levels. Within six months, his HbA1c levels, a measure of long-term blood sugar control, dropped significantly, and he was able to reduce his medication under his doctor’s supervision.
- Sarah’s Success: In a health magazine, Sarah, a 40-year-old woman with a family history of diabetes, described how adopting a plant-based diet helped her lose weight and reduce her risk of developing diabetes. Her regular health check-ups showed improved blood sugar levels and overall better health.
These insights and stories highlight the potential of a plant-based diet as a powerful tool in the prevention and management of diabetes. By focusing on nutrient-dense, low-glycemic foods, individuals can significantly impact their diabetes risk and improve their overall health.
5. Improved Digestive Health

A plant-based diet is renowned for its beneficial effects on digestive health, largely due to the high fiber content found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system, and a diet rich in plant-based foods can significantly enhance digestive health.
Role of Fiber in Digestive Health
- Promotes Regular Bowel Movements: Dietary fiber adds bulk to the stool, which helps regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation.
- Supports a Healthy Gut Microbiome: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding the beneficial bacteria in the gut. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for optimal digestion and overall health.
- Reduces the Risk of Digestive Disorders: High-fiber diets are associated with a lower risk of developing various digestive disorders, including diverticulitis, hemorrhoids, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Helps in Weight Management: Fiber-rich foods are more filling, which can lead to reduced calorie intake and help in maintaining a healthy weight, indirectly benefiting digestive health.
Relevant Study Findings
- A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that a higher intake of dietary fiber was linked to a lower risk of digestive conditions like gastric ulcers, reflux, and diverticulitis.
- Research in the Journal of Nutrition showed that individuals who consumed a plant-based diet rich in high-fiber foods experienced significant improvements in symptoms of IBS, including bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
Real-Life Examples
- Emma’s Experience: Emma, a 30-year-old woman, shared her story in a health forum, explaining how transitioning to a plant-based diet rich in fiber resolved her long-standing issues with constipation and bloating. She noticed a significant improvement in her digestive health within just a few weeks.
- Mark’s Transformation: In an interview with a health magazine, Mark, a 45-year-old with a history of diverticulitis, reported how his condition improved remarkably after he switched to a plant-based diet. His gastroenterologist noticed a decrease in inflammation and fewer episodes of diverticulitis flare-ups.
These findings and personal anecdotes underscore the impact of a plant-based diet on improving digestive health. By increasing the intake of fiber-rich plant foods, individuals can experience significant benefits, including regular bowel movements, a healthier gut microbiome, and a reduced risk of digestive disorders.
6. Environmental Benefits

The shift towards a plant-based diet is not only beneficial for individual health but also has profound environmental implications. The environmental impact of meat production compared to plant-based diets is substantial, with numerous studies highlighting the differences in resource use, greenhouse gas emissions, and overall ecological footprint.
Impact of Meat Production vs. Plant-Based Diets
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Animal agriculture is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, notably methane and nitrous oxide, which are more potent than carbon dioxide. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) reports that livestock is responsible for about 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Land Use: Meat production requires more land than plant-based foods. It is estimated that livestock uses about 77% of agricultural land, yet produces only 18% of the world’s calories and 37% of total protein.
- Water Usage: Animal agriculture is water-intensive. For example, it takes about 1,799 gallons of water to produce one pound of beef, whereas it takes about 43 gallons to produce a pound of vegetables.
- Deforestation and Biodiversity Loss: Large-scale meat production has led to significant deforestation, particularly in regions like the Amazon. This deforestation is not only a carbon issue but also a major factor in biodiversity loss.
Statistics and Data on Resource Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- According to a study published in Science, adopting a plant-based diet could reduce food’s greenhouse gas emissions by up to 73% in high-income nations.
- The EAT-Lancet Commission on Food, Planet, and Health suggests that a global shift toward plant-based diets could reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the food system by more than half.
- Research in the Journal of Cleaner Production found that the carbon footprint of a vegan diet is about 50% lower than that of a meat-based diet.
The environmental benefits of a plant-based diet are clear and substantial. By reducing meat consumption and increasing the intake of plant-based foods, individuals can significantly lower their environmental footprint, contributing to the mitigation of climate change, conservation of natural resources, and preservation of biodiversity. The move towards plant-based diets is not just a health choice, but also an essential step towards a more sustainable and responsible way of living on our planet.
7. Increased Energy and Better Mood
Many individuals who adopt a plant-based diet report experiencing increased energy levels and improvements in mood. While personal testimonials abound, there is also growing scientific evidence supporting these claims. The reasons for these benefits are multifaceted and can be attributed to various aspects of a plant-based diet.
Scientific Evidence and Possible Explanations
- Improved Nutrient Intake: Plant-based diets are high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Nutrients like folate, vitamin C, and magnesium, prevalent in fruits and vegetables, play a crucial role in energy production and mood regulation.
- Better Blood Sugar Control: High-fiber plant foods help in stabilizing blood sugar levels, preventing the spikes and crashes that can affect energy and mood. Stable blood sugar levels are associated with consistent energy and mood.
- Reduced Inflammation: Chronic inflammation, which can be exacerbated by consuming certain animal products, is linked to fatigue and mood disorders. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory plant foods can reduce inflammation and improve energy and mood.
- Healthy Gut Microbiome: The fiber in plant-based diets feeds the beneficial bacteria in the gut. A healthy gut microbiome is increasingly recognized for its role in mental health, including mood regulation.
Testimonials
- Alice’s Story: Alice, a 36-year-old software engineer, shared in a lifestyle magazine how switching to a plant-based diet improved her energy levels significantly. She noted that the mid-afternoon slump she used to experience disappeared and her overall mood became more stable.
- David’s Experience: In a podcast interview, David, a personal trainer, described how a plant-based diet enhanced his energy levels, contributing to better workouts and a more positive outlook on life.
Scientific Studies
- A study published in the Nutritional Neuroscience journal found that vegetarians reported better mood than meat-eaters, which was hypothesized to be due to the lower intake of omega-6 fatty acids and higher intake of plant-based omega-3s.
- Research in the American Journal of Health Promotion showed that participants following a plant-based diet reported higher energy levels and better general health compared to when they were consuming meat and dairy.
A plant-based diet has the potential to positively impact energy levels and mood. The combination of stable blood sugar, improved nutrient intake, reduced inflammation, and a healthier gut microbiome all contribute to these benefits. While individual experiences may vary, the overall trend suggests that plant-based eating can be an effective way to boost both physical and mental well-being.
8. Enhanced Longevity

The correlation between plant-based diets and increased lifespan has been a subject of considerable interest in nutritional and epidemiological research. Numerous studies have shown that populations consuming diets rich in plant-based foods tend to have longer lifespans and lower incidences of chronic diseases. This section delves into the research and analysis of populations that have thrived on plant-based diets.
Research Linking Plant-Based Diets to Increased Lifespan
- Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases: Studies consistently show that plant-based diets are associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, certain cancers, and type 2 diabetes, which are major factors affecting lifespan.
- Improved Metabolic Health: A diet high in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains can lead to better metabolic health, including lower blood pressure, improved cholesterol levels, and better blood sugar control, all of which contribute to longevity.
- Anti-Aging Properties of Plant Foods: Many plant foods are rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals that can protect cells from oxidative damage, a process linked to aging and age-related diseases.
Analysis of Populations with Plant-Based Diets
- The Blue Zones: Studies of the Blue Zones, areas in the world where people live the longest, reveal that these populations share common dietary traits, primarily plant-based diets. For example, in Okinawa, Japan, and Sardinia, Italy, diets are largely composed of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes.
- Seventh-day Adventists Study: Research on Seventh-day Adventists, a group known for their longevity and predominantly plant-based diets, has shown that they have lower rates of heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. This population’s lifestyle, which typically includes a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, has been linked to their increased lifespan.
Scientific Studies
- A study published in the Journal of Gerontology found that a high intake of fruits and vegetables was associated with reduced risk of mortality in older adults.
- Research in the Lancet showed that diets high in plant-based foods and low in animal-based foods were associated with lower risk of mortality.
In summary, the evidence suggests that plant-based diets are linked to increased lifespan and better health outcomes. The protective effects against chronic diseases, the improvement in metabolic health, and the anti-aging properties of plant-based foods all contribute to this correlation. The dietary patterns observed in populations known for their longevity further reinforce the potential benefits of a plant-based diet for enhancing lifespan.
9. Ethical and Compassionate Choices

The decision to adopt a plant-based diet often extends beyond personal health and environmental concerns, delving into the realm of ethics and compassion, particularly regarding animal welfare. This ethical stance is rooted in the belief that all creatures have a right to life and freedom and that the industrial practices of animal farming are in conflict with these principles.
Ethical Considerations Regarding Animal Welfare
- Opposition to Factory Farming: Many proponents of plant-based diets object to factory farming due to its inhumane conditions, where animals are often kept in cramped, unsanitary environments and subjected to painful procedures without anesthesia.
- Reducing Animal Suffering: By choosing plant-based foods, individuals can reduce the demand for animal products, thereby contributing to a decrease in the number of animals raised and killed for food.
- Respect for Sentient Beings: The ethical argument for plant-based diets is also based on the recognition of animals as sentient beings capable of feeling pain and suffering. Avoiding animal products is seen as a way to respect their sentience.
Personal Stories and Philosophical Perspectives
- Maria’s Story: Maria, a 42-year-old teacher, shared her journey to veganism in a blog post, describing how learning about the realities of factory farming and animal suffering led her to change her diet. She views her plant-based lifestyle as an extension of her values of compassion and non-violence.
- Philosophical Perspective: Renowned philosopher Peter Singer, in his book “Animal Liberation,” argues for the ethical treatment of animals and considers the shift to plant-based diets as a moral imperative. He posits that the ability to suffer is what gives a being the right to equal consideration and that animals are capable of suffering.
The Role of Compassion
- Compassionate Living: Advocates of plant-based diets often view their dietary choices as part of a broader philosophy of compassionate living, which extends kindness and empathy to all beings, human or non-human.
- Mindfulness and Awareness: Adopting a plant-based diet can also be a mindful choice to be more aware of the impact of one’s food choices on other beings and the planet.
For many, the move towards a plant-based diet is deeply intertwined with ethical considerations and a compassionate worldview. It is a choice that reflects a commitment to reducing harm and suffering, respecting the sentience of all living creatures, and aligning one’s actions with one’s values of empathy and kindness.
10. Diverse and Delicious Food Options

One of the most exciting aspects of a plant-based diet is the sheer variety and creativity it brings to cooking and meal planning. Far from being restrictive, plant-based diets open up a world of diverse and delicious food options, challenging the traditional notions of what makes a meal both satisfying and flavorful.
Exploring Global Cuisines
- Plant-based diets allow for the exploration of a multitude of global cuisines, many of which are naturally plant-centric or can be easily adapted. For example, Middle Eastern cuisine offers dishes like hummus, baba ganoush, and falafel, while Indian cuisine provides a rich array of vegetarian curries, dals, and veggie-packed snacks like samosas.
Creative Plant-Based Recipes
- Mushroom and Walnut Bolognese: A hearty, meat-free twist on the classic Italian Bolognese, using finely chopped mushrooms and walnuts as a satisfying substitute for ground meat, served over whole-grain pasta.
- Vegan Thai Green Curry: Made with coconut milk, a variety of vegetables (like bell peppers, zucchini, and eggplant), tofu, and Thai spices, this curry is both aromatic and nourishing.
- Quinoa and Black Bean Stuffed Peppers: A vibrant and nutritious dish, featuring bell peppers stuffed with a flavorful mixture of quinoa, black beans, corn, and spices, topped with avocado and lime.
- Vegan Sushi Rolls: Sushi rolls filled with an assortment of vegetables like cucumber, avocado, carrots, and bell peppers, along with tofu or tempeh for protein, offering a fresh and healthy meal option.
- Sweet Potato and Chickpea Buddha Bowl: A colorful bowl of roasted sweet potatoes, seasoned chickpeas, quinoa, and a mix of fresh vegetables, drizzled with a tahini dressing.
Desserts and Sweet Treats
- Plant-based diets don’t mean skipping desserts. Items like avocado chocolate mousse, vegan apple crisp, and dairy-free ice creams made from coconut or almond milk are delicious ways to indulge.
Seasonal and Fresh Ingredients
- Emphasizing seasonal and local produce not only brings freshness and flavor to meals but also supports sustainable practices. Plant-based diets encourage eating according to what’s available seasonally, which can inspire a range of creative dishes.
The plant-based culinary world is rich, diverse, and full of flavors. It encourages culinary exploration and creativity, leading to meals that are not only healthy but also deeply satisfying and delicious. Whether one is a seasoned vegan or just exploring plant-based options, the possibilities for crafting enjoyable, nourishing meals are endless.
Conclusion
The journey through the myriad benefits of a plant-based diet underscores its profound impact on various aspects of health and well-being, as well as on the environment and ethical considerations. To recap, the key benefits include:
- Improved Heart Health: A reduction in the risk of heart disease due to lower cholesterol levels and improved blood pressure.
- Weight Loss and Management: Effective weight control through nutrient-rich, lower-calorie foods.
- Lower Risk of Certain Cancers: Reduced risk of cancer, particularly those related to the digestive system.
- Diabetes Prevention and Control: Better blood sugar regulation and reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Improved Digestive Health: Enhanced gut health due to high fiber content.
- Environmental Benefits: A significant reduction in one’s ecological footprint, contributing to sustainability.
- Increased Energy and Better Mood: Enhanced physical energy and mental well-being.
- Enhanced Longevity: Potential for increased lifespan and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
- Ethical and Compassionate Choices: Alignment with ethical values concerning animal welfare.
- Diverse and Delicious Food Options: A rich array of flavorful and creative meal choices.
Embracing a plant-based diet can be a transformative experience, offering not just health benefits but also a chance to positively impact the planet and live in harmony with ethical values. Whether you’re considering a full transition to a plant-based diet or simply looking to incorporate more plant-based meals into your routine, the rewards are multifaceted and impactful.
To those curious about plant-based diets, the invitation is to explore, experiment, and educate oneself. The world of plant-based cuisine is rich and diverse, offering a plethora of options to suit every palate. By starting with small steps, like introducing plant-based meals a few times a week, one can gradually experience the benefits firsthand.
In conclusion, a plant-based diet is more than just a dietary choice; it’s a pathway to a healthier, more sustainable, and ethically conscious lifestyle. It’s an opportunity to nurture not only personal health but also contribute to the well-being of our planet and its inhabitants.







